如果你也在 怎样代写微分方程differential equation这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。微分方程differential equation在数学中,是将一个或多个未知函数及其导数联系起来的方程。在应用中,函数通常代表物理量,导数代表其变化率,而微分方程则定义了两者之间的关系。这种关系很常见;因此,微分方程在许多学科,包括工程、物理学、经济学和生物学中发挥着突出作用。
微分方程differential equation研究主要包括研究其解(满足每个方程的函数集合),以及研究其解的性质。只有最简单的微分方程可以用明确的公式求解;然而,一个给定的微分方程的解的许多属性可以在不精确计算的情况下确定。
my-assignmentexpert™ 微分方程differential equation作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的微分方程differential equation作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此微分方程differential equation作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的微分方程differential equation代写服务。我们的专家在数学mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微分方程differential equation相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的微分方程differential equation及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|微分方程代写differential equation代考|Gamma function
Definition 2.6. The gamma function is defined by the following infinite integral:
$$
\Gamma(z)=\int_{0}^{\infty} \mathrm{e}^{-t} t^{z-1} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
Theorem 2.2. An important property of the gamma function is
$$
\Gamma(z+1)=z \Gamma(z) .
$$
Theorem 2.3. As a special case, for a nonnegative integer $z$, the factorial formula can be derived directly from (2.2.3)
$$
\Gamma(z+1)=z \Gamma(z)=z(z-1) \Gamma(z-1) \cdots=z ! .
$$
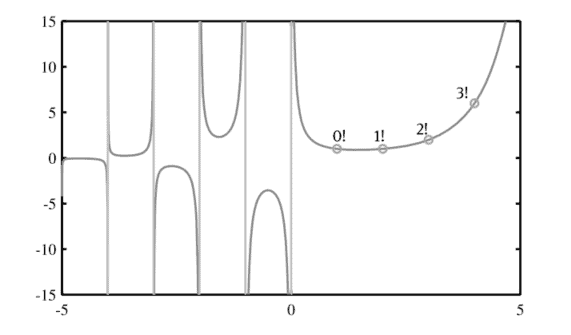
The gamma function can be regarded as an interpolation of the factorial, or it can be understood as an extension of the factorial to the noninteger $z$ domain. If $z$ is a negative integer, $\Gamma(z+1)$ explodes to $\pm \infty$. Function $\boldsymbol{y}=\operatorname{gamma}(\boldsymbol{x})$ in MATLAB can be used to evaluate the gamma function directly. If $\boldsymbol{x}$ is a vector, the result $\boldsymbol{y}$ is also a vector. Besides, $\boldsymbol{x}$ can be a matrix or any other data type, and the result $\boldsymbol{y}$ is of the same data type as $\boldsymbol{x}$. Note that function gamma() here can only handle real input arguments.
数学代写|微分方程代写differential equation代考|Hypergeometric functions
Hypergeometric functions are commonly used special functions, and they comprise also the foundation for some other special functions. In this section, definitions of hypergeometric functions are presented, and then computations of hypergeometric functions are addressed.
Definition 2.7. The general form of a hypergeometric function is ${ }^{[1]}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
{ }{p} \mathrm{~F}{q}(&\left.a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p} ; b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q} ; z\right) \
&=\frac{\Gamma\left(b_{1}\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(b_{q}\right)}{\Gamma\left(a_{1}\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(a_{p}\right)} \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{\Gamma\left(a_{1}+k\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(a_{p}+k\right)}{\Gamma\left(b_{1}+k\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(b_{q}+k\right)} \frac{z^{k}}{k !}
\end{aligned}
$$
where $b_{i}$ cannot be nonpositive integers. If $p \leqslant q$, the function is convergent for all $z$; If $p=q+1$, the function is convergent when $|z|<1$; If $p>q+1$, the function is divergent for all $z$.
Function hypergeom () provided in the Symbolic Math Toolbox in MATLAB can be used to compute the hypergeometric function
$$
{ }{p} \mathrm{~F}{q}\left(a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p} ; b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q} ; z\right)
$$
with the syntax
$y=$ hypergeom $\left(\left[a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p}\right],\left[b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q}\right], z\right)$
For instance, the hypergeometric function ${ }{1} \mathrm{~F}{1}(a, b ; z)$ can be evaluated with $y=$ hypergeom $(a, b, z)$, while function ${ }{2} \mathrm{~F}{1}(a, b ; c ; z)$ can be evaluated directly with $y=$ hypergeom $([a, b], c, z)$.
数学代写|微分方程代写DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION代考|Bessel differential equations
If the coefficients in the second-order differential equation in (2.2.1) have different forms, different forms of special differential equations can be constructed. For instance, the commonly used Bessel differential equations can be formulated. In this section, the mathematical form of Bessel differential equations is presented, and then various Bessel functions and their computations are summarized.
Definition 2.8. If the general form of a second-order homogeneous differential equation can be written as
$$
x^{2} \frac{\mathrm{d}^{2} y(x)}{\mathrm{d} x^{2}}+x \frac{\mathrm{d} y(x)}{\mathrm{d} x}+\left(x^{2}-v^{2}\right) y(x)=0
$$
the function is referred to as a Bessel differential equation.
微分方程代写
数学代写|微分方程代写DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION代考|GAMMA FUNCTION
定义 2.6。伽马函数由以下无限积分定义:
Γ(和)=∫0∞和−吨吨和−1 d吨
定理 2.2。伽马函数的一个重要性质是
Γ(和+1)=和Γ(和).
定理 2.3。作为一种特殊情况,对于非负整数和,阶乘公式可以直接从2.2.3
Γ(和+1)=和Γ(和)=和(和−1)Γ(和−1)⋯=和!.
gamma函数可以看成是阶乘的插值,也可以理解为阶乘到非整数的扩展和领域。如果和是一个负整数,Γ(和+1)爆炸到±∞. 功能是=伽玛(X)在 MATLAB 中可用于直接计算 gamma 函数。如果X是一个向量,结果是也是一个向量。除了,X可以是矩阵或任何其他数据类型,结果是是相同的数据类型X. 请注意,函数 gamma这里只能处理真正的输入参数。
数学代写|微分方程代写DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION代考|HYPERGEOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
超几何函数是常用的特殊函数,也是一些特殊函数的基础。在本节中,给出了超几何函数的定义,然后讨论了超几何函数的计算。
定义 2.7。超几何函数的一般形式是[1]
$$
\begin{aligned}
{ }{p} \mathrm{~F}{q}(&\left.a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p} ; b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q} ; z\right) \
&=\frac{\Gamma\left(b_{1}\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(b_{q}\right)}{\Gamma\left(a_{1}\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(a_{p}\right)} \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \frac{\Gamma\left(a_{1}+k\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(a_{p}+k\right)}{\Gamma\left(b_{1}+k\right) \cdots \Gamma\left(b_{q}+k\right)} \frac{z^{k}}{k !}
\end{aligned}
$$
where $b_{i}$ cannot be nonpositive integers. If $p \leqslant q$, the function is convergent for all $z$; If $p=q+1$, the function is convergent when $|z|<1$; If $p>q+1$, the function is divergent for all $z$.
其中b一世不能是非正整数。如果p⩽q, 函数对所有的都是收敛的和; 如果p=q+1, 当函数收敛时|和|<1; 如果p>q+1, 函数对所有人都是发散的和.
函数超几何MATLAB 中符号数学工具箱中提供的可用于计算超几何函数
provided in the Symbolic Math Toolbox in MATLAB can be used to compute the hypergeometric function
$$
{ }{p} \mathrm{~F}{q}\left(a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p} ; b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q} ; z\right)
$$
with the syntax
$y=$ hypergeom $\left(\left[a_{1}, \ldots, a_{p}\right],\left[b_{1}, \ldots, b_{q}\right], z\right)$
For instance, the hypergeometric function ${ }{1} \mathrm{~F}{1}(a, b ; z)$ can be evaluated with $y=$ hypergeom $(a, b, z)$, while function ${ }{2} \mathrm{~F}{1}(a, b ; c ; z)$ can be evaluated directly with $y=$ hypergeom $([a, b], c, z)$.
数学代写|微分方程代写DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION代考|BESSEL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
如果二阶微分方程中的系数2.2.1有不同的形式,可以构造不同形式的特殊微分方程。例如,可以制定常用的贝塞尔微分方程。本节介绍贝塞尔微分方程的数学形式,然后总结各种贝塞尔函数及其计算。
定义 2.8。如果二阶齐次微分方程的一般形式可以写成
X2d2是(X)dX2+Xd是(X)dX+(X2−v2)是(X)=0
该函数称为贝塞尔微分方程。

数学代写|微分方程代写differential equation代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。