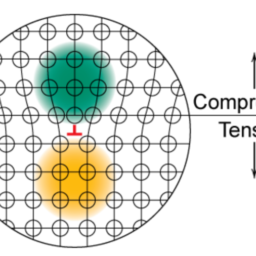
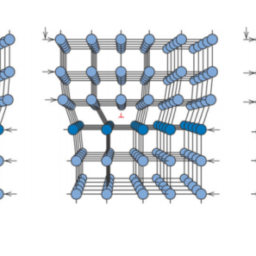
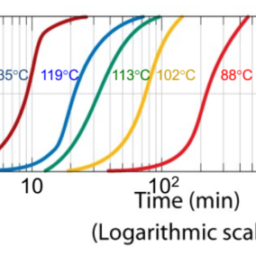
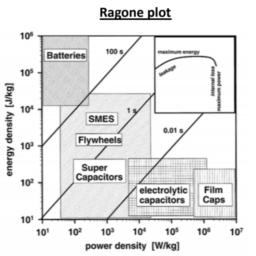
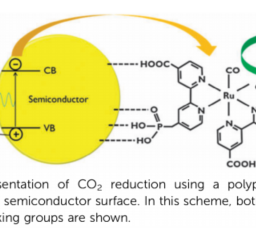
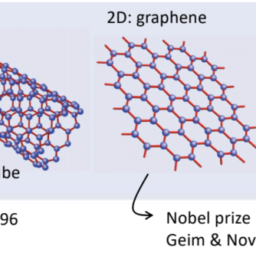
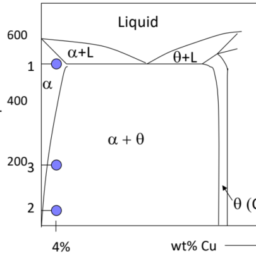
如果你也在 怎样代写材料物理Materials Physics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。材料物理Materials Physics是利用物理学来描述材料的物理特性。它是物理科学的综合,如化学、固体力学、固态物理学和材料科学。材料物理学被认为是凝聚态物理学的一个子集,并将基本的凝聚态概念应用于复杂的多相介质,包括具有技术意义的材料。
材料物理Materials Physics从事的领域包括电子、光学和磁性材料、新型材料和结构、材料中的量子现象、非平衡物理学和软凝聚态物理学。新的实验和计算工具正在不断改善材料系统的建模和研究方式,也是材料物理学家工作的领域。
my-assignmentexpert™ 材料物理Materials Physics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的材料物理Materials Physics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此材料物理Materials Physics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理physics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的材料物理Materials Physics代写服务。我们的专家在物理physics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种材料物理Materials Physics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的材料物理Materials Physics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:

物理代写|材料物理作业代写Materials Physics代考|Electrolyte
Purpose:
- Separates anode and cathode so that they do not react directly, i.e. ensures the current flows in the external circuit.
- Conduction of ions between anode and cathode to ensure both remain charge neutral during charging/discharging.
Electrolytes for Li-metal batteries: - Made of salt dissolved in a solvent
- Organic solvents: acetonitrile, dioxan, dimethylsulfoxide, tetrahydrofurane,…..
- NOT aqueous solvents as Li reacts explosively with water
- Salt should have high solubility, i.e. low lattice energy: occurs when small Li ion is paired with large anions. Examples: $\mathrm{LiClO}{4}, \mathrm{LiPF}{6}$, $\mathrm{LiBr}, \ldots .$
物理代写|材料物理作业代写Materials Physics代考|Cathode materials
- Solid cathode made of $\mathrm{FeS}{2}$ Overall cell reaction: $4 \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{FeS}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{Li}{2} \mathrm{~S}(\mathrm{~s})$ Shorthand notation: $\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s}) \mid \mathrm{LiPF}{6}, \mathrm{DMSO}^{\mid} \mathrm{FeS}_{2}(\mathrm{~s})$
Open-circuit voltage $=1.86 \mathrm{~V}$
Commercial operating voltage $=1.5 \mathrm{~V}$
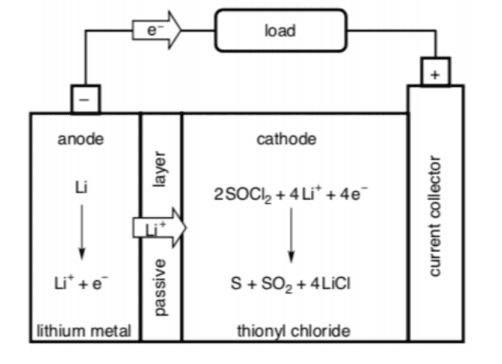
- Liquid cathode made of Thionyl chloride
Overall cell reaction:
$4 \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{SOCl}{2}(\mathrm{I}) \rightarrow \mathrm{S}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{SO}{2}$ (solv) $+4 \mathrm{LiCl}(\mathrm{s})$
Shorthand notation:
$\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})\left|\mathrm{LiAlCl}{4}, \mathrm{SOCl}{2}(\mathrm{l})\right| \mathrm{C}$ (s)
LiCl(s) precipitates on anode and forms a passive layer preventing direct reaction of $\mathrm{Li}$ with $\mathrm{SOCl}{2}$ but allowing $\mathrm{Li}$ ions produced at anode to pass through, plays the role of the electrolyte in other cells $\mathrm{LiAlCl}{4}$ increases conductivity. No organic solvents present, therefore this cell is termed “inorganic Li battery”
$C(s)$ is the inert current collector material
- Intercalation Cathodes
Overall cell reaction:
$n \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Li}{n} \mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}), \mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn}, \mathrm{Co}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{Mo}$ Shorthand notation: $\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})\left|\mathrm{LiClO}{4}, \mathrm{PC}\right| \mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \mid \mathrm{C}(\mathrm{s})$ $\mathrm{Li}^{+}$diffuses between the negatively charged layers of host material $\mathrm{XO}{2}$ forming an intercalation compound. $P C=$ polycarbonate (solvent),
$C(s)$ is the current collector material
Open-circuit voltage $=2.5-3.2 \mathrm{~V}(\mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn})$ 3.8-4.5 V ( $X=C o)$ very high!
Commercial operating voltage $=3.0 \mathrm{~V}(\mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn})$
材料物理代写
物理代写|材料物理作业代写MATERIALS PHYSICS代考|ELECTROLYTE
目的:
- 将阳极和阴极分开,使它们不会直接反应,即确保电流在外部电路中流动。
- 阳极和阴极之间的离子传导,以确保在充电/放电期间都保持电荷中性。
锂金属电池电解液: - 由溶解在溶剂中的盐制成
- 有机溶剂:乙腈、二恶烷、二甲亚砜、四氢呋喃……
- 不是水性溶剂,因为锂会与水发生爆炸性反应
- 盐应该具有高溶解度,即低晶格能:当小锂离子与大阴离子配对时发生。示例:$\mathrm{LiClO} {4},\mathrm{LiPF} {6},\mathrm{LiBr}, \ldots .$
物理代写|材料物理作业代写MATERIALS PHYSICS代考|CATHODE MATERIALS
- Solid cathode made of $\mathrm{FeS}{2}$ Overall cell reaction: $4 \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{FeS}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{Li}{2} \mathrm{~S}(\mathrm{~s})$ Shorthand notation: $\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s}) \mid \mathrm{LiPF}{6}, \mathrm{DMSO}^{\mid} \mathrm{FeS}_{2}(\mathrm{~s})$
Open-circuit voltage $=1.86 \mathrm{~V}$
Commercial operating voltage $=1.5 \mathrm{~V}$
- Liquid cathode made of Thionyl chloride
Overall cell reaction:
$4 \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{SOCl}{2}(\mathrm{I}) \rightarrow \mathrm{S}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{SO}{2}$ (solv) $+4 \mathrm{LiCl}(\mathrm{s})$
Shorthand notation:
$\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})\left|\mathrm{LiAlCl}{4}, \mathrm{SOCl}{2}(\mathrm{l})\right| \mathrm{C}$ (s)
LiCl(s) precipitates on anode and forms a passive layer preventing direct reaction of $\mathrm{Li}$ with $\mathrm{SOCl}{2}$ but allowing $\mathrm{Li}$ ions produced at anode to pass through, plays the role of the electrolyte in other cells $\mathrm{LiAlCl}{4}$ increases conductivity. No organic solvents present, therefore this cell is termed “inorganic Li battery”
$C(s)$ is the inert current collector material
- Intercalation Cathodes
Overall cell reaction:
$n \mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{Li}{n} \mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}), \mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn}, \mathrm{Co}, \mathrm{Ti}, \mathrm{Mo}$ Shorthand notation: $\mathrm{Li}(\mathrm{s})\left|\mathrm{LiClO}{4}, \mathrm{PC}\right| \mathrm{XO}{2}(\mathrm{~s}) \mid \mathrm{C}(\mathrm{s})$ $\mathrm{Li}^{+}$diffuses between the negatively charged layers of host material $\mathrm{XO}{2}$ forming an intercalation compound. $P C=$ polycarbonate (solvent),
$C(s)$ is the current collector material
Open-circuit voltage $=2.5-3.2 \mathrm{~V}(\mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn})$ 3.8-4.5 V ( $X=C o)$ very high!
Commercial operating voltage $=3.0 \mathrm{~V}(\mathrm{X}=\mathrm{Mn})$

物理代写|材料物理作业代写Materials Physics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。