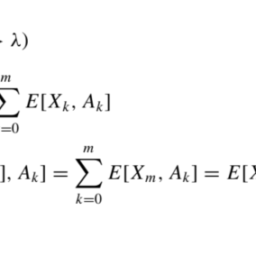如果你也在 怎样代写随机分析stochastic analysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。随机分析stochastic analysis是数学的一个分支,对随机过程进行操作。它允许为随机过程的积分定义一个关于随机过程的一致的积分理论。这个领域是由日本数学家伊藤清在第二次世界大战期间创建并开始的。
随机分析stochastic analysis应用随机微积分的最著名的随机过程是维纳过程(为纪念诺伯特-维纳而命名),它被用来模拟路易-巴切莱特在1900年和阿尔伯特-爱因斯坦在1905年描述的布朗运动以及其他受随机力作用的粒子在空间的物理扩散过程。自20世纪70年代以来,维纳过程被广泛地应用于金融数学和经济学中,以模拟股票价格和债券利率的时间演变。
my-assignmentexpert™ 随机分析stochastic analysis作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的随机分析stochastic analysis作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此随机分析stochastic analysis作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的随机分析stochastic analysis作业代写代写服务。我们的专家在数学mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种随机分析stochastic analysis相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的随机分析stochastic analysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|随机分析作业代写stochastic analysis代考|random variables
In this chapter, we call a sequence of random variables $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ a stochastic process.
Definition 2.4.1 We say that a stochastic process $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ is $\left(\left{\mathcal{F}{n}\right}{n=0}^{\infty}-\right)$ adapted, if a random variable $X_{n}$ is $\mathcal{F}{n}$-measurable for all $n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}$.
It is obvious that martingales are adapted.
Definition 2.4.2 We say that a stochastic process $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ is $\left(\left{\mathcal{F}{n}\right}{n=0^{-}}^{\infty}\right)$ predictable, if $X_{0}=0$ and a random variable $X_{n}$ is $\mathcal{F}{n-1}$-measurable for all $n \geqq 1$. Theorem 2.4.1 Let $\left{X{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ be an adapted process such that $E\left[\left|X_{n}\right|\right]<\infty, n=$ $0,1,2, \ldots$. Then we have the following.
(1) There exist a martingale $\left{M_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ with $M_{0}=0$ and a predictable process $\left{A_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ such that
$$
X_{n}=X_{0}+M_{n}+A_{n}, \quad n \geqq 0
$$
Moreover, if there is a martingale $\left{\tilde{M}{n}\right}{n=0}^{\infty}$ with $\tilde{M}{0}=0$ and a predictable process $\left{\tilde{A}{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ such that $X_{n}=X_{0}+\tilde{M}{n}+\tilde{A}{n}, n \geqq 0$, then $\tilde{M}{n}=M{n}$ a.s. and $\tilde{A}{n}=A{n}$ a.s., $n \geqq 0$.
数学代写|随机分析作业代写stochastic analysis代考|well-defined
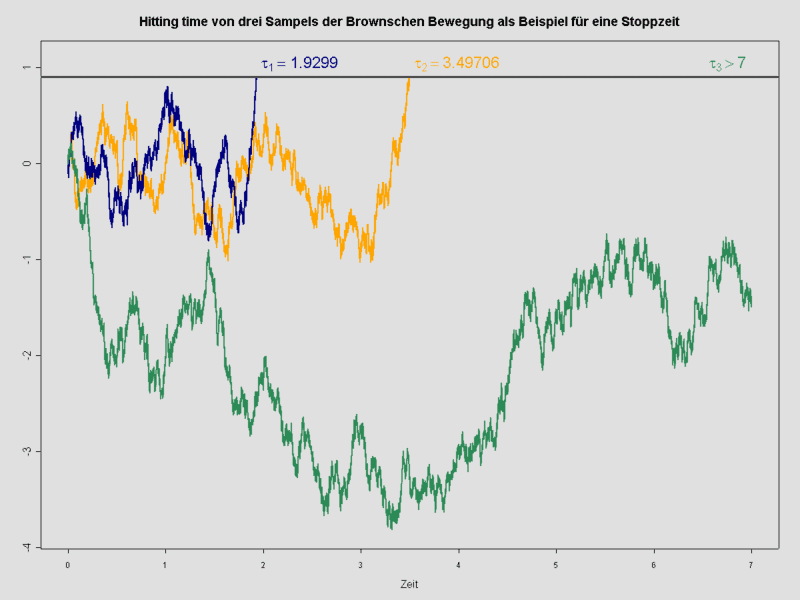
Proposition 2.4.1 Let $\tau$ be a stopping time and $\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ be an adapted stochastic process. Then a random variable $1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}$ is $\mathcal{F}{\tau}$-measurable. Here $1{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}$ is a random variable given by
$$
\left(1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}\right)(\omega)=\left{\begin{array}{cl}
X_{n}(\omega), & \text { if } \tau(\omega)=n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}, \ 0, & \text { if } \tau(\omega)=\infty \end{array}\right. $$ for $\omega \in \Omega$. Proof Our assertion follows from the fact that $1{(\tau<\infty)} X_{\tau}$ is well-defined and that
$$
\left{1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau} \in B\right} \cap{\tau=n}=\left{X_{n} \in B\right} \cap{\tau=n} \in \mathcal{F}{n}, \quad n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}
$$
for any $B \in \mathcal{B}([-\infty, \infty])$.
In the case that $P(\tau<\infty)=1$ we denote $1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}$ by $X_{\tau}$ for simplicity of notation.
For any stochastic processes $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ and $Y=\left{Y_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$, we define a stochastic process $Y \bullet X$ by
(Y \bullet X){0}=0, \text { and }(Y \bullet X){n}=\sum_{k=1}^{n} Y_{k}\left(X_{k}-X_{k-1}\right), \quad n \geqq 1
随机分析代写
数学代写|随机分析作业代写STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS代考|RANDOM VARIABLES
在本章中,我们称随机变量序列X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}一个随机过程。
定义 2.4.1 我们说一个随机过程 $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ is $\left(\left{\mathcal{F}{n}\right}{n=0}^{\infty}-\right)$ adapted, if a random variable $X_{n}$ is $\mathcal{F}{n}$-measurable for all $n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}$.
It is obvious that martingales are adapted.
Definition 2.4.2 We say that a stochastic process $X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ is $\left(\left{\mathcal{F}{n}\right}{n=0^{-}}^{\infty}\right)$ predictable, if $X_{0}=0$ and a random variable $X_{n}$ is $\mathcal{F}{n-1}$-measurable for all $n \geqq 1$. Theorem 2.4.1 Let $\left{X{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ be an adapted process such that $E\left[\left|X_{n}\right|\right]<\infty, n=$ $0,1,2, \ldots$. Then we have the following.
(1) There exist a martingale $\left{M_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ with $M_{0}=0$ and a predictable process $\left{A_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ such that
$$
X_{n}=X_{0}+M_{n}+A_{n}, \quad n \geqq 0
$$
Moreover, if there is a martingale $\left{\tilde{M}{n}\right}{n=0}^{\infty}$ with $\tilde{M}{0}=0$ and a predictable process $\left{\tilde{A}{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ such that $X_{n}=X_{0}+\tilde{M}{n}+\tilde{A}{n}, n \geqq 0$, then $\tilde{M}{n}=M{n}$ a.s. and $\tilde{A}{n}=A{n}$ a.s., $n \geqq 0$.
数学代写|随机分析作业代写STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS代考|WELL-DEFINED
命题 2.4.1 让τ是一个停止时间$\tau$ be a stopping time and $\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}$ be an adapted stochastic process. Then a random variable $1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}$ is $\mathcal{F}{\tau}$-measurable. Here $1{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}$ is a random variable given by
$$
\left(1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau}\right)(\omega)=\left{\begin{array}{cl}
X_{n}(\omega), & \text { if } \tau(\omega)=n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}, \ 0, & \text { if } \tau(\omega)=\infty \end{array}\right. $$ for $\omega \in \Omega$. Proof Our assertion follows from the fact that $1{(\tau<\infty)} X_{\tau}$ is well-defined and that
$$
\left{1_{{\tau<\infty}} X_{\tau} \in B\right} \cap{\tau=n}=\left{X_{n} \in B\right} \cap{\tau=n} \in \mathcal{F}{n}, \quad n \in \mathbf{Z}{\geqq 0}
$$
对于任何乙∈乙([−∞,∞]).
在这种情况下磷(τ<∞)=1我们表示1τ<∞Xτ经过Xτ为了符号的简单。
对于任何随机过程X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}X=\left{X_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}和Y=\left{Y_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty}Y=\left{Y_{n}\right}_{n=0}^{\infty},我们定义一个随机过程是∙X经过
(Y \bullet X){0}=0, \text { and }(Y \bullet X){n}=\sum_{k=1}^{n} Y_{k}\left(X_{k}-X_{k-1}\right), \quad n \geqq 1
数学代写|随机分析作业代写stochastic analysis代考 matlab代写请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。