如果你也在 怎样代写微观经济学Microeconomics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。微观经济学Microeconomics是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和公司在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和公司之间的互动。微观经济学侧重于研究单个市场、部门或行业,而不是宏观经济学所研究的整个国民经济。
微观经济学Microeconomics的一个目标是分析在商品和服务之间建立相对价格的市场机制,并在各种用途之间分配有限资源。微观经济学显示了自由市场导致理想分配的条件。它还分析了市场失灵,即市场未能产生有效的结果。微观经济学关注公司和个人,而宏观经济学则关注经济活动的总和,处理增长、通货膨胀和失业问题以及与这些问题有关的国家政策。微观经济学还处理经济政策(如改变税收水平)对微观经济行为的影响,从而对经济的上述方面产生影响。特别是在卢卡斯批判之后,现代宏观经济理论大多建立在微观基础上,即基于微观层面行为的基本假设。
my-assignmentexpert™ 微观经济学Microeconomics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的微观经济学Microeconomics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此微观经济学Microeconomics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在经济Economy作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的微观经济学Microeconomics代写服务。我们的专家在经济Economy代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微观经济学Microeconomics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的微观经济学Microeconomics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
经济代写|微观经济学作业代写Microeconomics代考|Background and problems
The impact of irreversibilities on the functioning of markets has of course preoccupied economists from the beginning. We could take as an example the many works devoted to the imperfection of information. For a long time, analysis was hindered by the domination of static models, which sometimes even resulted in inaccurate conjectures. However, certain works published over the last few decades have contributed to progress on this question. Here we will limit ourselves to citing the studies of Stigler on the economics of information (1961) and the analyses of J. Stiglitz (1967) and of S. Salop and J. Stiglitz (1982) on equilibrium in markets with imperfect information. These works have started to bring to the fore phenomena studied for some time by physicists working on the dynamics of irreversible systems, but they have yet to establish the general framework.
In fact, irreversibility implies ” $a$ breaking of symmetry between before and after” (Prigogine and Stengers, 1988). Hence the possibility of the occurrence of events. “By definition, an event cannot be deduced from a determinist law. It implies, in one way or another, that what has occurred could have not occurred, therefore reflecting a realm of possibles that no knowledge can reduce.” Nevertheless, an event is only of interest if it is significant, in other words likely to transform future evolution and thus generate new coherences.
These aspects, often hidden in the literature on the subject, will be brought out clearly in the models in this chapter.
经济代写|微观经济学作业代写Microeconomics代考|Canonical principles
We retain the conceptual framework used in chapter 2 :
- time is broken down into a series of periods,
- different categories of agents coexist in the market,
- the agents are constantly carrying out activities of exploration and exchange,
- during each period, the agents seek, discover and receive information and either modify or do not modify their exchange requirements accordingly,
- during choices, meetings or discoveries, random phenomena occur and the evolution of the market is thus described by a stochastic process.
On the contrary, the simplifying hypotheses that ensured the absence of irreversibilities have been removed. Now, if agents benefit from the utility obtained from exchanges, they also sustain information or adaptation costs, lay out expenditure in investment or see their performances or the conditions of their choices modified.
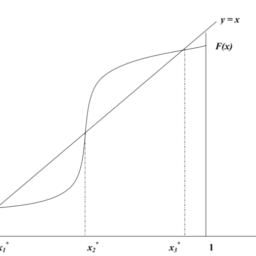
Unlike the simple market, which converges towards a stable state with a unique price, independent of its history (and therefore predictable), models with irreversibilities generate much more varied configurations.
- They may converge to a stable state dependent on the history of the market or endlessly generate fluctuations.
- From a given initial state, the market may end up in any one of a multiplicity of stable states, in each of which the jobs occupied and the workers employed are different.
- In each stable state, we may observe a unique price or price dispersion.
- The evolution of the markets may even, in certain models, lead to more original phenomena, such as the emergence of new markets.
微观经济学代写
经济代写|微观经济学作业代写MICROECONOMICS代考|BACKGROUND AND PROBLEMS
不可逆性对市场运作的影响当然从一开始就让经济学家们全神贯注。我们可以以许多致力于信息不完善的作品为例。长期以来,分析受制于静态模型的主导地位,有时甚至导致猜想不准确。然而,过去几十年出版的某些作品有助于在这个问题上取得进展。在这里,我们将限制自己引用斯蒂格勒关于信息经济学的研究1961以及 J. Stiglitz 的分析1967以及 S. Salop 和 J. Stiglitz1982关于信息不完全市场的均衡。这些工作已经开始突出研究不可逆系统动力学的物理学家一段时间以来所研究的现象,但他们尚未建立总体框架。
事实上,不可逆性意味着“一种打破前后对称性”磷r一世G这G一世n和一种nd小号吨和nG和rs,1988. 因此,事件发生的可能性。“根据定义,事件不能从决定论的定律中推断出来。它以某种方式暗示已经发生的事情可能不会发生,因此反映了任何知识都无法减少的可能性领域。” 然而,一个事件只有在它很重要时才有意义,换句话说,它可能会改变未来的演变,从而产生新的连贯性。
这些方面,通常隐藏在有关该主题的文献中,将在本章的模型中清楚地展示出来。
经济代写|微观经济学作业代写MICROECONOMICS代考|CANONICAL PRINCIPLES
我们保留第 2 章中使用的概念框架:
- 时间被分解成一系列的时期,
- 不同类别的代理商在市场上并存,
- 代理商不断开展探索交流活动,
- 在每个时期,代理寻求、发现和接收信息,并相应地修改或不修改其交换要求,
- 在选择、会议或发现过程中,随机现象发生,市场的演变因此被描述为一个随机过程。
相反,确保不存在不可逆性的简化假设已被删除。现在,如果代理人从交易所获得的效用中受益,他们也会维持信息或适应成本,安排投资支出或看到他们的表现或他们的选择条件得到修改。
与简单的市场不同,该市场以独特的价格趋于稳定状态,独立于其历史一种nd吨H和r和F这r和pr和d一世C吨一种bl和,具有不可逆性的模型会产生更多不同的配置。
- 它们可能会收敛到取决于市场历史的稳定状态,也可能会无休止地产生波动。
- 从一个给定的初始状态开始,市场可能最终处于多种稳定状态中的任何一种,在每个稳定状态中,所占据的工作和雇佣的工人都是不同的。
- 在每个稳定状态下,我们可能会观察到独特的价格或价格分散。
- 在某些模型中,市场的演变甚至可能导致更多的原创现象,例如新市场的出现。

经济代写|微观经济学作业代写MICROECONOMICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。