如果你也在 怎样代写有限元方法finite differences method这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。有限元方法finite differences method在数值分析中,是一类通过用有限差分逼近导数解决微分方程的数值技术。空间域和时间间隔(如果适用)都被离散化,或被分成有限的步骤,通过解决包含有限差分和附近点的数值的代数方程来逼近这些离散点的解的数值。
有限元方法finite differences method有限差分法将可能是非线性的常微分方程(ODE)或偏微分方程(PDE)转换成可以用矩阵代数技术解决的线性方程系统。现代计算机可以有效地进行这些线性代数计算,再加上其相对容易实现,使得FDM在现代数值分析中得到了广泛的应用。今天,FDM与有限元方法一样,是数值解决PDE的最常用方法之一。
my-assignmentexpert™ 有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此有限元方法finite differences method作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的有限元方法finite differences method代写服务。我们的专家在数学Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种有限元方法finite differences method相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的有限元方法finite differences method及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
调和函数 harmonic function
椭圆方程 elliptic equation
抛物方程 Parabolic equation
双曲方程 Hyperbolic equation
非线性方法 nonlinear method
变分法 Calculus of Variations
几何分析 geometric analysis
偏微分方程数值解 Numerical solution of partial differential equations
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|A two-point boundary-value problem
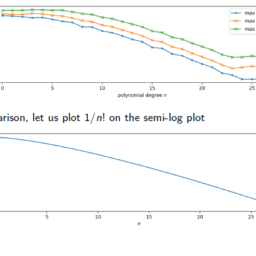
In Chapter 3 , the finite element philosophy was developed and illustrated by means of examples in which the interpolation functions were linear polynomials. There is no reason to choose linear functions only; indeed, higher-order polynomials are frequently used and in principle cause no more difficulty. We shall illustrate the approach using the Galerkin finite element method of Sections 3.2-3.5.
$$
-u^{\prime \prime}=f(x), \quad 0<x<1, \quad u(0)=1, \quad u^{\prime}(1)+2 u(1)=3 .
$$
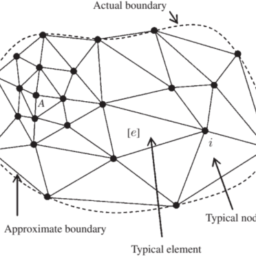
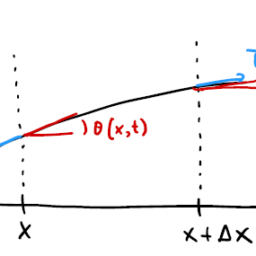
Suppose that the region $0 \leq x \leq 1$ is divided into $E$ elements, each element having three nodes; a typical element is shown in Fig. 4.1. In terms of its three nodal values, the variable $u$ may be uniquely interpolated as a quadratic polynomial, the interpolation being given by
$$
u^{e}=\mathbf{N}^{e} \mathbf{U}^{e},
$$
where $\mathbf{U}^{e}=\left[\begin{array}{lll}U_{1} & U_{2} & U_{3}\end{array}\right]^{T}$ and the shape function matrix is
$$
\mathbf{N}^{e}=\frac{1}{2}\left[\begin{array}{lll}
\xi^{2}-\xi & 2\left(1-\xi^{2}\right) & \xi^{2}+\xi
\end{array}\right] .
$$
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|Higher-order rectangular elements
The shape functions for the bilinear rectangular element, discussed in Section 3.7, were obtained by taking products of the Lagrange linear interpolation polynomials. This idea may be extended to develop higher-order rectangular elements; for example, the shape functions for the elements in Fig. $4.3$ are obtained by taking products of Lagrange quadratic, cubic and quartic polynomials.
Although the Lagrange family is convenient to use and easy to set up, it does have two drawbacks:
- The elements have many internal nodes and, in the overall system, these contribute to one element only. This may, however, be overcome by the ‘condensation’ procedure of Section 4.5.
- The expressions for the shape functions contain relatively high-order terms, while some lower-order terms are missing.
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|Higher-order triangular elements
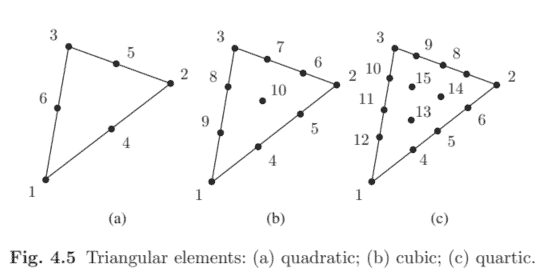
The quadratic, cubic and quartic triangular elements are shown in Fig. 4.5. The shape functions are very easy to generate in terms of the area coordinates given by eqn (3.62).
(a) Quadratic element.
Corner nodes:
$$
N_{i}=L_{i}\left(2 L_{i}-1\right)
$$
Mid-side nodes:
$$
N_{4}=4 L_{1} L_{2}, \text { etc. }
$$
(b) Cubic element.
Corner nodes:
$$
N_{i}=\frac{1}{2}\left(3 L_{i}-1\right)\left(3 L_{i}-2\right) .
$$
Side nodes:
$$
\begin{aligned}
&N_{4}=\frac{9}{2} L_{1} L_{2}\left(3 L_{1}-1\right), \
&N_{5}=\frac{9}{2} L_{1} L_{2}\left(3 L_{1}-2\right), \text { etc. }
\end{aligned}
$$
Node at centroid:
$$
N_{10}=27 L_{1} L_{2} L_{3} .
$$
(c) Quartic element. The shape functions are obtained in Exercise 4.5.
For all these triangular elements, the function values along a side are uniquely determined by the nodal values on that side. Consequently, these elements are conforming elements. The element matrices for both triangular and rectangular elements are obtained in the usual way; however, it is not difficult to see that the integrals involved make hand calculation impracticable for the cubic and higher-order elements. For this reason, it is usual to use numerical integration to obtain the matrices.
有限元方法代写
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|A TWO-POINT BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
在第 3 章中,通过插值函数是线性多项式的例子,发展和说明了有限元原理。没有理由只选择线性函数;事实上,高阶多项式经常被使用,原则上不会造成更多困难。我们将使用 3.2-3.5 节的 Galerkin 有限元方法来说明该方法。−在′′=F(X),0<X<1,在(0)=1,在′(1)+2在(1)=3.
假设区域0≤X≤1分为和元素,每个元素具有三个节点;一个典型的元素如图 4.1 所示。就其三个节点值而言,变量在可以作为二次多项式唯一插值,插值由下式给出
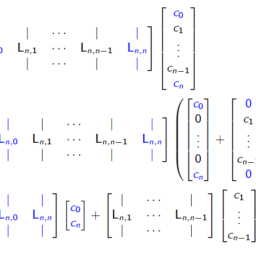
在和=ñ和在和,
在哪里在和=[在1在2在3]吨形状函数矩阵为
ñ和=12[X2−X2(1−X2)X2+X].
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|HIGHER-ORDER RECTANGULAR ELEMENTS
在第 3.7 节中讨论的双线性矩形元素的形状函数是通过拉格朗日线性插值多项式的乘积获得的。这个想法可以扩展到开发更高阶的矩形元素;例如,图 1 中元素的形状函数。4.3通过拉格朗日二次、三次和四次多项式的乘积获得。
尽管 Lagrange 系列使用方便且易于设置,但它确实有两个缺点:
- 元素有许多内部节点,在整个系统中,这些节点仅对一个元素有贡献。然而,这可以通过第 4.5 节的“浓缩”程序来克服。
- 形状函数的表达式包含相对高阶项,而缺少一些低阶项。
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|HIGHER-ORDER TRIANGULAR ELEMENTS
二次、三次和四次三角形元素如图 4.5 所示。根据 eqn 给出的区域坐标,形状函数很容易生成3.62.
一种二次元。
角节点:
ñ一世=大号一世(2大号一世−1)
中间节点:
ñ4=4大号1大号2, 等等
b立方元素。
角节点:
ñ一世=12(3大号一世−1)(3大号一世−2).
侧节点:
ñ4=92大号1大号2(3大号1−1), ñ5=92大号1大号2(3大号1−2), 等等
质心节点:
ñ10=27大号1大号2大号3.
C四次元。形状函数在练习 4.5 中获得。
对于所有这些三角形元素,沿一侧的函数值由该一侧的节点值唯一确定。因此,这些元素是符合元素。三角形和矩形元素的元素矩阵以通常的方式获得;然而,不难看出所涉及的积分使得手动计算对于三次和高阶元素是不切实际的。因此,通常使用数值积分来获得矩阵。

数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。