如果你也在 怎样代写数字信号处理digital signal process这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。数字信号处理digital signal process是指使用数字处理,如通过计算机或更专业的数字信号处理器,来进行各种信号处理操作。以这种方式处理的数字信号是一连串的数字,代表时间、空间或频率等领域中连续变量的样本。在数字电子学中,数字信号被表示为脉冲序列,它通常由晶体管的开关产生。
数字信号处理digital signal process和模拟信号处理是信号处理的子领域。DSP的应用包括音频和语音处理、声纳、雷达和其他传感器阵列处理、频谱密度估计、统计信号处理、数字图像处理、数据压缩、视频编码、音频编码、图像压缩、电信的信号处理、控制系统、生物医学工程和地震学等。
my-assignmentexpert™ 数字信号处理digital signal process作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的数字信号处理digital signal process作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此数字信号处理digital signal process作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在信息Information作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数字信号处理digital signal process代写服务。我们的专家在信息Information代写方面经验极为丰富,各种数字信号处理digital signal process相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的数字信号处理digital signal process及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
调和函数 harmonic function
椭圆方程 elliptic equation
抛物方程 Parabolic equation
双曲方程 Hyperbolic equation
非线性方法 nonlinear method
变分法 Calculus of Variations
几何分析 geometric analysis
偏微分方程数值解 Numerical solution of partial differential equations
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写digital signal process代考|Nyquist Sampling
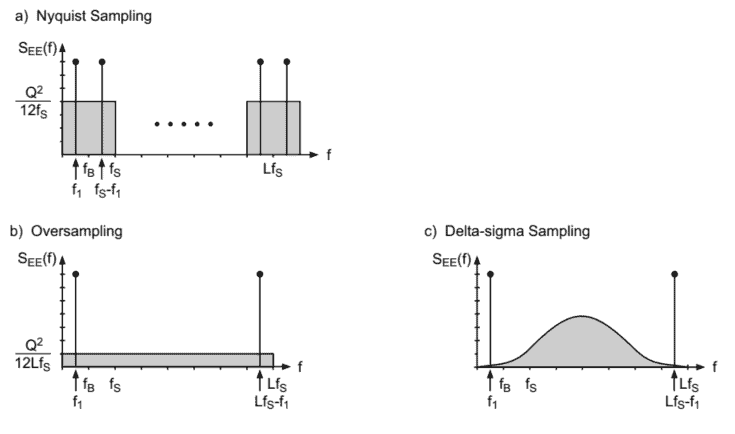
The sampling of a signal with sampling rate $f_{S}>2 f_{B}$ is called Nyquist sampling. The schematic diagram in Fig. 3.1 shows the procedure. The band-limiting of the input at $f_{S} / 2$ is carried out by an analog low-pass filter (Fig. 3.1a). The following sample-and-hold circuit samples the band-limited input at a sampling rate $f_{S}$. The constant amplitude of the time function over the sampling period $T_{S}=1 / f_{S}$ is converted to a number sequence $x(n)$ by a quantizer (Fig. 3.1b). This number sequence is fed to a digital signal processor (DSP) which performs signal processing algorithms. The output sequence $y(n)$ is delivered to a DA converter which gives a staircase as its output (Fig. 3.1c). Following this, a low-pass filter gives the analog output $y(t)$ (Fig. 3.1d). Figure $3.2$ demonstrates each step of AD/DA conversion in the frequency domain. The individual spectra in Fig. 3.2a-d correspond to the outputs in Fig. 3.1a-d.
After band-limiting (Fig. 3.2a) and sampling, a periodic spectrum with period $f_{S}$ of the sampled signal is obtained as shown in Fig. 3.2b. Assuming that consecutive quantization errors $e(n)$ are statistically independent of each other, the noise power has a spectral uniform distribution in the frequency domain $0 \leq f \leq f_{S}$. The output of the DA converter still has a periodic spectrum. However, this is weighted with the sinc function ( $\sin c=\sin (x) / x)$, of the sample-and-hold circuit (Fig. 3.2c). The zeros of the sinc function are at multiples of the sampling rate $f_{S}$. In order to reconstruct the output (Fig. $3.2 \mathrm{~d}$ ), the image spectra are eliminated by an analog low-pass of sufficient stop-band attenuation (see Fig. 3.2c).
The problems of Nyquist sampling lie in the steep band-limiting filter characteristics (anti-aliasing filter) of the analog input filter and the analog reconstruction filter (antiimaging filter) of similar filter characteristics and sufficient stop-band attenuation. Further, sinc distortion due to the sample-and-hold circuit needs to be compensated for.
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写digital signal process代考|Oversampling
In order to increase the resolution of the conversion process and reduce the complexity of analog filters, oversampling techniques are employed. Owing to the spectral uniform distribution of quantization error between 0 and $f_{S}$ (see Fig. 3.3a), it is possible to reduce the power spectral density in the pass-band $0 \leq f \leq f_{B}$ through oversampling by a factor $L$, i.e. with the new sampling rate $L f_{S}$ (see Fig. 3.3b). For identical quantization step size $Q$, the shaded areas (quantization error power $\sigma_{E}^{2}$ ) in Fig. 3.3a and Fig. 3.3b are equal. The increase in the signal-to-noise ratio can also be observed in Fig. 3.3.
It follows that in the pass-band at a sampling rate of $f_{S}=2 f_{B}$ the power spectral density given by
$$
S_{E E}(f)=\frac{Q^{2}}{12 f_{S}}
$$
66
AD/DA Conversion
leads to the noise power
$$
N_{B}^{2}=\sigma_{E}^{2}=2 \int_{0}^{f_{B}} S_{E E}(f) d f=\frac{Q^{2}}{12}
$$
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写digital signal process代考|Delta-sigma Modulation
Delta-sigma modulation using oversampling is a conversion strategy derived from delta modulation. In delta modulation (Fig. 3.6a), the difference between the input $x(t)$ and signal $x_{1}(t)$ is converted into a 1-bit signal $y(n)$ at a very high sampling rate $L f_{S}$. The sampling rate is higher than the necessary Nyquist rate $f_{S}$. The quantized signal $y(n)$ gives the signal $x_{1}(t)$ via an analog integrator. The demodulator consists of an integrator and a reconstruction low-pass filter.
The extension to delta-sigma modulation [Ino63] involves shifting the integrator from the demodulator to the input of the modulator (see Fig. 3.6b). With this, it is possible to combine the two integrators as a single integrator after addition. The corresponding signals are shown in Fig. 3.8.
A time-discrete model of the delta-sigma modulator is given in Fig. 3.7b. The $Z$ transform of the output signal $y(n)$ is given by
$$
Y(z)=\frac{H(z)}{1+H(z)} X(z)+\frac{1}{1+H(z)} E(z) \approx X(z)+\frac{1}{1+H(z)} E(z) .
$$
数字信号处理代写
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESS代考|NYQUIST SAMPLING
以采样率对信号进行采样F小号>2F乙称为奈奎斯特采样。图 3.1 中的示意图显示了该过程。输入的频带限制在F小号/2由模拟低通滤波器执行F一世G.3.1一种. 以下采样保持电路以采样率对带限输入进行采样F小号. 采样周期内时间函数的恒定幅度吨小号=1/F小号转换为数字序列X(n)通过量化器F一世G.3.1b. 该数字序列被馈送到数字信号处理器D小号磷它执行信号处理算法。输出序列是(n)传送到一个 DA 转换器,该转换器提供一个楼梯作为其输出F一世G.3.1C. 在此之后,低通滤波器给出模拟输出是(吨) F一世G.3.1d. 数字3.2演示了频域中 AD/DA 转换的每个步骤。图 3.2ad 中的各个光谱对应于图 3.1ad 中的输出。
限带后F一世G.3.2一种和采样,具有周期的周期性频谱F小号得到的采样信号如图 3.2b 所示。假设连续量化误差和(n)在统计上相互独立,噪声功率在频域中具有频谱均匀分布0≤F≤F小号. DA 转换器的输出仍然具有周期性频谱。但是,这是使用 sinc 函数加权的$罪C=罪(X/ X),这F吨H和s一种米pl和−一种nd−H这ldC一世rC在一世吨(F一世G.3.2C).吨H和和和r这s这F吨H和s一世nCF在nC吨一世这n一种r和一种吨米在l吨一世pl和s这F吨H和s一种米pl一世nGr一种吨和f_{S}.一世n这rd和r吨这r和C这ns吨r在C吨吨H和这在吨p在吨(F一世G.3.2 \mathrm{~d}$ ),图像光谱被足够阻带衰减的模拟低通消除s和和F一世G.3.2C.
奈奎斯特采样的问题在于陡峭的限带滤波器特性一种n吨一世−一种l一世一种s一世nGF一世l吨和r模拟输入滤波器和模拟重建滤波器一种n吨一世一世米一种G一世nGF一世l吨和r具有相似的滤波器特性和足够的阻带衰减。此外,需要补偿由于采样保持电路引起的正弦失真。
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESS代考|OVERSAMPLING
为了提高转换过程的分辨率并降低模拟滤波器的复杂性,采用了过采样技术。由于量化误差在 0 和F小号 s和和F一世G.3.3一种,可以降低通带中的功率谱密度0≤F≤F乙通过一个因子过采样大号,即使用新的采样率大号F小号 s和和F一世G.3.3b. 对于相同的量化步长问, 阴影区域q在一种n吨一世和一种吨一世这n和rr这rp这在和r$σ和2$在图 3.3a 和图 3.3b 中是相等的。在图 3.3 中也可以观察到信噪比的增加。
由此可见,在通带中,采样率为F小号=2F乙功率谱密度由下式给出
小号和和(F)=问212F小号
66
AD/DA 转换
导致噪声功率
ñ乙2=σ和2=2∫0F乙小号和和(F)dF=问212
信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESS代考|DELTA-SIGMA MODULATION
使用过采样的 Delta-sigma 调制是一种源自 delta 调制的转换策略。增量调制F一世G.3.6一种,输入之间的差异X(吨)和信号X1(吨)转换为 1 位信号是(n)以非常高的采样率大号F小号. 采样率高于必要的奈奎斯特率F小号. 量化信号是(n)发出信号X1(吨)通过模拟积分器。解调器由积分器和重建低通滤波器组成。
delta-sigma调制的扩展一世n这63涉及将积分器从解调器转移到调制器的输入s和和F一世G.3.6b. 这样,可以在相加后将两个积分器组合为一个积分器。相应的信号如图 3.8 所示。
图 3.7b 给出了 delta-sigma 调制器的时间离散模型。这从输出信号的变换是(n)是(谁)给的
$$
Y(z)=\frac{H(z)}{1+H(z)} X(z)+\frac{1}{1+H(z)} E(z) \approx X(z)+\frac{1}{1+H(z)} E(z) .
$$

信号代写|数字信号处理作业代写digital signal process代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。