如果你也在 怎样代写geography这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。geography是一个科学领域,致力于研究地球和行星的土地、特征、居民和现象。第一个使用γεωγραφία这个词的人是埃拉托色尼(公元前276-194年)。地理学是一门包罗万象的学科,它寻求对地球及其人类和自然的复杂性的理解–不仅仅是物体在哪里,还包括它们是如何变化和形成的。
geography通常被定义为两个分支:人文地理学和自然地理学。人文地理学关注的是对人及其社区、文化、经济的研究,以及通过研究他们与空间和地点的关系,与环境的相互作用。自然地理学关注的是对自然环境中的过程和模式的研究,如大气圈、水圈、生物圈和地圈。
my-assignmentexpert™ geography作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的geography作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此geography作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在地理Geography作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的geographyy代写服务。我们的专家在地理Geography代写方面经验极为丰富,各种geography相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的geography及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
非线性方法 nonlinear method functional analysis
变分法 Calculus of Variations
地理代写|geography代考|Overview of Migration Research
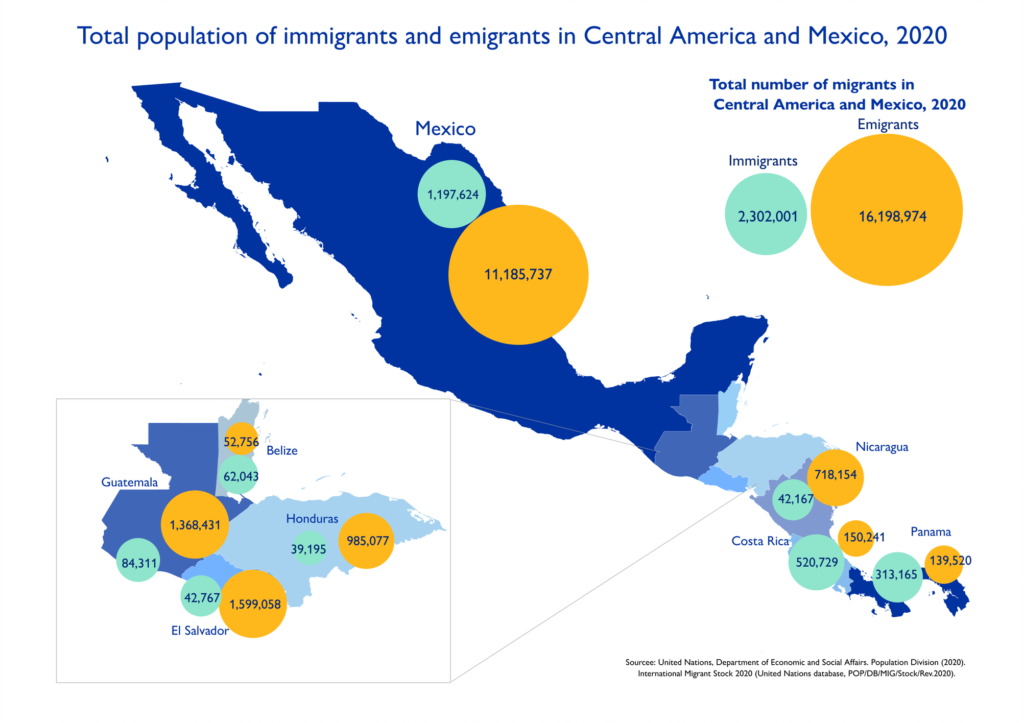
Changes in the spatial distribution of population in the United States have generated two views of the rationale for household migration. The historical migration of households to the Northeast and Great Lakes regions to pursue employment in manufacturing and the current migration in response to the agglomeration of innovative industries suggest one view. Another view is derived from the shifts in U.S. population beginning in the late 1960 s, when population moved from the Northeast and the Midwest to the South and West to access natural amenities such as mountain views, sunshine, and access to a coastline. The former is the foundation for the labor demand side view of voluntary migration. From this perspective, migration is associated with seeking better economic opportunity such as higher wages or improvement in employment prospects. The second view is grounded in the notion that migration is influenced by features of a location, where households select a location that optimizes the bundle of natural or public sector attributes. The labor demand and labor supply perspectives provide different economic explanations for population dynamics, leading to competing views of the impetus for regional development and different roles for public policy. This section describes the relevant literature that provides the foundation for today’s understanding of household migration and its consequences for people and places.
地理代写|geography代考|Empirical Topics
In this section, we address three topics with regard to empirical studies of migration: choice set, selectivity, and the use of panel data. One of the most vexing issues in migration research is the appropriate choice set from which households make decisions. With the availability of microdata sets (PUMS, NLSY) and computational advancements, discrete choice models such as conditional logit and nested logit have resulted in contributions to the migration literature, particularly with regard to the appropriate specification of the choice set from which households select a destination.
Polychotomous choice models such as conditional and nested logit offer alternatives to binary choice models which typically pose a “mover/stayer” decision, where the latter is of limited value for studies of the determinants of where the household locates. Conditional logit and nested logit are random utility models where
$$
\mathrm{U} \text { (location choice } \mathrm{j} \text { for household } \mathrm{i} \text { ) }=\mathrm{U}{\mathrm{ij}}=\mathrm{V}{\mathrm{ij}}+\varepsilon_{\mathrm{ij}}
$$
The utility level $\mathrm{U}{\mathrm{ij}}$ is determined by the systematic component of utility $\mathrm{V}{\mathrm{ij}}$ and $\varepsilon_{\mathrm{ij}}$ is the random disturbance term that is assumed to be independently and identically distributed with a Gumbel distribution.
地理代写|GEOGRAPHY代考|People and Place Issues
In this section, we address several contemporary topics in migration studies. First, we survey the research on the channels by which human capital and place interact to influence the returns to migration. We then briefly discuss the influence of migrants’ skill and demographic characteristics on the spatial distribution of income and identify gaps in the existing literature on income inequality. We then examine the literature on life course migration. Finally, we summarize the literature on family migration, including a discussion of the possible influence on individuals and places as a consequence of the location decisions of “power couples”.
Human capital theory predicts that migrants calculate the expected present value of the difference between the benefits and costs of a location and choose the destination which maximizes earnings or utility. From this perspective, the expected returns to migration are positive. An important finding in the returns to migration literature is that all migrants do not experience wage gains, and the returns to migration vary by subgroup. Yankow (2003) found gains to migrants with more than a high school education. Knapp et al. (2013) show that primary and onward migration types yield positive returns in earnings, with greatest gains to onward migration of the college educated. Knapp and White (2016) found that white male adult earnings gains from migration differ by youth county poverty rates, rurality, education, and ability. These authors found heterogeneity within onward migrants, especially with regard to the interaction of human capital and place characteristics. When the onward migration type was disaggregated by youth county poverty rates, rurality, education attainment, and ability, Knapp et al., found initial earnings losses associated with higher youth county poverty rates and rural county of origin.
geography代写
地理代写|GEOGRAPHY代考|OVERVIEW OF MIGRATION RESEARCH
美国人口空间分布的变化对家庭迁移的基本原理产生了两种看法。历史上家庭向东北和大湖地区迁移到制造业就业,以及当前响应创新产业集聚的迁移表明了一种观点。另一种观点来自于 1960 年代后期开始的美国人口变化,当时人口从东北部和中西部迁移到南部和西部,以获得山景、阳光和海岸线等自然设施。前者是自愿迁移劳动力需求侧观点的基础。从这个角度来看,移民与寻求更好的经济机会有关,例如更高的工资或改善就业前景。第二种观点的基础是迁移受地点特征的影响,家庭选择一个可以优化自然或公共部门属性的地点。劳动力需求和劳动力供给的观点为人口动态提供了不同的经济解释,导致对区域发展的推动力和公共政策的不同作用的不同观点。本节介绍了相关文献,这些文献为当今理解家庭迁移及其对人和地方的影响奠定了基础。劳动力需求和劳动力供给的观点为人口动态提供了不同的经济解释,导致对区域发展的推动力和公共政策的不同作用的不同观点。本节介绍了相关文献,这些文献为当今理解家庭迁移及其对人和地方的影响奠定了基础。劳动力需求和劳动力供给的观点为人口动态提供了不同的经济解释,导致对区域发展的推动力和公共政策的不同作用的不同观点。本节介绍了相关文献,这些文献为当今理解家庭迁移及其对人和地方的影响奠定了基础。
地理代写|GEOGRAPHY代考|EMPIRICAL TOPICS
在本节中,我们将讨论与迁移实证研究有关的三个主题:选择集、选择性和面板数据的使用。One of the most vexing issues in migration research is the appropriate choice set from which households make decisions. 随着微数据集的可用性磷在米小号,ñ大号小号是随着计算的进步,离散选择模型(如条件 logit 和嵌套 logit)对移民文献做出了贡献,特别是在家庭选择目的地的选择集的适当规范方面。
多分选择模型(例如条件和嵌套 logit)提供了二元选择模型的替代方案,二元选择模型通常构成“移动者/停留者”决策,后者对于研究家庭所在地的决定因素的价值有限。条件 logit 和嵌套 logit 是随机效用模型,其中
$$
\mathrm{U} \text { (location selection } \mathrm{j} \text { for family } \mathrm{i} \text { ) }=\mathrm{U } {\mathrm{ij}}=\mathrm{V} {\mathrm{ij}}+\varepsilon_{\mathrm{ij}}
$$
效用级 $\mathrm{U} {\mathrm{ij}}一世sd和吨和r米一世n和db是吨H和s是s吨和米一种吨一世CC这米p这n和n吨这F在吨一世l一世吨是\ mathrm {V} {\ mathrm {ij一种nd\varepsilon_{\mathrm{ij}}$ 是随机扰动项,假设它与 Gumbel 分布独立同分布。
地理代写|GEOGRAPHY代考|PEOPLE AND PLACE ISSUES
在本节中,我们将讨论移民研究中的几个当代主题。首先,我们调查了关于人力资本和地点相互作用以影响迁移回报的渠道的研究。然后,我们简要讨论了移民的技能和人口特征对收入空间分布的影响,并确定了现有文献中关于收入不平等的差距。然后,我们检查有关生命历程迁移的文献。最后,我们总结了有关家庭迁移的文献,包括讨论“权力夫妇”的位置决定可能对个人和地点产生的影响。
人力资本理论预测,移民计算一个地点的收益和成本之间差异的预期现值,并选择使收入或效用最大化的目的地。从这个角度来看,移民的预期回报是正的。移民回报文献中的一个重要发现是,并非所有移民都能获得工资增长,而且移民回报因亚组而异。扬科2003为受过高中以上教育的移民找到了收益。纳普等人。2013表明初级和后续迁移类型在收入方面产生了正回报,其中受过大学教育的继续迁移收益最大。纳普和怀特2016发现白人男性成年人从移民中获得的收入因青年县贫困率、农村、教育和能力而异。这些作者发现了外来移民的异质性,特别是在人力资本和地方特征的相互作用方面。当继续迁移类型按青年县贫困率、农村地区、教育程度和能力进行分类时,Knapp 等人发现,初始收入损失与较高的青年县贫困率和农村原籍县有关。

地理代写|geography代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。

