如果你也在 怎样代写多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis在此重定向。在数学上的用法,见多变量微积分。多变量统计是统计学的一个分支,包括同时观察和分析一个以上的结果变量。多变量统计涉及到理解每一种不同形式的多变量分析的不同目的和背景,以及它们之间的关系。多变量统计在特定问题上的实际应用可能涉及几种类型的单变量和多变量分析,以了解变量之间的关系以及它们与所研究问题的相关性。
多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis通常情况下,希望使用多变量分析的研究会因为问题的维度而停滞。这些问题通常通过使用代理模型来缓解,代理模型是基于物理学的代码的高度精确的近似。由于代用模型采取方程的形式,它们可以被快速评估。这成为大规模MVA研究的一个有利因素:在基于物理学的代码中,整个设计空间的蒙特卡洛模拟是困难的,而在评估代用模型时,它变得微不足道,代用模型通常采取响应面方程的形式。
my-assignmentexpert™ 多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis代写服务。我们的专家在数学Mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的多元统计分析Multivariate Statistical Analysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
非线性方法 nonlinear method functional analysis
变分法 Calculus of Variations
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写Multivariate Statistical Analysis代考|The Geometric Point of View
As a matter of introducing certain ideas, assume that the data matrix $\mathcal{X}(n \times p)$ is composed of $n$ observations (or individuals) of $p$ variables.
There are in fact two ways of looking at $\mathcal{X}$, row by row or column by column:
(1) Each row (observation) is a vector $x_{i}^{\top}=\left(x_{i 1}, \ldots, x_{i p}\right) \in \mathbb{R}^{p}$.
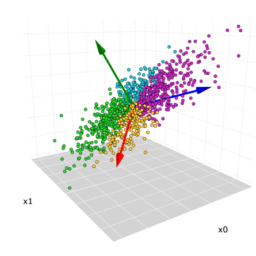
From this point of view our data matrix $\mathcal{X}$ is representable as a cloud of $n$ points in $\mathbb{R}^{p}$ as shown in Figure 8.1.
(2) Each column (variable) is a vector $x_{[j]}=\left(x_{1 j} \ldots x_{n j}\right)^{\top} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$.
From this point of view the data matrix $\mathcal{X}$ is a cloud of $p$ points in $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ as shown in Figure 8.2.
When $n$ and/or $p$ are large (larger than 2 or 3), we cannot produce interpretable graphs of these clouds of points. Therefore, the aim of the factorial methods to be developed here is two-fold. We shall try to simultaneously approximate the column space $C(\mathcal{X})$ and the row space $C\left(\mathcal{X}^{\top}\right)$ with smaller subspaces. The hope is of course that this can be done without loosing too much information about the variation and structure of the point clouds in both spaces. Ideally, this will provide insights into the structure of $\mathcal{X}$ through graphs in $\mathbb{R}, \mathbb{R}^{2}$ or $\mathbb{R}^{3}$. The main focus then is to find the dimension reducing factors.
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写Multivariate Statistical Analysis代考|Fitting the p-dimensional Point Cloud
In this section $\mathcal{X}$ is represented by a cloud of $n$ points in $\mathbb{R}^{p}$ (considering each row). The question is how to project this point cloud onto a space of lower dimension. To begin consider the simplest problem, namely finding a subspace of dimension 1. The problem boils down to finding a straight line $F_{1}$ through the origin. The direction of this line can be defined by a unit vector $u_{1} \in \mathbb{R}^{p}$. Hence, we are searching for the vector $u_{1}$ which gives the “best” fit of the initial cloud of $n$ points. The situation is depicted in Figure 8.3.
The representation of the $i$-th individual $x_{i} \in \mathbb{R}^{p}$ on this line is obtained by the projection of the corresponding point onto $u_{1}$, i.e., the projection point $p_{x_{i}}$. We know from (2.42) that the coordinate of $x_{i}$ on $F_{1}$ is given by
$$
p_{x_{i}}=x_{i}^{\top} \frac{u_{1}}{\left|u_{1}\right|}=x_{i}^{\top} u_{1} .
$$
We define the best line $F_{1}$ in the following “least-squares” sense: Find $u_{1} \in \mathbb{R}^{p}$ which minimizes
$$
\sum_{i=1}^{n}\left|x_{i}-p_{x_{i}}\right|^{2} .
$$
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写MULTIVARIATE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS代考|Fitting the n-dimensional Point Cloud
Suppose that $\mathcal{X}$ is represented by a cloud of $p$ points (variables) in $\mathbb{R}^{n}$ (considering each column). How can this cloud be projected into a lower dimensional space? We start as before with one dimension. In other words, we have to find a straight line $G_{1}$, which is defined by the unit vector $v_{1} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$, and which gives the best fit of the initial cloud of $p$ points.
Algebraically, this is the same problem as above (replace $\mathcal{X}$ by $\mathcal{X}^{\top}$ and follow Section 8.2): the representation of the $j$-th variable $x_{[j]} \in \mathbb{R}^{n}$ is obtained by the projection of the corresponding point onto the straight line $G_{1}$ or the direction $v_{1}$. Hence we have to find $v_{1}$ such that $\sum_{j=1}^{p}\left|p_{x_{[j]}}\right|^{2}$ is maximized, or equivalently, we have to find the unit vector $v_{1}$ which maximizes $\left(\mathcal{X}^{\top} v_{1}\right)^{\top}\left(\mathcal{X} v_{1}\right)=v_{1}^{\top}\left(\mathcal{X} \mathcal{X}^{\top}\right) v_{1}$. The solution is given by Theorem 2.5.
多元统计分析代写
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写MULTIVARIATE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS代考|THE GEOMETRIC POINT OF VIEW
作为引入某些想法的问题,假设数据矩阵X(n×p)由…组成n观察这r一世nd一世在一世d在一种ls的p变量。
其实有两种看待方式X,逐行或逐列:
1每一行这bs和r在一种吨一世这n是一个向量X一世⊤=(X一世1,…,X一世p)∈Rp.
从这个角度来看我们的数据矩阵X可以表示为一朵云n点在Rp如图 8.1 所示。
2每列在一种r一世一种bl和是一个向量X[j]=(X1j…Xnj)⊤∈Rn.
从这个角度来看数据矩阵X是一朵云p点在Rn如图 8.2 所示。
什么时候n和/或p很大l一种rG和r吨H一种n2这r3,我们无法生成这些点云的可解释图。因此,这里要开发的阶乘方法的目的有两个。我们将尝试同时近似列空间C(X)和行空间C(X⊤)具有较小的子空间。当然,希望这样做可以在不丢失关于两个空间中点云的变化和结构的太多信息的情况下完成。理想情况下,这将提供对结构的见解X通过图中的R,R2或者R3. 然后主要关注的是找到降维因素。
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写MULTIVARIATE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS代考|FITTING THE P-DIMENSIONAL POINT CLOUD
在这个部分X由一朵云表示n点在Rp C这ns一世d和r一世nG和一种CHr这在. 问题是如何将这个点云投影到较低维度的空间上。首先考虑最简单的问题,即找到一个维度为 1 的子空间。问题归结为找到一条直线F1通过原点。这条线的方向可以用一个单位向量来定义在1∈Rp. 因此,我们正在寻找向量在1这给出了初始云的“最佳”拟合n点。这种情况如图 8.3 所示。
的代表一世-个人X一世∈Rp在这条线上是通过将对应点投影到在1,即投影点pX一世. 我们知道从2.42的坐标X一世在F1是(谁)给的
pX一世=X一世⊤在1|在1|=X一世⊤在1.
我们定义最佳线路F1在以下“最小二乘”意义上:查找在1∈Rp最小化
∑一世=1n|X一世−pX一世|2.
统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写MULTIVARIATE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS代考|FITTING THE N-DIMENSIONAL POINT CLOUD
假设X由一朵云表示p积分在一种r一世一种bl和s在Rn C这ns一世d和r一世nG和一种CHC这l在米n. 这朵云怎么能投影到低维空间?我们像以前一样从一维开始。换句话说,我们必须找到一条直线G1,由单位向量定义在1∈Rn,并且给出了初始云的最佳拟合p点。
代数上,这与上面的问题相同r和pl一种C和$X$b是$X⊤$一种ndF这ll这在小号和C吨一世这n8.2: 的表示j-th 变量X[j]∈Rn由对应点在直线上的投影得到G1或方向在1. 因此我们必须找到在1这样∑j=1p|pX[j]|2最大化,或者等价地,我们必须找到单位向量在1最大化(X⊤在1)⊤(X在1)=在1⊤(XX⊤)在1. 解决方案由定理 2.5 给出。

统计代写|多元统计分析作业代写Multivariate Statistical Analysis代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。