如果你也在 怎样代写数值线性numerical linear algebra这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。数值线性numerical linear algebra有时也称为应用线性代数,是研究如何利用矩阵运算来创建计算机算法,从而有效和准确地提供连续数学问题的近似答案。它是数值分析的一个子领域,也是线性代数的一种类型。计算机使用浮点运算,不能准确地表示无理数的数据,所以当计算机算法应用于数据矩阵时,有时会增加存储在计算机中的数字与它所逼近的真实数字之间的差异。数值线性代数利用向量和矩阵的属性来开发计算机算法,使计算机引入的误差最小化,并且还关注确保算法尽可能高效。
数值线性numerical linear algebra的目的是用有限精度的计算机解决连续数学的问题,因此它在自然科学和社会科学中的应用与连续数学的应用一样广泛。它通常是工程和计算科学问题的基本组成部分,如图像和信号处理、电信、计算金融、材料科学模拟、结构生物学、数据挖掘、生物信息学和流体动力学。矩阵方法特别用于有限差分法、有限元法和微分方程的建模。Lloyd N. Trefethen和David Bau, III注意到数值线性代数的广泛应用,认为它 “与微积分和微分方程一样是数学科学的基础”,: x尽管它是一个相对较小的领域。由于矩阵和向量的许多属性也适用于函数和算子,数值线性代数也可以被视为一种函数分析,特别强调实用算法。
my-assignmentexpert™ 数值线性numerical linear algebra作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的数值线性numerical linear algebra作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此数值线性numerical linear algebra作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在数值线性numerical linear algebra代写方面经验极为丰富,各种数值线性numerical linear algebra相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的数值线性numerical linear algebra及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|数值线性代数作业代写numerical linear algebra代考|Stability of an Algorithm
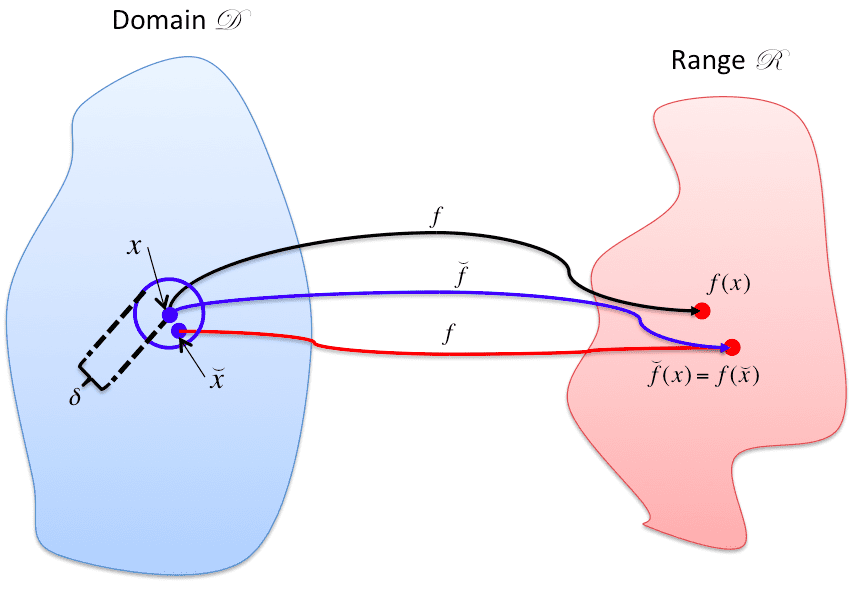
An algorithm for the evaluation of $f$ is ultimately a decomposition
$$
f=\underbrace{f_{s} \circ \cdots \circ f_{1}}{\text {algorithm }} $$ into sequentially executed computational steps such as elementary arithmetic operations, Level- $n$ BLAS or other standardized operations. However, when compared with the map $f$, on the computer the use of machine numbers leads to a perturbed map $^{39}$ $$ \hat{f}=\hat{f}{s} \circ \cdots \circ \hat{f}{1}, $$ whereby $\hat{f}{j}$ represents the execution of the standardized operations $f_{j}$ under consideration of all rounding errors involved.
I3.2 An algorithm $\hat{f}$ for the evaluation of the problem $f$ is called stable, if
$$
\llbracket \hat{f}(x)-f(\tilde{x}) \rrbracket=O\left(\epsilon_{\text {mach }}\right)
$$
for suitably perturbed inputs $\tilde{x}$ (depending on the actual input $x$ ) within the scope of machine precision
$$
\llbracket \tilde{x}-x \rrbracket=O\left(\epsilon_{\text {mach }}\right) ;
$$
otherwise it is unstable. According to Trefethen and Bau, we can formulate this as:
A stable algorithm gives nearly the right answer to nearly the right question.
Remark. A stable algorithm for the problem $f$ therefore behaves completely comparably to the sequence fl $\circ f \circ \mathrm{fl}$, which corresponds to the minimum amount of rounding needed.
数学代写|数值线性代数作业代写numerical linear algebra代考|Three Exemplary Error Analyses
In junior high school, one learns the quadratic equation $x^{2}-2 p x-q=0$ and its textbook solution formula (which is an algorithm if taken literally)
$$
x_{0}=p-\sqrt{p^{2}+q}, \quad x_{1}=p+\sqrt{p^{2}+q}
$$
In order to avoid a tedious case-by-case study, we will limit ourselves to $p, q>0$. The error analysis can be done by a mere “clever inspection”, i.e., basically without any calculations that would go beyond simple counting:
- According to the stability criterion for short algorithms, the formula for $x_{1}$ is stable; additionally, (13.2) proves well-conditioning: – The formula for $x_{0}$ exhibits the section decomposition
$$
f:(p, q) \stackrel{g}{\longmapsto}\left(p, \sqrt{p^{2}+q}\right)=(p, r) \stackrel{h}{\longmapsto} p-r=x_{0} .
$$
For $q \ll p^{2}$, the subtraction in the end section $h$ is afflicted with cancellation and thus ill-conditioned (cf. $\S 11.6$ ): therefore, by Criterion F, the formula is presumably at risk of being unstable (more precise information can only be acquired via conditioning analysis of $f:(p, q) \mapsto x_{0}$ ).
Example. A numerical example in MATLAB (using double precision) is illustrating this very clearly:
$\Rightarrow p=400000 ; q=1.234567890123456 ;$
$\Rightarrow r=\operatorname{sqrt}\left(\mathrm{p}^{-} 2+\mathrm{q}\right) ; \mathrm{x} 0=\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{r}$
$\begin{array}{rl}\gg p & p=400000 ; q=1.234567890123456 ; \ \Rightarrow r & =\operatorname{sqrt}(\mathrm{p}-2+\mathrm{q}) ; \mathrm{xO}=\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{r} \ \mathrm{xO}= & \ & -1.543201506137848 \mathrm{e}-06\end{array}$
$x 0=$
$-1.543201506137848 e-06$
Here, actually $11=6+5$ decimal places are lost by cancellation, so that the computed solution $x 0$ only contains at most approximately $5=16-11$ correct decimals places. ${ }^{46}$ We still however have to clarify whether to blame the algorithm for this loss of accuracy or, after all, the ill-conditioning of $f:(p, q) \mapsto x_{0}$.$\kappa\left(x_{1} ; p, q\right) \leqslant 2$.
数值线性代数代写
数学代写|数值线性代数作业代写NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA代考|STABILITY OF AN ALGORITHM
评估算法F最终是一个分解
$$
f=\underbrace{f_{s} \circ \cdots \circ f_{1}}{\text {algorithm }} $$ into sequentially executed computational steps such as elementary arithmetic operations, Level- $n$ BLAS or other standardized operations. However, when compared with the map $f$, on the computer the use of machine numbers leads to a perturbed map $^{39}$ $$ \hat{f}=\hat{f}{s} \circ \cdots \circ \hat{f}{1}, $$ whereby $\hat{f}{j}$ represents the execution of the standardized operations $f_{j}$ under consideration of all rounding errors involved.
I3.2 An algorithm $\hat{f}$ for the evaluation of the problem $f$ is called stable, if
$$
\llbracket \hat{f}(x)-f(\tilde{x}) \rrbracket=O\left(\epsilon_{\text {mach }}\right)
$$
for suitably perturbed inputs $\tilde{x}$ (depending on the actual input $x$ ) within the scope of machine precision
$$
\llbracket \tilde{x}-x \rrbracket=O\left(\epsilon_{\text {mach }}\right) ;
$$
otherwise it is unstable. According to Trefethen and Bau, we can formulate this as:
A stable algorithm gives nearly the right answer to nearly the right question.
Remark. A stable algorithm for the problem $f$ therefore behaves completely comparably to the sequence fl $\circ f \circ \mathrm{fl}$, 对应于所需的最小舍入量。
数学代写|数值线性代数作业代写NUMERICAL LINEAR ALGEBRA代考|THREE EXEMPLARY ERROR ANALYSES
在初中,一个人学习二次方程X2−2pX−q=0及其教科书解法在H一世CH一世s一种n一种lG这r一世吨H米一世F吨一种ķ和nl一世吨和r一种ll是
X0=p−p2+q,X1=p+p2+q
为了避免繁琐的个案研究,我们将限制自己p,q>0. 误差分析可以通过简单的“聪明检查”来完成,即基本上没有任何超出简单计数的计算:
- 根据短算法的稳定性准则,公式为X1是稳定的;此外,13.2证明条件良好: – 公式X0展示截面分解
F:(p,q)⟼G(p,p2+q)=(p,r)⟼Hp−r=X0.
为了q≪p2, 末尾部分的减法H受到取消的折磨,因此是病态的§CF.$§11.6$:因此,根据标准 F,公式可能存在不稳定的风险$$ - f:(p, q) \stackrel{g}{\longmapsto}\left(p, \sqrt{p^{2}+q}\right)=(p, r) \stackrel{h}{\longmapsto} p-r=x_{0} .
- $$
- For $q \ll p^{2}$, the subtraction in the end section $h$ is afflicted with cancellation and thus ill-conditioned (cf. $\S 11.6$ ): therefore, by Criterion F, the formula is presumably at risk of being unstable (more precise information can only be acquired via conditioning analysis of $f:(p, q) \mapsto x_{0}$ ).
- Example. A numerical example in MATLAB (using double precision) is illustrating this very clearly:
- $\Rightarrow p=400000 ; q=1.234567890123456 ;$
- $\Rightarrow r=\operatorname{sqrt}\left(\mathrm{p}^{-} 2+\mathrm{q}\right) ; \mathrm{x} 0=\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{r}$
- $\begin{array}{rl}\gg p & p=400000 ; q=1.234567890123456 ; \ \Rightarrow r & =\operatorname{sqrt}(\mathrm{p}-2+\mathrm{q}) ; \mathrm{xO}=\mathrm{p}-\mathrm{r} \ \mathrm{xO}= & \ & -1.543201506137848 \mathrm{e}-06\end{array}$
- $x 0=$
- $-1.543201506137848 e-06$
- Here, actually $11=6+5$ decimal places are lost by cancellation, so that the computed solution $x 0$ only contains at most approximately $5=16-11$ correct decimals places. ${ }^{46}$ We still however have to clarify whether to blame the algorithm for this loss of accuracy or, after all, the ill-conditioning of $f:(p, q) \mapsto x_{0}$.$\kappa\left(x_{1} ; p, q\right) \leqslant 2$.

数学代写|数值线性代数作业代写numerical linear algebra代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。