如果你也在 怎样代写电动力学Electrodynamics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。电动力学Electrodynamics研究与运动中的带电体和变化的电场和磁场有关的现象;由于运动的电荷会产生磁场,所以电动力学关注磁、电磁辐射和电磁感应等效应,包括发电机和电动机等实际应用。
电动力学Electrodynamics电动力学的这一领域,通常被称为经典电动力学,是由物理学家詹姆斯-克拉克-麦克斯韦首次系统地解释的。麦克斯韦方程,一组微分方程,非常普遍地描述了这个领域的现象。最近的发展是量子电动力学,它的制定是为了解释电磁辐射与物质的相互作用,量子理论的规律适用于此。物理学家P. A. M. Dirac, W. Heisenberg, 和W. Pauli是制定量子电动力学的先驱者。当所考虑的带电粒子的速度与光速相当时,必须进行涉及相对论的修正;该理论的这个分支被称为相对论电动力学。它被应用于粒子加速器和电子管所涉及的现象,这些电子管承受着高电压和重电流。
my-assignmentexpert™ 电动力学Electrodynamics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的电动力学Electrodynamics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此电动力学Electrodynamics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理Physical作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的物理Physical代写服务。我们的专家在电动力学Electrodynamics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种电动力学Electrodynamics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的电动力学Electrodynamics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
物理代写|电动力学作业代写Electrodynamics代考|Radiation Field and Manifest Gauge Invariance
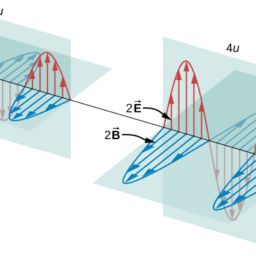
As pointed out in Sect. 3.2.3, the introduction of the vector potential is unavoidable if one wants to derive the laws of electrodynamics from a variational principle, the latter being, in turn, the indispensable starting point for the quantization of the theory. On the other hand, the approaches that, in addition to the electromagnetic field, involve explicitly the vector potential, entail the disadvantage of violating manifest gauge invariance. In the context of classical electrodynamics the introduction of the vector potential constitutes, actually, only a matter of convenience, as it can make the analysis of certain phenomena easier. We saw, for example, that the introduction of the vector potential, together with the Fourier transform, allowed to solve Maxwell’s equations in vacuum in a simple way. However, it is important to realize that it is possible – not only in principle, but also in practice – to solve the fundamental equations of classical electrodynamics, in full generality, in terms of only the electromagnetic field $F^{\mu \nu}$. The obvious advantages of such an approach are that one never introduces non-physical elements, and that gauge invariance is manifest at all stages. To illustrate this alternative framework, below we again solve Maxwell’s equations in vacuum by relying only on the electromagnetic field. In this perspective we must solve the system of equations
$$
\begin{aligned}
\partial_{\mu} F^{\mu \nu} &=0 \
\partial_{[\mu} F_{\nu \rho]} &=\frac{1}{3}\left(\partial_{\mu} F_{\nu \rho}+\partial_{\nu} F_{\rho \mu}+\partial_{\rho} F_{\mu \nu}\right)=0
\end{aligned}
$$
where we included again the Bianchi identity. We prove first of all that all components of the Maxwell tensor must satisfy the wave equation. Applying to the Bianchi identity the derivative operator $\partial^{\mu}$ we obtain the equation
$$
\frac{1}{3}\left(\square F_{\nu \rho}+\partial_{\nu} \partial^{\mu} F_{\rho \mu}+\partial_{\rho} \partial^{\mu} F_{\mu \nu}\right)=0
$$
物理代写|电动力学作业代写Electrodynamics代考|Initial Value Problem
We address now the initial value problem for the free electromagnetic field. In the light of Eqs. (5.118) and (5.119), from the analysis of Sect. $5.2 .2$ we know already how to write $F^{\mu \nu}(x)$ in terms of the initial data $F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{x})$ and $\partial_{0} F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{x})$, and of the antisymmetric kernel $D(x)$, see (5.48),
$$
F^{\mu \nu}(x)=\int\left(D(t, \mathbf{x}-\mathbf{y}) \partial_{0} F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{y})+\partial_{0} D(t, \mathbf{x}-\mathbf{y}) F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{y})\right) d^{3} y
$$
On the other hand, the time derivatives $\partial_{0} F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{x})$ are tied to the initial values of the fields $F^{\mu \nu}(0, \mathbf{x})$ through Eqs. (5.116) and (5.117), that is to say
$$
\frac{\partial \mathbf{E}}{\partial t}=\nabla \times \mathbf{B}, \quad \frac{\partial \mathbf{B}}{\partial t}=-\nabla \times \mathbf{E} .
$$
物理代写|电动力学作业代写ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|Time-Reversal Invariance
Property (5.54) asserts that $D(x)$ is antisymmetric in the time variable
$$
D(-t, \mathbf{x})=-D(t, \mathbf{x}),\left.\quad \frac{\partial}{\partial t^{}} D\left(t^{}, \mathbf{x}\right)\right|{t^{}=-t}=\frac{\partial}{\partial t} D(t, \mathbf{x}) . $$ This feature is by no means a coincidence being, rather, strictly related to the timereversal invariance of electrodynamics. Returning for a moment to the simpler case of the wave equation for a scalar field $\square \varphi=0$, and to the corresponding Lagrangian $\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{2} \partial{\mu} \varphi \partial^{\mu} \varphi$, we see that both are invariant under time reversal. As $t$ goes into $t^{}=-t$, the scalar field transforms in fact according to the rule $\varphi^{}\left(t^{}, \mathbf{x}\right)=\varphi(t, \mathbf{x})$, or $\varphi^{}(t, \mathbf{x})=\varphi(-t, \mathbf{x})$. Consequently, if $\varphi(x)$ is a solution of the wave equation, so is $\varphi^{}(x)$. More precisely, replacing in the solution (5.48) $t$ with $-t$, and using (5.127), we see that $\varphi^{}(x)$ is a solution of the wave equation with the correct initial data $\varphi^{}(0, \mathbf{x})=\varphi(0, \mathbf{x})$ and $\partial_{0} \varphi^{*}(0, \mathbf{x})=-\partial_{0} \varphi(0, \mathbf{x})$.
电动力学代写
物理代写|电动力学作业代写ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|RADIATION FIELD AND MANIFEST GAUGE INVARIANCE
正如 Sect 中指出的那样。3.2.3,如果想要从变分原理推导出电动力学定律,矢量势的引入是不可避免的,而变分原理又是理论量化不可或缺的起点。另一方面,除了电磁场之外,还明确涉及矢量势的方法具有违反明显规范不变性的缺点。在经典电动力学的背景下,向量势的引入实际上只是一个方便的问题,因为它可以使某些现象的分析更容易。例如,我们看到向量势的引入以及傅里叶变换允许以简单的方式在真空中求解麦克斯韦方程组。然而,Fμν. 这种方法的明显优点是永远不会引入非物理元素,并且规范不变性在所有阶段都表现出来。为了说明这个替代框架,下面我们再次仅依靠电磁场在真空中求解麦克斯韦方程。从这个角度来看,我们必须求解方程组
$$
\begin{aligned}
\partial_{\mu} F^{\mu \nu} &=0 \
\partial_{[\mu} F_{\nu \rho]} &=\frac{1}{3}\left(\partial_{\mu} F_{\nu \rho}+\partial_{\nu} F_{\rho \mu}+\partial_{\rho} F_{\mu \nu}\right)=0
\end{aligned}
$$
我们再次包含了 Bianchi 身份。我们首先证明麦克斯韦张量的所有分量都必须满足波动方程。将导数运算符应用于 Bianchi 恒等式∂μ我们得到方程
$$
\frac{1}{3}\left(\square F_{\nu \rho}+\partial_{\nu} \partial^{\mu} F_{\rho \mu}+\partial_{\rho} \partial^{\mu} F_{\mu \nu}\right)=0
$$
物理代写|电动力学作业代写ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|INITIAL VALUE PROBLEM
我们现在解决自由电磁场的初值问题。根据方程式。5.118和5.119,从宗派的分析。5.2.2我们已经知道怎么写了Fμν(X)就初始数据而言Fμν(0,X)和∂0Fμν(0,X), 和反对称核D(X), 看5.48,
Fμν(X)=∫(D(吨,X−是)∂0Fμν(0,是)+∂0D(吨,X−是)Fμν(0,是))d3是
另一方面,时间导数∂0Fμν(0,X)与字段的初始值相关联Fμν(0,X)通过方程式。5.116和5.117, 也就是说
$$
\frac{\partial \mathbf{E}}{\partial t}=\nabla \times \mathbf{B}, \quad \frac{\partial \mathbf{B}}{\partial t}=-\nabla \times \mathbf{E} .
$$
物理代写|电动力学作业代写ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|TIME-REVERSAL INVARIANCE
财产5.54断言D(X)在时间变量
$$
D(-t, \mathbf{x})=-D(t, \mathbf{x}),\left.\quad \frac{\partial}{\partial t^{}} D\left(t^{}, \mathbf{x}\right)\right|{t^{}=-t}=\frac{\partial}{\partial t} D(t, \mathbf{x}) . $$ This feature is by no means a coincidence being, rather, strictly related to the timereversal invariance of electrodynamics. Returning for a moment to the simpler case of the wave equation for a scalar field $\square \varphi=0$, and to the corresponding Lagrangian $\mathcal{L}=\frac{1}{2} \partial{\mu} \varphi \partial^{\mu} \varphi$, we see that both are invariant under time reversal. As $t$ goes into $t^{}=-t$, the scalar field transforms in fact according to the rule $\varphi^{}\left(t^{}, \mathbf{x}\right)=\varphi(t, \mathbf{x})$, or $\varphi^{}(t, \mathbf{x})=\varphi(-t, \mathbf{x})$. Consequently, if $\varphi(x)$ is a solution of the wave equation, so is $\varphi^{}(x)$. More precisely, replacing in the solution (5.48) $t$ with $-t$, and using (5.127), we see that $\varphi^{}(x)$ is a solution of the wave equation with the correct initial data $\varphi^{}(0, \mathbf{x})=\varphi(0, \mathbf{x})$ and $\partial_{0} \varphi^{*}(0, \mathbf{x})=-\partial_{0} \varphi(0, \mathbf{x})$.
物理代写|电动力学作业代写Electrodynamics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。