如果你也在 怎样代写金融数学financial mathematics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融数学financial mathematics也被称为定量金融和金融数学,是应用数学的一个领域,涉及到金融市场的数学建模。一般来说,存在两个需要高级量化技术的独立金融分支:一方面是衍生品定价,另一方面是风险和投资组合管理。后者侧重于应用和建模,通常借助于随机资产模型,而前者除了分析之外,还侧重于为模型建立实施工具。与此相关的还有量化投资,它在管理投资组合时依赖于统计和数字模型(以及最近的机器学习),而不是传统的基本分析。
金融数学financial mathematics该学科与金融经济学学科有着密切的关系,金融经济学关注的是金融数学中涉及的许多基础理论。一般来说,数学金融学会以观察到的市场价格为输入,推导和扩展数学或数字模型,而不一定与金融理论建立联系。需要的是数学上的一致性,而不是与经济理论的兼容性。因此,例如,金融经济学家可能会研究一家公司可能有某种股价的结构性原因,而金融数学家则可能将股价作为一个给定值,并试图使用随机微积分来获得股票的相应衍生品价值。见。期权的估价;金融建模;资产定价。无套利定价的基本定理是数学金融学的关键定理之一,而布莱克-斯科尔斯方程和公式是其中的关键结果。
my-assignmentexpert™ 金融数学financial mathematics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的金融数学financial mathematics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融数学financial mathematics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在金融数学financial mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种金融数学financial mathematics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的金融数学financial mathematics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
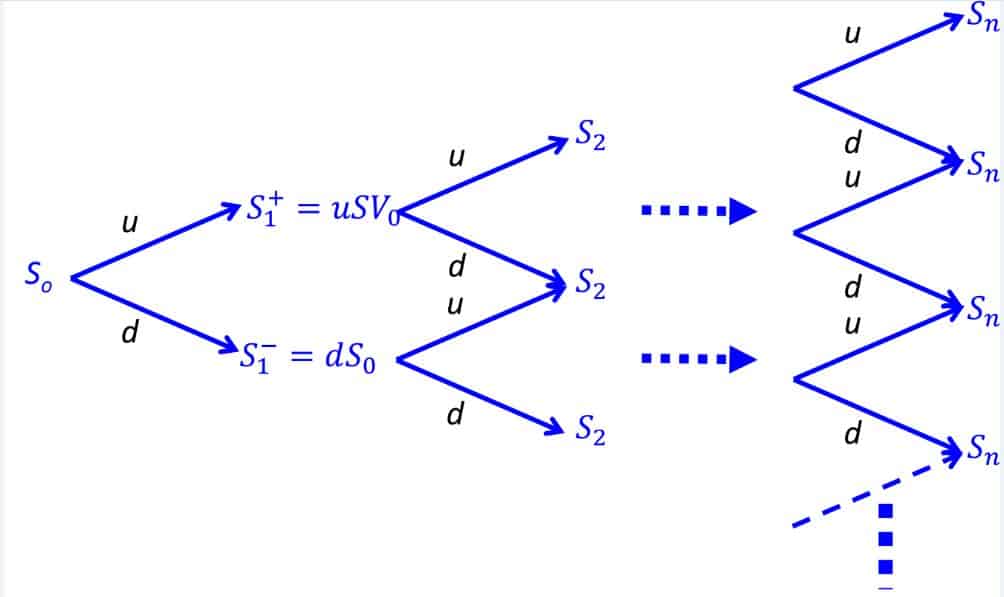
数学代写|金融数学代写financial mathematics代考|Completeness
In the following, we work with a viable Cox, Ross and Rubinstein market model: $d<r<u$. We will start by finding the conditions under which the market is also complete.
THEOREM 6.2.-Let $p=\frac{r-d}{u-d}$. Then, the discounted risky asset $\left(\widetilde{S}{n}^{1}\right){0 \leq n \leq N}$ is $a$ martingale under $\mathbb{P}^{*}$ if and only if the multiplicative increments $T_{1}, \ldots, T_{N}$
- are independent under $\mathbb{P}^{*}$ and
- are identically distributed under $\mathbb{P}^{}$, given by $\mathbb{P}^{}\left(T_{n}=1+u\right)=p$.
PROOF.- Let us assume that $T_{n}$ are i.i.d. in the distribution given by $p$. We then have by independence, since $\mathcal{F}{n}=\sigma\left(T{1}, \ldots, T_{n}\right)$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\mathbb{E}^{}\left[T_{n+1} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right] &=\mathbb{E}^{}\left[T{n+1}\right] \
&=(1-p)(1+d)+p(1+u) \
&=\frac{u-r}{u-d}(1+d)+\frac{r-d}{u-d}(1+u) \
&=1+r .
\end{aligned}
$$
数学代写|金融数学代写financial mathematics代考|Value of European options
We now seek to find the value of call options and put options in the Cox, Ross and Rubinstein model. We use $C_{n}$ and $P_{n}$ to denote the value of a European call option and a European put option, respectively, at the time $n$ in the Cox, Ross and Rubinstein model, with the maturity date $N$, a strike price $K$ and the underlying asset $\left(S_{n}^{1}\right)_{0 \leq n \leq N}$.
PROPOSITION 6.2.-The value of the call option is $C_{n}=c\left(n, S_{n}^{1}\right)$, where $c$ is the deterministic function defined by
$$
c(n, x)=(1+r)^{n-N} \sum_{j=0}^{N-n} C_{N-n}^{j} p^{j}(1-p)^{N-n-j}\left(x(1+u)^{j}(1+d)^{N-n-j}-K\right){+} . $$ PROOF. – Using the general formula for options in Proposition 6.1, it is known that we have $$ \begin{aligned} C{n} &=(1+r)^{n-N} \mathbb{E}^{}\left[\left(S_{N}^{1}-K\right){+} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right] \
&=(1+r)^{n-N} \mathbb{E}^{}\left[\left(S_{n}^{1} T_{n+1} \cdots T_{N}-K\right){+} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right]
\end{aligned}
$$
数学代写|金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|Hedging European options
We finally study the construction of an explicit hedging strategy.
PROPOSITION 6.4.- It is possible to explicitly construct an admissible strategy that allows the hedging of a European call option in the Cox, Ross and Rubinstein model. The number of shares held between the instant $n$ and the instant $n+1$ are
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\phi_{n+1}^{0}=\Delta^{0}\left(n+1, S_{n}^{1}\right) \
&\phi_{n+1}^{1}=\Delta^{1}\left(n+1, S_{n}^{1}\right)
\end{aligned}
$$
for risk-free and risky assets, respectively, where $\Delta^{0}$ and $\Delta^{1}$ are the deterministic functions defined by
$$
\begin{aligned}
\Delta^{0}(n, x) &=\frac{(1+u) c(n, x(1+d))-(1+d) c(n, x(1+u))}{(1+r)^{n}(u-d)} \
\Delta^{1}(n, x) &=\frac{c(n, x(1+d))-c(n, x(1+u))}{x(u-d)},
\end{aligned}
$$
using the function c from Proposition 6.2.
PROOF.- Since the market is complete, there exists an admissible strategy $\Phi$ such that
$$
\phi_{n}^{0}(1+r)^{n}+\phi_{n}^{1} S_{n}^{1}=C_{n}=c\left(n, S_{n}^{1}\right)
$$
金融数学代写
数学代写|金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|COMPLETENESS
在下文中,我们使用可行的 Cox、Ross 和 Rubinstein 市场模型:d<r<在. 我们将首先找到市场也完整的条件。
定理 6.2.-让p=r−d在−d. 那么,贴现的风险资产 $\left(\widetilde{S} {n}^{1}\right) {0 \leq n \leq N}一世s一种米一种r吨一世nG一种l和在nd和r\mathbb{P}^{*}一世F一种nd这nl是一世F吨H和米在l吨一世pl一世C一种吨一世在和一世nCr和米和n吨sT_{1}, \ldots, T_{N}$
- are independent under $\mathbb{P}^{*}$ and
- are identically distributed under $\mathbb{P}^{}$, given by $\mathbb{P}^{}\left(T_{n}=1+u\right)=p$.
PROOF.- Let us assume that $T_{n}$ are i.i.d. in the distribution given by $p$. We then have by independence, since $\mathcal{F}{n}=\sigma\left(T{1}, \ldots, T_{n}\right)$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\mathbb{E}^{}\left[T_{n+1} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right] &=\mathbb{E}^{}\left[T{n+1}\right] \
&=(1-p)(1+d)+p(1+u) \
&=\frac{u-r}{u-d}(1+d)+\frac{r-d}{u-d}(1+u) \
&=1+r .
\end{aligned}
$$
数学代写|金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|VALUE OF EUROPEAN OPTIONS
我们现在寻求在 Cox、Ross 和 Rubinstein 模型中找到看涨期权和看跌期权的价值。我们用Cn和磷n分别表示当时欧式看涨期权和欧式看跌期权的价值n在 Cox、Ross 和 Rubinstein 模型中,到期日ñ, 行使价ķ和标的资产(小号n1)0≤n≤ñ.
命题 6.2.-看涨期权的价值是Cn=C(n,小号n1), 在哪里C
是由$$
c(n, x)=(1+r)^{n-N} \sum_{j=0}^{N-n} C_{N-n}^{j} p^{j}(1-p)^{N-n-j}\left(x(1+u)^{j}(1+d)^{N-n-j}-K\right){+} . $$ PROOF. – Using the general formula for options in Proposition 6.1, it is known that we have $$ \begin{aligned} C{n} &=(1+r)^{n-N} \mathbb{E}^{}\left[\left(S_{N}^{1}-K\right){+} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right] \
&=(1+r)^{n-N} \mathbb{E}^{}\left[\left(S_{n}^{1} T_{n+1} \cdots T_{N}-K\right){+} \mid \mathcal{F}{n}\right]
\end{aligned}
$$
数学代写|金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS代考|HEDGING EUROPEAN OPTIONS
我们最后研究了显式对冲策略的构建。
命题 6.4.- 可以在 Cox、Ross 和 Rubinstein 模型中明确构建一个允许对冲欧式看涨期权的可接受策略。瞬间之间持有的股份数量n和瞬间n+1是
φn+10=Δ0(n+1,小号n1) φn+11=Δ1(n+1,小号n1)
对于无风险资产和风险资产,分别为Δ0和Δ1是由以下定义的确定性函数
Δ0(n,X)=(1+在)C(n,X(1+d))−(1+d)C(n,X(1+在))(1+r)n(在−d) Δ1(n,X)=C(n,X(1+d))−C(n,X(1+在))X(在−d),
使用命题 6.2 中的函数 c。
证明-由于市场是完整的,因此存在可接受的策略披这样
$$
\phi_{n}^{0}(1+r)^{n}+\phi_{n}^{1} S_{n}^{1}=C_{n}=c\left(n, S_{n}^{1}\right)
$$

数学代写|金融数学代写financial mathematics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。