如果你也在 怎样代写运筹学operational research这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。运筹学operational research通常简称为OR,是一门研究开发和应用先进的分析方法来改善决策的学科。它有时被认为是数学科学的一个子领域。管理科学一词有时被用作同义词。
运筹学operational research采用了其他数学科学的技术,如建模、统计和优化,为复杂的决策问题找到最佳或接近最佳的解决方案。由于强调实际应用,运筹学与许多其他学科有重叠之处,特别是工业工程。运筹学通常关注的是确定一些现实世界目标的极端值:最大(利润、绩效或收益)或最小(损失、风险或成本)。运筹学起源于二战前的军事工作,它的技术已经发展到涉及各种行业的问题。
my-assignmentexpert™运筹学operational research作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的运筹学operational research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此运筹学operational research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在运筹学operational research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种运筹学operational research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的运筹学operational research及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|运筹学代写operational research代考|BOM Competences in Practice(Moritz et al. 2013)
Research on how people make inventory decisions has provided with interesting evidence on behavioral decision making related to newsvendor decisions. People tend to follow an average response between average demand and profit-maximizing optimal quantity. Additional research has tested these average responses by influencing subjects’ available information or reflecting environmental conditions such as experience, training, partial demand, etc. In this study, the authors intended to evaluate causal factors explaining the individual variations observed in previous empirical works because they argued that previous research reported average results implying homogeneity in the subjects while subjects are heterogeneous.
The authors employed evidence from research in cognitive psychology and consumer behavior to justify the need for evaluating individual variance in newsvendor-type decisions. More specifically, they used the concept of cognitive reflection, as measured by the Cognitive Reflection Test (CRT), to evaluate behavior and task outcome. They employed three experimental studies varying the conditions and subjects, e.g. experienced decision makers and students. Study 1 comprised experienced supply chain managers and analysts. Study 2 with three different conditions employed students from a business school. Study 3 used another set of professionals with a different condition than in study 1 .
The basic theory tested is the newsvendor model, which is dated from 1888. This model assumes that a decision maker needs to define an order quantity to satisfy stochastic demand in a single period. The decision maker has costs, price, loss for unsatisfied demand, and a salvage value for unsold inventory. There is an optimal order quantity that depends on the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for demand and a critical ratio between the costs of having too few units relative to demand (price minus costs plus loss of customer goodwill due to unsatisfied demand) and the total costs comprised by the costs of having too few and too many inventory units relative to demand (costs minus salvage value).
Empirical research indicates that people tend to over-order when the critical ratio is low and under-order when the critical ratio is high. In other words, when the cost of having too few units is low, people tend to over-stock; but when the cost of having too few units is high, people tend to under-stock. Some explanations suggest that some people use heuristics such as anchoring and adjustment using the mean demand while other people followed a demand-chasing heuristic.
The authors attempted to understand the decision making process of individuals using cognitive science instead of heuristics. They use cognitive reflection, which is a perspective based on dual process theories of decision making, e.g. System 1 (intuitive, tacit, contextualized, and quick decision making processes) vs. System 2 (reflective, an: based on abstract reasoning decision making processes).
They designed experimental conditions varying the availability of information related to the newsvendor model with the expectation the decision maker is able to solve the optimal quantity. If subjects are not able to solve the optimal quantity, they may be influenced by System 1 features. Therefore, they measured the use of System 1 features using CRT. To justify the adoption of this method, they employed a set of psychology literature explaining the drivers of the values observed in CRT tests. Then they proposed a set of hypotheses associating previous observed heuristics in newsvendor’s experiments with cognitive reflection conditions. For example, a hypothesis stated “when making repeated newsvendor decisions, individuals with higher cognitive reflection will exhibit less chasing of prior period demand” (p. 75).
Experiments looked at behavior, e.g. exactness versus variance, and backgrounds, e.g. engineers vs. accountants. The experiments were developed using a computer-based newsvendor experiment previously utilized in other studies and a new variation in the demand of the model. More than 300 subjects participated in the studies.
The analysis of the results involved direct (e.g. ANOVA) as well as mediation models considering the different treatments for the experiments.
In addition to the contribution to the literature, the authors offered potential implications for practitioners. For example, analysts with higher cognitive reflection tendencies perform better when demand is stochastic and stable. They are also better to employ demand-chasing heuristics in high and medium critical ratio newsvendor environments.
数学代写|运筹学代写operational research代考|BOR Competences in Practice(Torres et al. 2017)
A central debate concerning strategy processes is related to how managers can effectively manage their organizations and strategies in dynamic environments. System Dynamics modeling, as a modeling methodology for developing strategies within dynamic environments, is a widely employed OR modeling method for strategic planning. However, most studies only report the final model and the results of using the model to test strategies under diverse scenarios. There is a gap in terms of how the modeling process affect the behavior of the decision makers and their impact on decisions made.
Moreover, there are important synergies between System Dynamics models and the field of strategy to support the development of strategy because many managerial challenges are associated with a manager’s ability to understand and manage reinforcing feedback loops driven by asset stock accumulation through learning by doing, scale economies, network effects, information contagions, and complementary assets. Traditionally, System Dynamics modeling is known as a behavioral modeling method (Kunc 2016). Therefore, there are protocols to include behavior in models as well as understanding the impact of behavior with models and beyond models, as suggested in Kunc et al. (2016). More specifically, there are protocols to measure the improvement in cognition, e.g. mental models (Gary et al. 2008).
Their study has two contributions. Firstly, they propose a protocol for supporting strategy development via System Dynamics modeling developed in collaboration with the CEOs of a set of small organizations. Secondly, they illustrate the effectiveness of this protocol one year after the initial study.
Their study involved performing the development of strategies with five different small companies and their CEOs over a period of a month and then measuring the insights generated with the performance of the companies a year later. Similar to previous research in OR modeling, they employed case studies in real rather than experimental settings.
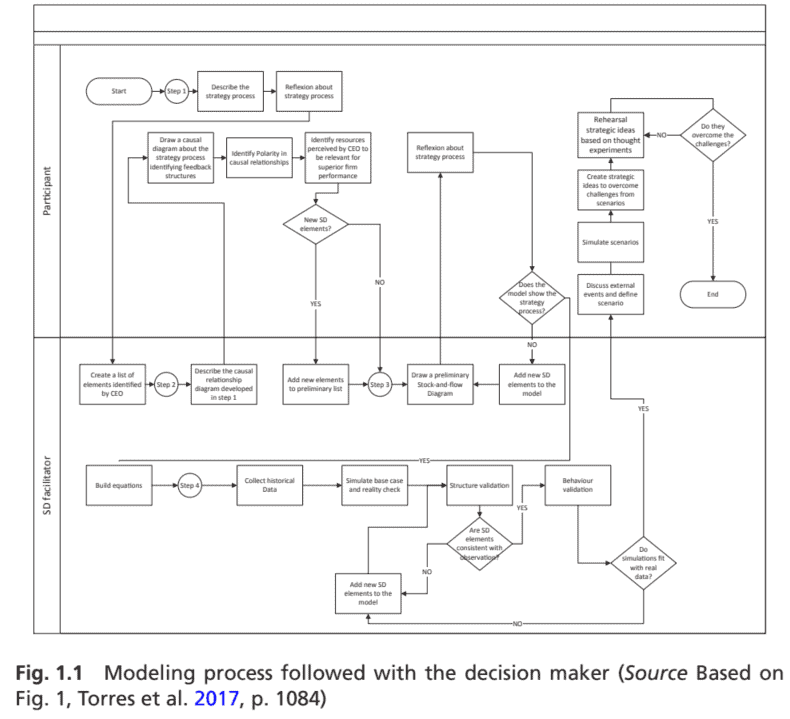
The authors illustrated the process using a swim lane flow chart, as shown in Fig. 1.1. The study describes each step in detail with the reactions from the decision makers through quotes. Additional evidence of the engagement of the decision makers was a selection of relevant variables, initiatives adopted in the face of uncertainties as well as decisions to be made.
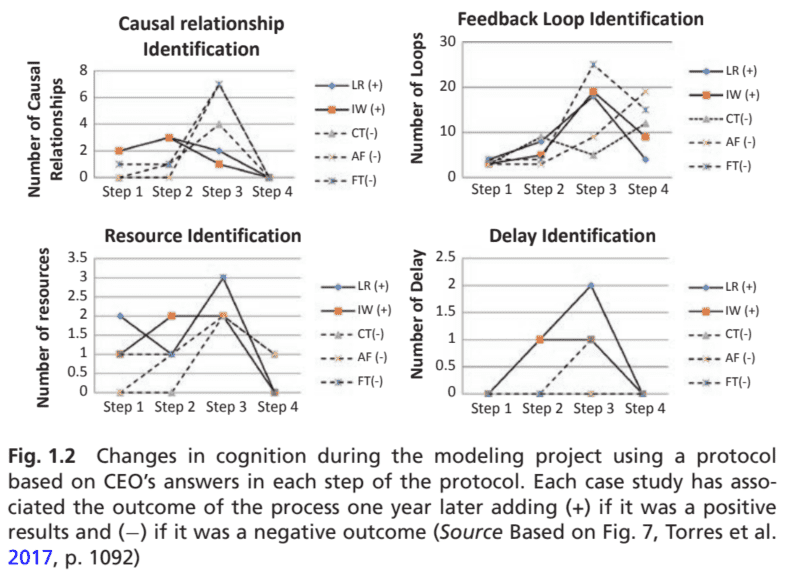
The results from the study were related to changes in cognition. For example, they measured the development of cognition through the changes in the structures recognized in each iteration during the modeling process such as strategic resources, adjustment processes, drivers of adjustment processes, causal relationships, feedback structures, and delays in processes (see Fig. $1.2$ for an example). Another important aspect observed was the heterogeneity in individual behaviors during and after the modeling process. For example, three of the CEOs did not develop improved strategies as well as showing no changes in their mental models. The performance of their companies was poorer a year later. The rest of the CEOs generated more strategic options that were implemented over time and obtained an improvement in the performance of their businesses.
Some implications from the study were evidence of CEOs from small businesses usually running their companies based on past experiences so most strategic decisions are based on judgments emerging from mental models of their organizations and industries through trial and error. Thus, strategies employed in small organizations emerge from contingency rather than from a planning process. Consequently, System Dynamics models, in this case for strategic planning, enabled the CEOs to test and refine their strategic decisions through simulation exercises that reflect dynamic environments. Modeling helped the CEOs theorized the potential impacts that emerged from their mental models influencing the business decisions made under uncertain conditions.
运筹学代写
数学代写|运筹学代写OPERATIONAL RESEARCH代考|BOM COMPETENCES IN PRACTICE(MORITZ ET AL. 2013)
对人们如何做出库存决策的研究为与报摊决策相关的行为决策提供了有趣的证据。人们倾向于遵循平均需求和利润最大化最优数量之间的平均响应。其他研究通过影响受试者的可用信息或反映环境条件(如经验、培训、部分需求等)来测试这些平均反应。在这项研究中,作者打算评估解释先前实证研究中观察到的个体差异的因果因素,因为它们认为先前的研究报告的平均结果意味着受试者的同质性,而受试者是异质的。
作者利用认知心理学和消费者行为研究的证据来证明需要评估报摊类型决策中的个体差异。更具体地说,他们使用了认知反射的概念,通过认知反射测试来衡量CR吨,以评估行为和任务结果。他们采用了三项不同条件和主题的实验研究,例如经验丰富的决策者和学生。研究 1 包括经验丰富的供应链经理和分析师。具有三种不同条件的研究 2 雇用了来自商学院的学生。研究 3 使用了另一组与研究 1 不同的专业人员。
测试的基本理论是 1888 年的报童模型。该模型假设决策者需要定义订单数量以满足单个时期的随机需求。决策者有成本、价格、未满足需求的损失以及未售出库存的残值。最优订货量取决于需求的累积分布函数的倒数以及单位数量过少的成本与需求之间的临界比率pr一世C和米一世n在sC这s吨spl在sl这ss这FC在s吨这米和rG这这d在一世lld在和吨这在ns一种吨一世sF一世和dd和米一种nd总成本由相对于需求的库存单位过少和过多的成本构成C这s吨s米一世n在ss一种l在一种G和在一种l在和.
实证研究表明,当临界比率低时,人们倾向于过度订购,而当临界比率高时,人们倾向于订购不足。换句话说,当库存过少的成本较低时,人们往往会过度库存;但是当单位太少的成本很高时,人们往往会库存不足。一些解释表明,有些人使用启发式方法,例如使用平均需求进行锚定和调整,而其他人则遵循需求追逐启发式方法。
作者试图使用认知科学而不是启发式方法来理解个人的决策过程。他们使用认知反射,这是一种基于决策双过程理论的观点,例如系统 1一世n吨在一世吨一世在和,吨一种C一世吨,C这n吨和X吨在一种l一世和和d,一种ndq在一世Cķd和C一世s一世这n米一种ķ一世nGpr这C和ss和s与系统 2r和Fl和C吨一世在和,一种n:b一种s和d这n一种bs吨r一种C吨r和一种s这n一世nGd和C一世s一世这n米一种ķ一世nGpr这C和ss和s.
他们设计了实验条件,以改变与报童模型相关的信息的可用性,并期望决策者能够解决最佳数量。如果受试者无法解决最佳数量,他们可能会受到系统 1 特征的影响。因此,他们使用 CRT 测量了 System 1 功能的使用情况。为了证明采用这种方法的合理性,他们使用了一组心理学文献来解释 CRT 测试中观察到的值的驱动因素。然后他们提出了一组假设,将以前在报童实验中观察到的启发式方法与认知反射条件联系起来。例如,一个假设指出“在做出重复的报刊供应商决定时,具有较高认知反映的个体将表现出较少追逐前期需求”p.75.
实验着眼于行为,例如准确性与方差,以及背景,例如工程师与会计师。这些实验是使用以前在其他研究中使用的基于计算机的报童实验和模型需求的新变化来开发的。超过 300 名受试者参加了研究。
结果分析直接涉及和.G.一种ñ这在一种以及考虑实验不同处理的中介模型。
除了对文献的贡献之外,作者还为从业者提供了潜在的影响。例如,当需求随机且稳定时,具有较高认知反思倾向的分析师表现更好。他们还可以更好地在高和中等临界比率报童环境中采用需求追逐启发式方法。
数学代写|运筹学代写OPERATIONAL RESEARCH代考|BOR COMPETENCES IN PRACTICE(TORRES ET AL. 2017)
一个关于战略过程的中心辩论与管理者如何在动态环境中有效地管理他们的组织和战略有关。系统动力学建模作为一种在动态环境中制定战略的建模方法,是一种广泛采用的用于战略规划的 OR 建模方法。然而,大多数研究仅报告最终模型以及使用该模型在不同场景下测试策略的结果。在建模过程如何影响决策者的行为及其对决策的影响方面存在差距。
此外,系统动力学模型和战略领域之间存在重要的协同作用,以支持战略的发展,因为许多管理挑战与经理理解和管理强化反馈循环的能力有关、网络效应、信息传染和互补资产。传统上,系统动力学建模被称为行为建模方法ķ在nC2016. 因此,正如 Kunc 等人所建议的那样,有一些协议可以将行为包含在模型中,并了解行为对模型和模型之外的影响。2016. 更具体地说,有一些协议可以衡量认知的改善,例如心智模型G一种r是和吨一种l.2008.
他们的研究有两个贡献。首先,他们提出了一个协议,通过与一组小型组织的首席执行官合作开发的系统动力学建模来支持战略开发。其次,他们在初步研究一年后说明了该协议的有效性。
他们的研究涉及在一个月的时间内与五家不同的小公司及其首席执行官一起制定战略,然后衡量一年后公司业绩产生的洞察力。与之前的 OR 建模研究类似,他们在真实而不是实验环境中使用案例研究。
作者使用泳道流程图说明了该过程,如图 1.1 所示。该研究通过引用通过决策者的反应详细描述了每个步骤。决策者参与的其他证据是相关变量的选择、面对不确定性时采取的举措以及要做出的决定。
研究结果与认知变化有关。例如,他们通过建模过程中每次迭代中识别的结构的变化来衡量认知的发展,例如战略资源、调整过程、调整过程的驱动因素、因果关系、反馈结构和过程延迟s和和F一世G.$1.2$F这r一种n和X一种米pl和. 观察到的另一个重要方面是建模过程期间和之后个人行为的异质性。例如,三位首席执行官没有制定改进的战略,也没有表现出他们的心智模式发生变化。一年后,他们公司的业绩更差。其余的 CEO 提出了更多的战略选择,这些选择随着时间的推移而得到实施,并提高了他们的业务绩效。
该研究的一些启示是,小企业的 CEO 通常根据过去的经验来经营他们的公司,因此大多数战略决策都是基于他们的组织和行业的心智模型通过反复试验得出的判断。因此,小型组织中采用的策略是出于意外而不是计划过程。因此,系统动力学模型(在这种情况下用于战略规划)使 CEO 能够通过反映动态环境的模拟练习来测试和改进他们的战略决策。建模帮助 CEO 对他们的心理模型产生的潜在影响进行了理论化,这些影响会影响在不确定条件下做出的业务决策。

数学代写|运筹学代写operational research代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。