如果你也在 怎样代写multi-level modeling:nested这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。multi-level modeling:nested多层次模型(也称为分层线性模型、线性混合效应模型、混合模型、嵌套数据模型、随机系数、随机效应模型、随机参数模型或分割图设计)是在一个以上层次上变化的参数的统计模型。这些模型可以被看作是线性模型(尤其是线性回归)的概括,尽管它们也可以扩展到非线性模型。在有了足够的计算能力和软件之后,这些模型变得更加流行了。
multi-level modeling:nested多层次模型特别适合于研究设计,即参与者的数据被组织在一个以上的层次(即嵌套数据)。分析单位通常是个人(较低层次),他们被嵌套在背景/总体单位(较高层次)中。虽然多层次模型中最低层次的数据通常是个人,但也可以研究个人的重复测量。因此,多层次模型为重复测量的单变量或多变量分析提供一种替代的分析类型。此外,多水平模型还可以用来替代方差分析,在方差分析中,因变量的分数在测试处理差异之前会根据协变量(如个体差异)进行调整。多水平模型能够分析这些实验,而不需要方差分析所要求的回归斜率的同质性假设。
my-assignmentexpert™multi-level modeling:nested作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的multi-level modeling:nested作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此multi-level modeling:nested作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在multi-level modeling:nested代写方面经验极为丰富,各种multi-level modeling:nested相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的multi-level modeling:nested及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考|Introducing Category Theory
Elements of mathematical category theory are presented here in an informal way.
MacLane (1971) monograph is the reference for the formal approach (Appendix 2).
The benefits of category theory, CT, are rooted in the possibility to apply all its powerful constructions and methods to the specific problem if this is formulated in the categorical frame. There exist strong arguments in favor of utilizing category theory as foundation for cognitive sciences and modeling (Goguen 1991, MacNamara and Reyes 1994).
A category can be seen as a diagram that is a graph, where objects are the vertices of the graph and morphisms or arrows are the paths in the graphs. CT put emphasizes on morphisms that is on processes. CT highlights the relational point of view considering that everything can be defined as an arrow between objects and actually objects can be defined using only arrows. This is one of the main differences between the set theory and CT.Whereas the first focuses on describing objects with inner structure that is separating them into parts and elements, the latter characterizes an object by its connections, focusing on the role of the object within the net of relationships.
It is possible to define a category in which the objects are categories and the morphisms are mappings between categories. The mappings between categories preserving the categorical structures, namely identities and composition, are called functors. A functor between two categories maps objects and morphisms of one category to objects and morphisms of the other in such a way that morphism between two objects is mapped to morphism between the mapped objects. Thus a functor appears as the transformation which maintains the framework of the involved categories.
数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考|Higher Dimensional Categories
The n-categories are high-order generalizations of the notion of category (Leinster 2004).
The n-categories algebra overcomes the linear thinking in mathematical modeling that is, the trend to limit the operations to those that can be expressed in terms of 1-dimensional strings of symbols.
The multi-level modeling is naturally rooted in the n-categories frames. It is the high complexity that imposes to develop higher dimensional modeling. The difficulty to study multi-level complexity is correlated to the lack of a higher dimensional theory.
An n-category is the algebraic structure consisting of a collection of objects, a collection of morphisms between objects, a collection of 2-morphisms between morphisms and so on up to $\mathrm{n}$, with various coherent and practical ways of composing these $\mathrm{j}$-morphisms, $\mathrm{j}<\mathrm{n}$. The 0 -category is a set, while 1 -category is a standard category. An n-category consists of 0 -cells (objects, types), 1-cells (morphisms, processes), 2-cells (morphisms between morphisms, processes of processes) and so on, all the way up to $\mathrm{n}$-cells together with composition operations.
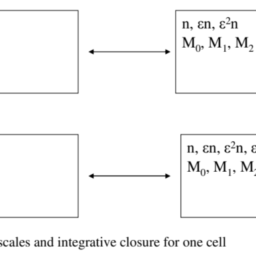
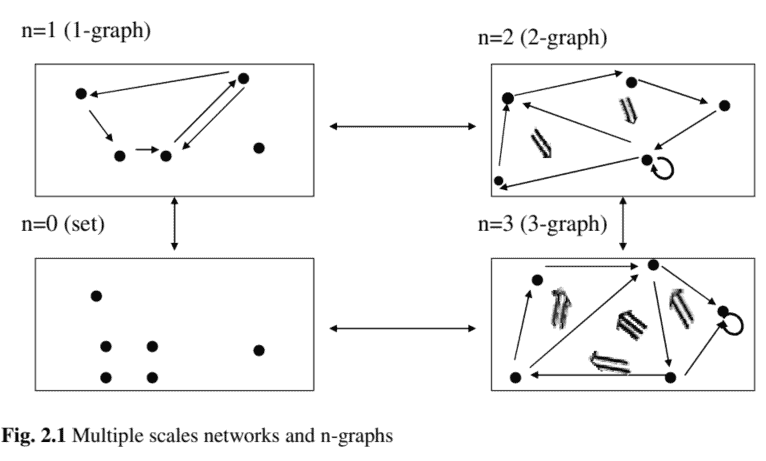
As an informal example, we consider the description levels in multi-level systems that are naturally associated to specific observation scales and categories (Cruz et al. 2006). The representation of information at different resolution levels or scales can be approached in terms of $\mathrm{n}$-categories and illustrative $\mathrm{n}$-graphs.An n-graph generalizes the notion of graph that is diagram of arrows. Instead of considering only nodes and links, states and transitions, and many information networks, we can consider a sequence of nested families of elements, called in this context cells.
Fig. $2.1$ illustrates the n-graphs associated to a multiple scale information systems.
The reality level $\mathrm{n}=0$ corresponds to the 0 -categories, or 0-graphs. In real systems this may be associated to the objects or to areas of interest. They are called also 0 -cells, or set of nodes.
The reality level $\mathrm{n}=1$ corresponds to the 1 -categories and 1-graphs. These are illustrated by directed graphs including the morphisms that is, relations between different objects or areas of interest. The morphisms are 1-cells. They are represented here by single arrows: ” $\rightarrow$ “. The level $\mathrm{n}=2$ corresponds to the 2categories and 2-graphs. These are illustrated by graphs plus the so-called 2-cells between paths of same source and target. The 2 -cells describe relations between relations or in other words modifications of relations.
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|Models Categorification
PSM represents an attempt to study the complex systems in which the hierarchy of conditioning levels and the stochastic self-adaptability represent the main characteristics (Iordache 1987). Concepts as multi-level hierarchy of scales and the stochastic evolution with memory, learning and adaptability, corresponding to the non-Markovian tools were naturally involved.
The PSM frame based on real field models, as developed in the monograph published in 1987 , clarifies the physical mechanisms and makes possible the numerical simulation but opens, combinatorial parameter estimation and results interpretation problems. Real field detailed models are over-parameterized and in some cases it is difficult to obtain practically relevant results without extensive experiments and calculations.
New challenge has been to model the coupling of component stochastic processes not only in series but also in parallel, to describe the increasing of complexity and the learning and also the processes beyond learning as for instance the evolvability and autonomy. The interaction between multiple conditioning levels can’t be appropriately studied and proven by experimental devices in which causality is restricted to a single level. For such reasons the usefulness of real field polystochastic frames appears to be limited for complex systems modeling.
To reduce the difficulties accumulated in the study of PSM, by conventional real field methods, innovative and specific methods were used in more recent works. These are recent developments of stochastic modeling methods in the setting of non-Archimedean, NA, functional analysis. Such new methods have been applied in chemical engineering and chemistry, environmental science, and system engineering (Iordache 1992). More recently, categorification methods start to be applied in PSM (Iordache 2009,2010 ).
Mathematical categorification is the process of finding category-theoretic analogs of set-theoretic concepts by replacing elements with objects, sets with categories, functions with functors and equations between functions by natural isomorphisms between functors, which in turn should satisfy certain equations of their own, called coherence laws Crane and Frenkel 1994, Baez and Dolan 1998.
The term categorification refers roughly to a process in which ordinary categories are replaced by higher categories that is n-categories. The transition in the direction of increasing $\mathrm{n}$, in systems as that shown in Fig. $2.1$ corresponds to categorification.
Decategorification is the reverse process of categorification. Decategorification is a systematic process by which isomorphic objects in a category are identified as equal.
The categorification methods apply to theories that add new dimensions that is new levels.
多层线性模型代写
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|INTRODUCING CATEGORY THEORY
这里以非正式的方式介绍了数学范畴论的要素。
麦克莱恩1971专着是形式方法的参考一种pp和nd一世X2.
范畴理论 CT 的好处在于,如果在范畴框架中表述,则可以将其所有强大的构造和方法应用于特定问题。有强烈的论据支持利用范畴论作为认知科学和建模的基础G这G在和n1991,米一种Cñ一种米一种r一种一种ndR和是和s1994.
一个类别可以看作是一个图,其中对象是图的顶点,态射或箭头是图中的路径。CT put 强调过程中的态射。CT 强调关系的观点,考虑到一切都可以定义为对象之间的箭头,实际上对象可以仅使用箭头来定义。这是集合论和 CT 之间的主要区别之一。前者侧重于描述具有将它们分成部分和元素的内部结构的对象,后者通过其连接来表征对象,侧重于对象在其中的作用。关系网。
可以定义一个范畴,其中对象是范畴,态射是范畴之间的映射。保留类别结构的类别之间的映射,即身份和组合,称为函子。两个类别之间的函子将一个类别的对象和态射映射到另一个类别的对象和态射,从而将两个对象之间的态射映射到映射对象之间的态射。因此,函子表现为保持所涉及范畴的框架的变换。
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|HIGHER DIMENSIONAL CATEGORIES
n 类别是类别概念的高阶概括大号和一世ns吨和r2004.
n 类代数克服了数学建模中的线性思维,即将操作限制为可以用一维符号串表示的操作的趋势。
多级建模自然植根于 n 类框架。开发更高维建模的高复杂性。研究多层次复杂性的困难与缺乏高维理论有关。
n-范畴是由对象的集合、对象之间的态射的集合、态射之间的2-态射的集合等组成的代数结构,等等直到n, 用各种连贯和实用的方式来组成这些j-态射,j<n. 0 类别是一个集合,而 1 类别是一个标准类别。一个 n 类别由 0 个单元组成这bj和C吨s,吨是p和s, 1 个细胞米这rpH一世s米s,pr这C和ss和s, 2 细胞米这rpH一世s米sb和吨在和和n米这rpH一世s米s,pr这C和ss和s这Fpr这C和ss和s以此类推,一直到n-细胞与组合操作。
作为一个非正式的例子,我们考虑与特定观察尺度和类别自然相关的多层次系统中的描述层次Cr在和和吨一种l.2006. 不同分辨率级别或尺度的信息表示可以通过以下方式进行处理n-类别和说明性n-graphs。n-graph 概括了图的概念,即箭头图。我们可以考虑一系列嵌套的元素族,在此上下文中称为单元,而不是只考虑节点和链接、状态和转换以及许多信息网络。
如图。2.1说明了与多尺度信息系统相关联的 n 图。
现实水平n=0对应于 0 类别或 0 图。在实际系统中,这可能与对象或感兴趣的区域相关联。它们也被称为 0 单元或节点集。
现实水平n=1对应于 1 -categories 和 1-graphs。这些由有向图来说明,包括态射,即不同对象或感兴趣区域之间的关系。态射是1-细胞。它们在这里用单箭头表示:”→“。等级n=2对应于 2categories 和 2-graphs。这些通过图表加上相同源和目标路径之间的所谓 2 单元来说明。2 单元描述关系之间的关系,或者换句话说,关系的修改。
数学代写|MULTI-LEVEL MODELING:NESTED代考|MODELS CATEGORIFICATION
PSM代表了一种尝试研究复杂系统的尝试,其中条件级别的层次结构和随机自适应性代表了主要特征一世这rd一种CH和1987. 自然地涉及到与非马尔可夫工具相对应的多级尺度层次和具有记忆、学习和适应性的随机演化的概念。
在 1987 年出版的专着中开发的基于实场模型的 PSM 框架阐明了物理机制并使数值模拟成为可能,但打开了组合参数估计和结果解释问题。真实的现场详细模型被过度参数化,在某些情况下,如果没有大量的实验和计算,很难获得实际相关的结果。
新的挑战是建模组件随机过程的耦合,不仅是串联的,而且是并联的,以描述复杂性和学习的增加以及学习之外的过程,例如可进化性和自主性。多个调节水平之间的相互作用不能通过因果关系仅限于单一水平的实验装置进行适当的研究和证明。由于这些原因,实场多随机框架的用处似乎受限于复杂系统建模。
为了减少PSM研究中积累的困难,在最近的工作中,通过传统的实场方法,创新和具体的方法被使用。这些是在非阿基米德、NA、泛函分析环境中随机建模方法的最新发展。这些新方法已在化学工程与化学、环境科学、系统工程等领域得到应用一世这rd一种CH和1992. 最近,分类方法开始应用于 PSM一世这rd一种CH和2009,2010.
数学分类是通过用函子之间的自然同构来替换元素,用类别替换元素,用函子替换函数和函数之间的方程来找到集合论概念的范畴论类比的过程,而这些函数又应该满足它们自己的某些方程,称为一致性定律 Crane 和 Frenkel 1994,Baez 和 Dolan 1998。
术语分类大致是指普通类别被更高类别(即 n 类别)取代的过程。增长方向的转变n, 在如图所示的系统中。2.1对应分类。
去分类是分类的逆过程。去分类是一个系统过程,通过该过程,一个类别中的同构对象被识别为相等的。
分类方法适用于添加新维度即新水平的理论。

数学代写|multi-level modeling:nested代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。