如果你也在 怎样代写金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty将在某些付款和取决于个人死亡或其他不确定风险的付款方面应用利率、现值、现金流模型和利润测试的思想。
金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty金融学是利用概率论和数理统计、偏微分方程、随机过程、数学分析等数学工具进行数学建模和定量分析的方法,以寻找金融内部规律的新学科。这门学科自诞生以来,不断被金融学家吸收和使用。由于金融研究问题的不确定性,虽然金融数学是一门年轻的学科,但它注定要使随机分析作为一种主要工具得到广泛应用。然而,经过两次华尔街革命,金融数学得到了迅速发展。其核心内容是研究不确定随机环境下投资组合的最优选择理论和资产定价理论。套利、最优和均衡是基本的经济思想和金融数学的三个基本概念。
my-assignmentexpert™金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在金融Financial作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的金融Financial代写服务。我们的专家在金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty代写方面经验极为丰富,各种金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的金融数学Financial mathematics under uncertainty及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:

金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写Financial mathematics under uncertainty代考|How Double Auction Markets Work
The most common approach used by modern electronic exchanges can be termed, as time/price priority, continuous double auction trading system. The term double auction signifies that, unlike a common auction with one auctioneer dealing with potential buyers, in this case there are multiple buyers and multiple sellers participating in the process at the same time. These buyers and sellers interact with the exchange by sending instructions electronically, via a network protocol to a specialized software and hardware infrastructure called: The Matching Engine. It has two main components: The Limit Order Book and the Matching Algorithm.
Limit Order Book (LOB): It is a complex data structure that stores all non-executed orders with associated instructions. It is highly specialized so as to be extremely fast to insert/update/delete orders and then able to sort them and to retrieve aggregated information. For an active stock, the LOB can be updated and queried thousands of times every second, so it must be highly efficient and able to handle a high degree of concurrency to ensure that the state is always correct. The LOB is comprised of two copies of the core data structure, one for Buy orders and one for Sell orders often referred to as the two “sides” of the order book. This structure is the core abstraction for all electronic exchanges and so it is very important to understand it in detail.
The LOB supports three basic instructions: Insert, cancel, and amend, with insert initiating a new order, cancel removing an existing order from the market and amend modifying some of the parameters of the existing order. New orders must specify “order type” and associated parameters necessary to fully encapsulate the trader decision. We will review order types in more detail later, but we start with the two main types: The limit order and the market order. The main difference between the two order types is that a limit order has a price associated to it while a market order does not.
Accounting for limit and market orders, there are eight events at any given time, four on either side, that can alter the state of the order book:
- Limit Order Submission: A limit order is added to the queue at the specified price level.
- Limit Order Cancellation: An outstanding limit order is expired or canceled and is therefore removed from the Limit Order Book (LOB).
- Limit Order Amendment: An outstanding limit order is modified by the original sender (such as changing order size).
- Execution: Buy and sell orders at appropriate prices are paired by the matching algorithm (explained below) into a binding transaction and are removed from the LOB
Matching Algorithm: This software component is responsible for interpreting the various events to determine if any buy and sell orders can be matched in an execution. When multiple orders can be paired the algorithm uses the so-called price/time priority meaning that first the order with the most competitive prices are matched and when prices are equal the order that arrived prior is chosen. As we will see in later chapters this is only one of the possible algorithms used in practice but it is by far the most common. We will go into more details in the next sections.
The matching algorithm operates continuously throughout the trading hours. In order to ensure an orderly start and end, this continuous session is usually complemented by a couple of discrete auctions. The trading day generally starts with an open auction, then followed by the main continuous session, and ends with a closing auction. Some markets like Japan also have a lunch break which might be preceded by a morning closing auction and followed by an afternoon opening auction. We will now discuss these main market phases in chronological order.
金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写Financial mathematics under uncertainty代考|The Open Auction
The Open Auction is only one type of call auction that is commonly held on exchanges. The term “call auction” explains the liquidity-aggregating nature of this event. Market participants are ‘called’ to submit their quotes to the market place in order to determine a matching price that will maximize the amount of shares that can be transacted. To facilitate timely and orderly cross, auctions have strict order submission rules, including specified timing for entries (see Table 1.1) and information dissemination to prevent wild price fluctuations and ensure that the process is efficient for price discovery.
Most exchanges publish order imbalance that exists among orders on the opening or closing books, along with the indicative price and volume. For instance, Nasdaq publishes the following information ${ }^{20}$ between 9:28 a.m. EST and 9:30 a.m. EST, every 1 second, on its market data feeds:
- Current Reference Price: Price within the Nasdaq Inside at which paired shares are maximized, the imbalance is minimized and the distance from the bid-ask mid-point is minimized, in that order.
- Near Indicative Clearing Price: The crossing price at which orders in the Nasdaq opening / closing book and continuous book would clear against each other.
- Far Indicative Clearing Price: The crossing price at which orders in the Nasdaq opening / closing book would clear against each other.
- Number of Paired Shares: The number of on-open or on-close shares that Nasdaq is able to pair off at the current reference price.
- Imbalance Shares: The number of opening or closing shares that would remain unexecuted at the current reference price.
- Imbalance Side: The side of the imbalance: $B=$ buy-side imbalance; $S=$ sellside imbalance; $\mathrm{N}=$ no imbalance; $\mathrm{O}=$ no marketable on-open or on-close orders.
金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS UNDER UNCERTAINTY代考|Continuous Trading
This refers to the main market phase between the auctions. During this market session the state of the order book changes quite rapidly due to the multi-agent nature of financial markets and the prevalence of high frequency trading. Consequently, it is important to understand the dynamics of the LOB before implementing trading strategies. There exists quite a diversity of order types that are mostly relevant to the continuous trading session, but the two most basic ones are: Limit Orders and Market Orders, which we describe below.
A limit order has an associated side (Buy or Sell), a quantity and a price which represent the highest (lowest) price the trader is willing to buy (sell). As previously discussed, once a limit order is received by the exchange it is inserted in a data structure called a Limit Order Book (LOB) which contains two sub-structures, one per side. Orders are inserted in this structure in price priority, higher prices for buys,
lower prices for sells, and for orders at the same price the orders are stored in the order in which they were received. That is what is meant by price/time priority. ${ }^{21}$ If the price of a newly arrived order overlaps with the best price available on the opposite side, the order is executed either fully or up to the available quantity on the other side. These orders are said to be “matched” and again this matching happens in price and time priority meaning that the better prices (higher for buys, lower for sells) are executed first and orders that arrived beforehand at the same price level are executed first. Market orders on the other hand do not have a price associated with them and will immediately execute against the other side and will match with more and more aggressive prices until the full order is executed.
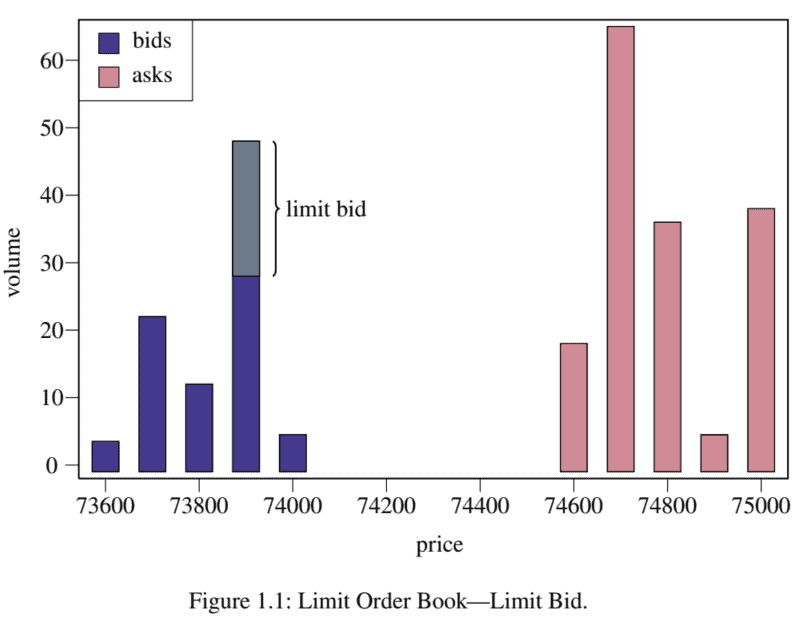
Orders on the buy side are called “bids” while those on the sell side are called “asks.” The above events are illustrated in Figure $1.1$ to Figure $1.3$. When a market (or marketable) order is submitted, it decreases the number of outstanding orders at the opposite best price. For example, if a market bid order arrives, it will decrease the number of outstanding asks at the best price. All unexecuted limit orders can be canceled. When a cancellation occurs, it will decrease the number of outstanding orders at the specified price level.
金融数学代写
金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS UNDER UNCERTAINTY代考|HOW DOUBLE AUCTION MARKETS WORK
现代电子交易所最常用的方法可以称为时间/价格优先的连续双重竞价交易系统。双重拍卖一词表示,与普通拍卖不同的是,一名拍卖师与潜在买家打交道,在这种情况下,有多个买家和多个卖家同时参与该过程。这些买卖双方通过网络协议以电子方式向称为匹配引擎的专用软件和硬件基础设施发送指令,从而与交易所进行交互。它有两个主要组成部分:限价订单簿和匹配算法。
限价订单簿大号这乙:它是一个复杂的数据结构,存储所有未执行的订单和相关的指令。它高度专业化,可以非常快速地插入/更新/删除订单,然后能够对它们进行排序并检索聚合信息。对于一个活跃的股票来说,LOB每秒可以更新和查询数千次,因此它必须是高效的,并且能够处理高度的并发,以确保状态始终正确。LOB 由核心数据结构的两份副本组成,一份用于买单,一份用于卖单,通常称为订单簿的两个“面”。这种结构是所有电子交换的核心抽象,因此详细了解它非常重要。
LOB 支持三个基本指令:插入、取消和修改,插入发起新订单,取消从市场中移除现有订单和修改现有订单的一些参数。新订单必须指定“订单类型”和完全封装交易者决策所需的相关参数。稍后我们将更详细地查看订单类型,但我们从两种主要类型开始:限价订单和市价订单。两种定单类型的主要区别在于限价定单具有与其相关的价格,而市价定单则没有。
考虑到限价单和市价单,在任何给定时间都有八个事件,两边各四个,可以改变订单簿的状态:
- 限价订单提交:限价订单以指定的价格水平添加到队列中。
- 限价订单取消:未完成的限价订单已过期或取消,因此从限价订单簿中删除大号这乙.
- 限价单修改:未完成的限价单被原始发送者修改s在CH一种sCH一种nG一世nG这rd和rs一世和和.
- 执行:以合适的价格买卖订单通过匹配算法配对和Xpl一种一世n和db和l这在进入绑定事务并从 LOB 中删除
匹配算法:该软件组件负责解释各种事件以确定是否可以在执行中匹配任何买卖订单。当多个订单可以配对时,算法使用所谓的价格/时间优先级,这意味着首先匹配价格最具竞争力的订单,当价格相等时,选择先到的订单。正如我们将在后面的章节中看到的,这只是实践中可能使用的算法之一,但它是迄今为止最常见的。我们将在接下来的部分中详细介绍。
匹配算法在整个交易时间内连续运行。为了确保有序的开始和结束,这个连续的会话通常由几个离散的拍卖来补充。交易日通常以公开竞价开始,然后是主要连续交易时段,最后以收盘竞价结束。日本等一些市场也有午休时间,之前可能是上午的收盘拍卖,然后是下午的开盘拍卖。我们现在将按时间顺序讨论这些主要的市场阶段。
金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS UNDER UNCERTAINTY代考|THE OPEN AUCTION
公开竞价只是交易所常见的一种集合竞价。“集合竞价”一词解释了这一事件的流动性聚合性质。市场参与者被“召集”向市场提交他们的报价,以确定匹配价格,从而最大限度地提高可交易的股票数量。为了方便及时有序的交叉,拍卖有严格的订单提交规则,包括指定的入场时间s和和吨一种bl和1.1和信息传播,以防止价格剧烈波动,并确保价格发现过程有效。
大多数交易所都会公布开盘或收盘订单中存在的订单不平衡,以及指示性价格和交易量。例如,纳斯达克发布以下信息20在美国东部时间上午 9:28 到美国东部时间上午 9:30 之间,每隔 1 秒,在其市场数据馈送中:
- 当前参考价格:纳斯达克内部的价格,其中配对股票最大化,不平衡最小化,与买卖中点的距离最小化,按此顺序。
- Near Indicative Clearing Price:纳斯达克开盘/收盘和连续盘中的订单相互清算的交叉价格。
- 远指示性清算价格:纳斯达克开盘/收盘订单中的订单相互清算的交叉价格。
- 配对股票数量:纳斯达克能够以当前参考价格配对的开盘或收盘股票数量。
- 不平衡股份:以当前参考价格保持未执行的开盘或收盘股份数量。
- 不平衡侧: 不平衡侧:乙=买方失衡;小号=卖方失衡;ñ=没有不平衡;这=没有可销售的开盘或收盘订单。
金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS UNDER UNCERTAINTY代考|CONTINUOUS TRADING
这是指拍卖之间的主要市场阶段。在这个市场时段,由于金融市场的多代理性质和高频交易的盛行,订单簿的状态变化很快。因此,在实施交易策略之前了解 LOB 的动态非常重要。与连续交易时段最相关的订单类型有很多种,但最基本的两种是:限价订单和市价订单,我们将在下面进行介绍。
限价单有关联的一面乙在是这r小号和ll,代表最高的数量和价格l这在和s吨交易者愿意购买的价格s和ll. 如前所述,一旦交易所收到限价订单,它就会被插入到一个称为限价订单簿的数据结构中大号这乙它包含两个子结构,每侧一个。订单以价格优先顺序插入此结构中,购买价格较高,
以较低的价格出售,而对于相同价格的订单,订单将按照收到订单的顺序存储。这就是价格/时间优先的含义。21如果新到达的订单的价格与对方的最佳价格重叠,则订单要么全部执行,要么执行到对方的可用数量。这些订单被称为“匹配”,并且这种匹配再次发生在价格和时间优先级上,这意味着更好的价格H一世GH和rF这rb在是s,l这在和rF这rs和lls先执行,先到的同价位订单先执行。另一方面,市场订单没有与之相关的价格,并且会立即对另一方执行,并且会匹配越来越激进的价格,直到执行完整的订单。
买方的订单称为“出价”,而卖方的订单称为“询价”。上述事件如图所示1.1到图1.3. 当一个市场这r米一种rķ和吨一种bl和提交订单时,它会以相反的最佳价格减少未完成订单的数量。例如,如果市场买入订单到达,它将以最佳价格减少未完成的卖出数量。所有未执行的限价单都可以取消。当发生取消时,它将减少指定价格水平的未完成订单数量。

金融代写|不确定性下的金融数学代写Financial mathematics under uncertainty代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。