如果你也在 怎样代写有限元方法finite differences method ENGR7961这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。有限元方法finite differences method在数值分析中,是一类通过用有限差分逼近导数解决微分方程的数值技术。空间域和时间间隔(如果适用)都被离散化,或被分成有限的步骤,通过解决包含有限差分和附近点的数值的代数方程来逼近这些离散点的解的数值。
有限元方法finite differences method有限差分法将可能是非线性的常微分方程(ODE)或偏微分方程(PDE)转换成可以用矩阵代数技术解决的线性方程系统。现代计算机可以有效地进行这些线性代数计算,再加上其相对容易实现,使得FDM在现代数值分析中得到了广泛的应用。今天,FDM与有限元方法一样,是数值解决PDE的最常用方法之一。
有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此有限元方法finite differences method作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在数学Mathematics代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在微积分Calculus Assignment代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微积分Calculus Assignment相关的作业也就用不着 说。
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|PLATE ELEMENTS
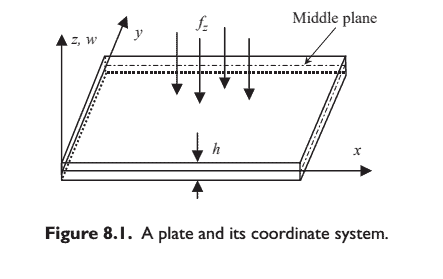
As discussed in Chapter 2, a plate structure is geometrically similar to the structure of the 2D plane stress problem, but it usually carries only transversal loads that lead to bending deformation in the plate. For example, consider the horizontal boards on a bookshelf that support the books. Those boards can be approximated as a plate structure, and the transversal loads are of course the weight of the books. Higher floors of a building are a typical plate structure that carries most of us every day, as are the wings of aircraft, which usually carry loads like the engines, as shown in Figure 2.13. The plate structure can be schematically represented by its middle plane laying on the $x-y$ plane, as shown in Figure 8.1. The deformation caused by the transverse loading on a plate is represented by the deflection and rotation of the normals of the middle plane of the plate, and they will be independent of $z$ and a function of only $x$ and $y$. The element to be developed to model such plate structures is aptly known as the plate element. The formulation of a plate element is very much the same as for the 2D solid element, except for the process for deriving the strain matrix in which the theory of plates is used.
Plate elements are normally used to analyse the bending deformation of plate structures and the resulting forces such as shear forces and moments. In this aspect, it is similar to the beam element developed in Chapter 5 , except that the plate element is two-dimensional whereas the beam element is one-dimensional. Like the $2 \mathrm{D}$ solid element, a plate element can also be triangular, rectangular or quadrilateral in shape. In this book, we cover the development of the rectangular element only, as it is often used. Matrices for the triangular element can also be developed easily using similar procedures, and those for the quadrilateral element can be developed using the idea of an isoparametric element discussed for $2 \mathrm{D}$ solid elements. In fact, the development of a quadrilateral element is much the same as the rectangular element, except for an additional procedure of coordinate mapping, as shown for the case of $2 \mathrm{D}$ solid elements.
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|Shape Functions
It can be seen from the above analysis of the constitutive equations that the rotations, $\theta_x$ and $\theta_y$ are independent of the deflection $w$. Therefore, when it comes to interpolating the generalized displacements, the deflection and rotations can actually be interpolated separately using independent shape functions. Therefore, the procedure of field variable interpolation is the same as that for 2D solid problems, except that there are three instead of two DOFs, for a node.
For four-node rectangular thick plate elements, the deflection and rotations can be summed as
$$
w=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i w_i, \quad \theta_x=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i \theta_{x_i}, \quad \theta_y=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i \theta_{y_i}
$$
where the shape function $N_i$ is the same as the four-node 2D solid element in Chapter 7, i.e.
$$
N_i=\frac{1}{4}\left(1+\xi_i \xi\right)\left(1+\eta_i \eta\right)
$$
有限元方法代写
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|PLATE ELEMENTS
如第2 章所述,板结构在几何上类似于二维平面应力问题的结构,但它通常只承受导致板弯曲变形的横向载荷。例 如,考虑书架上支撑书籍的水平板。那些木板可以近似为板状结构,横向荷载当然是书本的重量。建筑物的较高楼 层是典型的板结构,每天承载着我们大多数人,飞机的机翼也是如此,通常承载像发动机一样的负载,如图 2.13 所 示。板结构可以示意性地表示为它的中平面位于 $x-y$ 平面,如图 8.1所示。板的横向载荷引起的变形由板中平面法 线的偏转和旋转表示,它们将与 $z$ 并且只有一个函数 $x$ 和 $y$. 为模拟这种板结构而开发的单元被恰当地称为板单元。板 单元的公式与 $2 D$ 实体单元非常相似,除了使用板理论推导应变矩阵的过程。
板单元通常用于分析板结构的弯曲变形及其产生的力,例如剪力和力矩。在这方面,它类似于第 5 章中开发的梁单 元,只是板单元是二维的,而梁单元是一维的。像 $2 \mathrm{D}$ 除了实体单元,板单元也可以是三角形、矩形或四边形。在本 书中,我们只介绍矩形元素的开发,因为它经常被使用。三角形单元的矩阵也可以使用类似的程序轻松开发,四边 形单元的矩阵可以使用讨论的等参单元的思想开发 $2 \mathrm{D}$ 固体元素。事实上,四边形单元的开发与矩形单元非常相似, 只是多了一个坐标映射过程,如 $2 \mathrm{D}$ 固体元素。
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写FINITE DIFFERENCES METHOD代考|SHAPE FUNCTIONS
从以上本构方程的分析可以看出,旋转, $\theta_x$ 和 $\theta_y$ 与偏转无关 $w$. 因此,在对广义位移进行揷值时,偏转和旋转实际上 可以使用独立的形函数分别进行揷值。因此,场变量揷值的过程与二维实体问题的过程相同,只是对于一个节点有 三个而不是两个自由度。
对于四节点矩形厚板单元,挠度和旋转可以总结为
$$
w=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i w_i, \quad \theta_x=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i \theta_{x_i}, \quad \theta_y=\sum_{i=1}^4 N_i \theta_{y_i}
$$
其中形状函数 $N_i$ 与第 7 章中的四节点二维实体单元相同,即
$$
N_i=\frac{1}{4}\left(1+\xi_i \xi\right)\left(1+\eta_i \eta\right)
$$

数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。