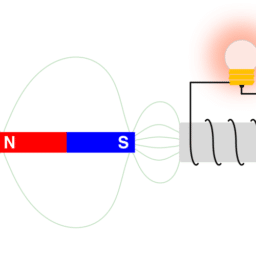
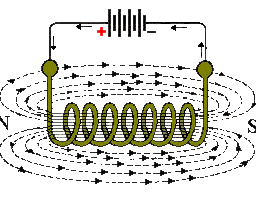
MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™可以为您提供 catalog.ycp.edu PHYS350 Electromagnetism电磁学的代写代考和辅导服务!
这是宾夕法尼亚州约克学院的电磁学课程的代写成功案例。

PHYS350课程简介
This course introduces Maxwell’s equations and their applications to engineering problems. Topics covered include electrostatics, magnetostatics, magnetic fields and matter, induction, and electromagnetic waves. The reflection, transmission, and propagation of waves are studied. Applications to waveguides, transmission lines, radiation, and antennas are introduced as time permits. Prerequisite: 2.0 or higher in both ECE 270, EGR 240.
3 credit hours
Prerequisites
You should assume that the person reading the paper has taken PHYS 350 and has a knowledge of electromagnetism at the level of the class. In your paper, you should (1) introduce the topic, and explain the background to the problem and why it is interesting, (2) carefully describe (preferably with the help of a diagram or two) the basic physics of the process, device, or experiment, and (3) perform a simple calculation (at the “back of the envelope” level) which determines the basic quantities involved, and illustrates the physics. For example, you could describe the basic physics that causes a fridge magnet to stick to the metal door, and estimate the strength of the typical magnet needed, or describe the processes involved in a lightning strike, and estimate the charge transferred, typical currents, and frequency of lightning strikes around the globe.
PHYS350 Electromagnetism HELP(EXAM HELP, ONLINE TUTOR)
Let $\mathbf{c}$ be a constant vector and $\mathbf{r}$ the position vector. Calculate the gradient of $\mathbf{c} \cdot \mathbf{r}$ and the divergence and the curl of $\mathbf{r}$ and $\mathbf{c} \times \mathbf{r}$. Prove that, if a fluid experiences a pure rotation, the divergence of its velocity is zero and the curl of its velocity is twice the angular velocity.
Given a scalar $f(\mathbf{x})$, two vectors $\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{x})$ and $\mathbf{B}(\mathbf{x})$, and a volume $V$ surrounded by a surface $S$, prove the following relations:
(a) $\int_V \nabla f d \tau=\int_S f \mathbf{n} d S$
(b) $\int_S \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{B} \cdot \mathbf{n}) d S=\int_V \mathbf{A}(\boldsymbol{\nabla} \cdot \mathbf{B}) d \tau+\int_V(\mathbf{B} \cdot \boldsymbol{\nabla}) \mathbf{A} d \tau$
The points of a plane rotate about a fixed point with an angular velocity $\omega=\omega(r), r$ being the distance from the fixed point. What function must $\omega(r)$ be in order for the velocity $\mathbf{v}$ to have $\nabla \times \mathbf{v}=0$ ?
Prove the following relation:
$$
\int_S(\nabla \phi \times \nabla \psi) \cdot d \mathbf{S}=\oint_l \phi d \psi
$$
where $S$ is a surface of contour $l$.
The Cartesian components of a vector are
$$
a_x=y \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z}-z \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}
$$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& a_y=z \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}-x \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} \
& a_z=x \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y}-y \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x}
\end{aligned}
$$
where $\phi=\phi(x, y, z)$. Express a as the cross product of two vectors and show that
$$
\begin{aligned}
\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{r} & =0 \
\mathbf{a} \cdot \nabla \phi & =0
\end{aligned}
$$

MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™可以为您提供 CATALOG.YCP.EDU PHYS350 ELECTROMAGNETISM电磁学的代写代考和辅导服务!