如果你也在 怎样代写数学建模Mathematical Modeling这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。数学建模Mathematical Modeling是使用数学概念和语言对一个具体系统的抽象描述。建立数学模型的过程被称为数学建模。数学模型被用于自然科学(如物理学、生物学、地球科学、化学)和工程学科(如计算机科学、电气工程),以及非物理系统,如社会科学(如经济学、心理学、社会学、政治学)。使用数学模型来解决商业或军事行动中的问题是运筹学领域的一个重要部分。数学模型也被用于音乐、语言学、和哲学(例如,集中用于分析哲学)。
数学建模Mathematical Modeling可以有很多形式,包括动态系统、统计模型、微分方程或博弈论模型。这些和其他类型的模型可以重叠,一个特定的模型涉及各种抽象结构。一般来说,数学模型可能包括逻辑模型。在许多情况下,一个科学领域的质量取决于在理论方面开发的数学模型与可重复的实验结果的吻合程度。理论上的数学模型和实验测量结果之间缺乏一致性,往往导致更好的理论被开发出来,从而取得重要进展。
数学建模Mathematical Modeling代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的数学建模Mathematical Modeling作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此数学建模Mathematical Modeling作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
数学代写|数学建模代写Mathematical Modeling代考|The general scheme of the Hamiltonian principle
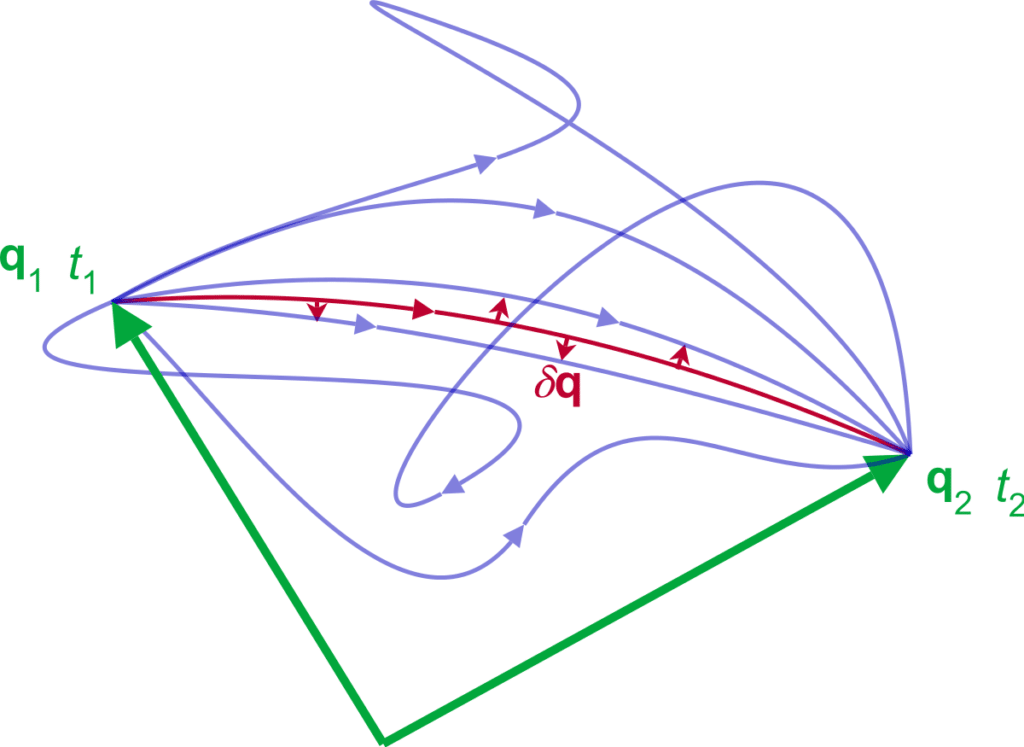
The general scheme of the Hamiltonian principle. Consider a mechanical system, without giving its formal and rigorous definition, taking into account that the interaction between all its elements is determined by the laws of mechanics (one of the simplest examples is the “ball-spring” system considered in section 2.4). Introduce the concept of a generalized coordinate $Q(t)$, completely defining the position of the mechanical system in space. The quantity $Q(t)$ can coincide with the Cartesian coordinate (for example, the coordinate $r$ of the system “ball-spring”), the radius-vector, the angular coordinate, the set of coordinates of mass points, etc. It is natural to label the quantity $d Q / d t$ as generalized velocity of the mechanical system in the moment of time $t$. The set of magnitudes $Q(t)$ and $d Q / d t$ determines the state of a mechanical system at all moments in time.
To describe the mechanical system the Lagrange function is introduced; its derivation is a separate problem, considered in more detail in chapter III. In the simplest cases the Lagrange function has a clear content and is denoted as
$$
L(Q, d Q / d t)=E_k-E_p,
$$
where $E_k, E_p$ are the kinetic and potential energies of the system respectively. For the purposes of the present section there is no need to give the general definition of quantities $E_k, E_p$, in so far as they are calculated in obvious manner in the considered examples.
Let us introduce the quantity $S[Q]$, named an action:
$$
S[Q]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2} L\left(Q, \frac{d Q}{d t}\right) d t
$$
数学代写|数学建模代写Mathematical Modeling代考|The third way of deriving the model of the system “ballspring”
We use the Hamiltonian principle to construct the model of the motion of the ball connected with a spring (section 2.4). As generalized coordinates of the system it is natural to chose the usual Eulerian coordinate of the ball $r(t)$. Then the generalized velocity $d r / d t=v(t)$ is the usual velocity of the ball. The Lagrangian function (1), $L=E_k-E_p$, is rewritten using values of kinetic and potential energies of the system (already found in section 2.4):
$$
L=\frac{m(d r / d t)^2}{2}-k \frac{r^2}{2}
$$
For the action we obtain
$$
S[r]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2} L\left(r, \frac{d r}{d t}\right) d t=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d r}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2} r^2\right] d t
$$
Now, in view of the correspondence with the scheme seen in subsection 1 , we calculate the action over the variations $\varepsilon \varphi(t)$ of the coordinates $r(t)$ :
$$
S[r+\varepsilon \varphi]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d(r+\varepsilon \varphi)}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2}(r+\varepsilon \varphi)^2\right] d t
$$
Now, in view of the correspondence with the scheme seen in subsection 1 , we calculate the action over the variations $\varepsilon \varphi(t)$ of the coordinates $r(t)$ :
$$
S[r+\varepsilon \varphi]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d(r+\varepsilon \varphi)}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2}(r+\varepsilon \varphi)^2\right] d t .
$$
数学建模代写
数学代写|数学建模代写MATHEMATICAL MODELING代考|THE GENERAL SCHEME OF THE HAMILTONIAN PRINCIPLE
哈密顿原理的一般方案。考虑一个机械系统,不给出其正式和严格的定义,考虑到其所有元素之间的相互作用是由力学定律决定的 oneofthesimplestexamplesisthe “ball – spring” systemconsideredinsection 2.4 . 引入广义坐标的概念 $Q(t)$ ,完全定义了机 械系统在空间中的位置。数量 $Q(t)$ 可以与笛卡尔坐标重合forexample, thecoordinate\$r \$ofthesystem “ball – spring”, radiusvector, 角坐标, 质点坐标集合等。自然要标注数量 $d Q / d t$ 作为机械系统在瞬间的广义速度 $t$. 幅度集 $Q(t)$ 和 $d Q / d t$ 确定机械系统在所有 时刻的状态。
为了描述机械系统,引入了拉格朗日函数;它的推导是一个单独的问题,在第三章中有更详细的讨论。在最简单的情况下,拉格朗 日函数具有明确的内容并表示为
$$
L(Q, d Q / d t)=E_k-E_p
$$
在哪里 $E_k, E_p$ 分别是系统的动能和势能。就本节而言,无需给出数量的一般定义 $E_k, E_p$ ,只要它们在所考虑的示例中以明显的方式 计算。
让我们介绍一下数量 $S[Q]$, 命名一个动作:
$$
S[Q]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2} L\left(Q, \frac{d Q}{d t}\right) d t
$$
数学代写|数学建模代写MATHEMATICAL MODELING代考|THE THIRD WAY OF DERIVING THE MODEL OF THE SYSTEM “BALLSPRING”
我们使用哈密顿原理来构建连接㫜簧的球的运动模型 section 2.4. 作为系统的广义坐标,自然选择球的常用欧拉坐标 $r(t)$. 那么广义速 度 $d r / d t=v(t)$ 是球的通常速度。拉格朗日函数1, $L=E_k-E_p$, 使用系统的动能和势能值重写alreadyfoundinsection 2.4:
$$
L=\frac{m(d r / d t)^2}{2}-k \frac{r^2}{2}
$$
对于我们获得的行动
$$
S[r]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2} L\left(r, \frac{d r}{d t}\right) d t=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d r}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2} r^2\right] d t
$$
现在,鉴于与第 1 小节中看到的方案的对应关系,我们计算了对变化的作用 $\varepsilon \varphi(t)$ 的坐标 $r(t)$ :
$$
S[r+\varepsilon \varphi]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d(r+\varepsilon \varphi)}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2}(r+\varepsilon \varphi)^2\right] d t
$$
现在,鉴于与第 1 小节中看到的方案的对应关系,我们计算了对变化的作用 $\varepsilon \varphi(t)$ 的坐标 $r(t)$ :
$$
S[r+\varepsilon \varphi]=\int_{t_1}^{t_2}\left[\frac{m}{2}\left(\frac{d(r+\varepsilon \varphi)}{d t}\right)^2-\frac{k}{2}(r+\varepsilon \varphi)^2\right] d t
$$

数学代写|数学建模代写Mathematical Modeling代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。