MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™可以为您提供sydney MATH1002 Linear Algebra线性代数的代写代考和辅导服务!
这是悉尼大学线性代数课程的代写成功案例。
MATH1002课程简介
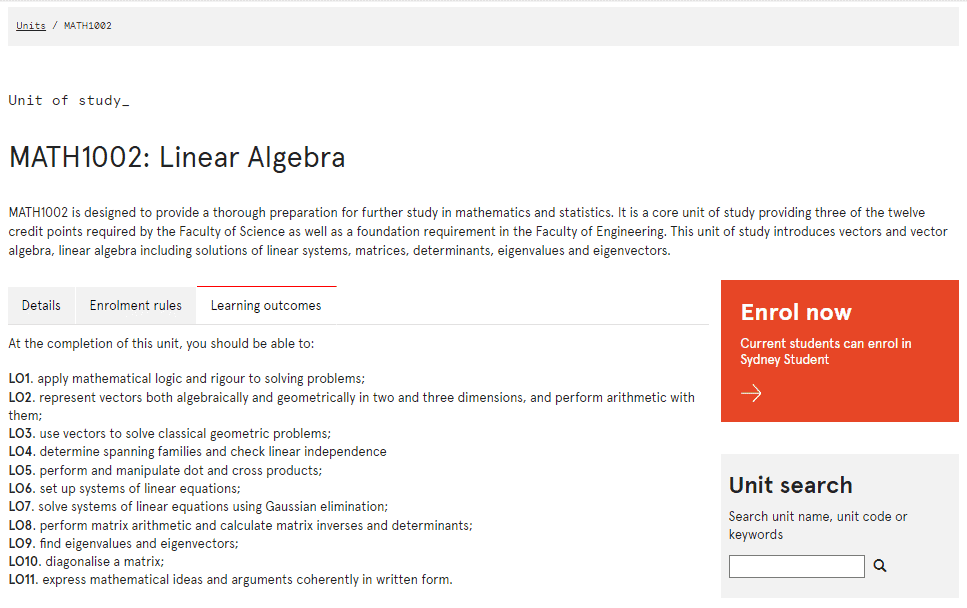
MATH1002 is designed to provide a thorough preparation for further study in mathematics and statistics. It is a core unit of study providing three of the twelve credit points required by the Faculty of Science as well as a foundation requirement in the Faculty of Engineering. This unit of study introduces vectors and vector algebra, linear algebra including solutions of linear systems, matrices, determinants, eigenvalues and eigenvectors.
Prerequisites
At the completion of this unit, you should be able to:
- LO1. apply mathematical logic and rigour to solving problems;
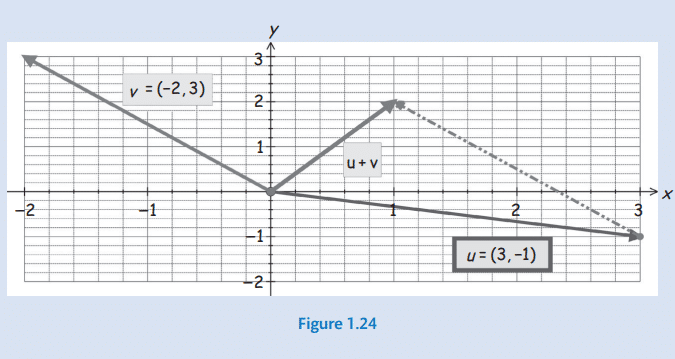
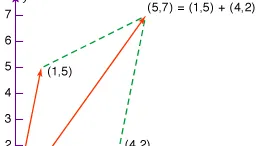
- LO2. represent vectors both algebraically and geometrically in two and three dimensions, and perform arithmetic with them;
- LO3. use vectors to solve classical geometric problems;
- LO4. determine spanning families and check linear independence
- LO5. perform and manipulate dot and cross products;
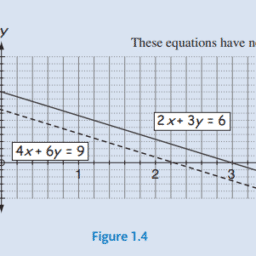
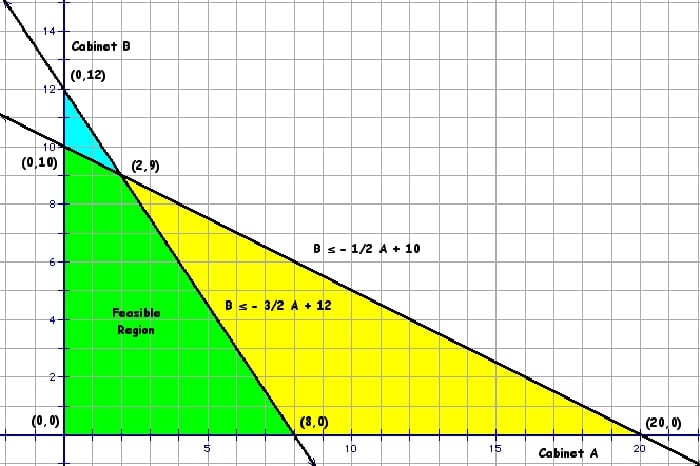
- LO6. set up systems of linear equations;
- LO7. solve systems of linear equations using Gaussian elimination;
- LO8. perform matrix arithmetic and calculate matrix inverses and determinants;
- LO9. find eigenvalues and eigenvectors;
- LO10. diagonalise a matrix;
- LO11. express mathematical ideas and arguments coherently in written form.
MATH1002 Linear algebra HELP(EXAM HELP, ONLINE TUTOR)
True or false questions:
(a) If rows of a matrix are linearly independent, so are the columns.
(b) If the columns of an $n$-by- $n$ matrix span $\mathbb{R}^n$, so do the rows.
(c) If $A, B$, and $C$ are $n$-by- $n$ invertible matrices, so is the matrix $A B^T C$.
(d) If $A B=A C$ and $A$ is not equal to zero matrix, then $B=C$.
(e) If $A C=B C$ and $C$ is invertible, then $A=B$.
(f) Let $A$ and $B$ be same size square matrices. If $\operatorname{det} A=3$ and $\operatorname{det} B=5$, then $\operatorname{det}(A+B)=3+5$.
\begin{prob}
\begin{prob}
Let $T: \mathbb{R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^m$ be a linear transformation. True or false questions:
(a) If $n \leq m$, then $T$ is one-to-one.
(b) If $n \geq m$, then $T$ is onto.
(c) If $n=m$, then $T$ is one-to-one and onto.
(d) If $T$ is one-to-one, then $n \leq m$.
(e) If $T$ is onto, then $n \geq m$.
(f) If $T$ is one-to-one and onto, then $n=m$.
Let $T: \mathbb{R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^m$ be a linear transformation defined below. Determine whether $T$ is one-to-one, or onto, or invertible?
(a) $f\left(x_1, x_2, x_3\right)=\left(x_2+7 x_3, x_1+3 x_2-2 x_3\right)$.
(b) $f\left(x_1, x_2, x_3\right)=\left(x_1+2 x_3, 2 x_1-x_2+3 x_3, 4 x_1+x_2+8 x_3\right)$.
(c) $f\left(x_1, x_2, x_3\right)=\left(x_1+x_2+x_3, x_1+2 x_2, x_1+2 x_3\right)$.
Compute $\operatorname{det} A, \operatorname{det} A^T, \operatorname{det} A^4, \operatorname{det} A^{-5}, A^{-1},\left(A^T\right)^{-1},\left(A^{-1}\right)^T$, where
$$
A=\left[\begin{array}{llll}
1 & 1 & 1 & 1 \
1 & 2 & 2 & 2 \
1 & 3 & 6 & 8 \
1 & 4 & 8 & 9
\end{array}\right] .
$$
Let $T: \mathbb{R}^n \rightarrow \mathbb{R}^m$ be a linear transformation. Then $T$ is one-to-one if and only if $T$ preserves linear independence (i.e., $T\left(\boldsymbol{v}_1\right), \ldots, T\left(\boldsymbol{v}_k\right)$ are linearly independent in $\mathbb{R}^m$ whenever $\boldsymbol{v}_1, \ldots, \boldsymbol{v}_k$ are linearly independent in $\left.\mathbb{R}^n\right)$.

MY-ASSIGNMENTEXPERT™可以为您提供SYDNEY MATH1002 LINEAR ALGEBRA线性代数的代写代考和辅导服务!