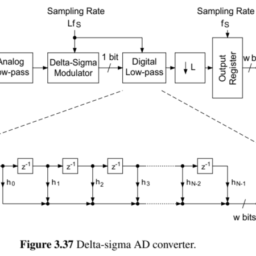
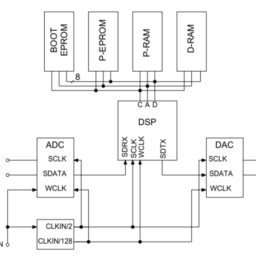
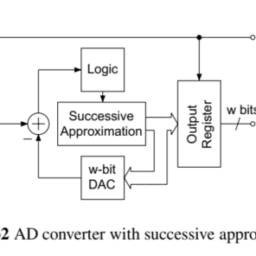
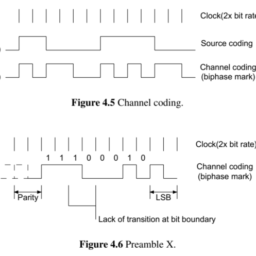
如果你也在 怎样代写信号和系统signals and systems这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。信号和系统signals and systems信号是对一个参数如何随另一个参数变化的描述。例如,电子电路中电压随时间变化,或图像中亮度随距离变化。一个系统是任何对输入信号产生输出信号的过程。
信号和系统signals and systems是对模拟和数字信号处理的介绍,这一主题构成了许多不同领域的工程系统的一个组成部分,包括地震数据处理、通信、语音处理、图像处理、国防电子、消费电子和消费产品。
my-assignmentexpert™ 信号和系统signals and systems作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的信号和系统signals and systems作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此信号和系统signals and systems作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在信息Information作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的信号和系统signals and systems代写服务。我们的专家在信息Information代写方面经验极为丰富,各种信号和系统signals and systems相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的信号和系统signals and systems及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
调和函数 harmonic function
椭圆方程 elliptic equation
抛物方程 Parabolic equation
双曲方程 Hyperbolic equation
非线性方法 nonlinear method
变分法 Calculus of Variations
几何分析 geometric analysis
偏微分方程数值解 Numerical solution of partial differential equations
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写signals and systems代考|Analytical development
In Section $5.1$, the CTFT pair, $x(t) \stackrel{\text { CTFT }}{\longleftrightarrow} X(\mathrm{j} \omega)$, was defined as follows:
CTFT synthesis equation $x(t)=\frac{1}{2 \pi} \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} X(\mathrm{j} \omega) \mathrm{e}^{\mathrm{j} \omega t} \mathrm{~d} \omega$;
CTFT analysis equation $\quad X(\mathrm{j} \omega)=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{j} \omega t} \mathrm{~d} t$.
In Eqs. (6.1) and (6.2), the CTFT of $x(t)$ is expressed as $X(\mathrm{j} \omega)$, instead of the earlier notation $X(\omega)$, to emphasize that the CTFT is computed on the imaginary $\mathrm{j} \omega$-axis in the complex s-plane. For a CT signal $x(t)$, the expression for the bilateral Laplace transform is derived by considering the CTFT of the modified version, $x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}$, of the signal. Based on Eq. (6.2), the CTFT of the modified signal $x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}$ is given by
$$
\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{j} \omega t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
which reduces to
$$
\begin{aligned}
\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right} &=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-(\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega) t} \mathrm{~d} t \
&=X(\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega) .
\end{aligned}
$$
Substituting $s=\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega$ in Eq. (6.4) leads to the following definition for the bilateral Laplace transform: ${ }^{\dagger}$
Laplace analysis equation $\quad X(s)=\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-s t} \mathrm{~d} t$.
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写signals and systems代考|Unilateral Laplace transform
In Section 6.1, we introduced the bilateral Laplace transform that is used to analyze both causal and non-causal LTIC systems. In signal processing, most physical systems and signals are causal. Applying the causality condition, the bilateral Laplace transform reduces to a simpler version of the Laplace transform. The Laplace transform for causal signals and systems is referred to as the unilateral Laplace transform and is defined as follows:
$$
X(s)=L{x(t)}=\int_{0^{-}}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-s t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
where the initial conditions of the system are incorporated by the lower limit $\left(t=0^{-}\right)$. In our subsequent discussions, we will mostly use the unilateral Laplace transform. For simplicity, we will omit the term “unilateral,” therefore the Laplace transform implies the unilateral Laplace transform. When we refer to the bilateral Laplace transform, the term “bilateral” will be explicitly stated. To clarify further the differences between the unilateral and bilateral Laplace transform, we summarize the major points.
(1) The unilateral Laplace transform simplifies the analysis of causal LTIC systems. However, it cannot analyze non-causal systems directly. Since most physical systems are naturally causal, we will use the unilateral Laplace transform in our computations. The bilateral transform will be used only to analyze non-causal systems.
(2) For causal signals and systems, the unilateral and bilateral Laplace transforms are the same.
(3) The synthesis equation used for calculating the inverse of the unilateral Laplace transform is the same as Eq. (6.7) used for evaluating the inverse of the bilateral transform.
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS代考|Inverse Laplace transform
Evaluation of the inverse Laplace transform is an important step in the analysis of LTIC systems. The inverse Laplace transform can be calculated directly by solving the complex integral in the synthesis equation, Eq. (6.7). This approach involves contour integration, which is beyond the scope of this text. In cases where the Laplace transform takes the following rational form:
$$
X(s)=\frac{N(s)}{D(s)}=\frac{b_{m} s^{m}+b_{m-1} s^{m-1}+b_{m-2} s^{m-2}+\cdots+b_{1} s+b_{0}}{s^{n}+a_{n-1} s^{n-1}+a_{n-2} s^{n-2}+\cdots+a_{1} s+a_{0}}
$$
an alternative approach based on the partial fraction expansion is commonly used. The approach eliminates the need for computing Eq. (6.7) and consists of the following steps.
(1) Calculate the roots of the characteristic equation of the rational fraction, Eq. (6.11). The characteristic equation is obtained by equating the denominator $D(s)$ in Eq. (6.11) to zero, i.e.
$$
D(s)=s^{n}+a_{n-1} s^{n-1}+a_{n-2} s^{n-2}+\cdots+a_{1} s+a_{0}=0
$$
For an $n$ th-order characteristic equation, there will be $n$ first-order roots. Depending on the value of the coefficients $\left{b_{l}\right}, 0 \leq l \leq(n-1)$, roots $\left{p_{r}\right}, 1 \leq r \leq n$, of the characteristic equation may be real-valued and/or complex-valued. Assuming that roots are real-valued and do not repeat, the Laplace transform $X(s)$ is represented as
$$
X(s)=\frac{N(s)}{\left(s-p_{1}\right)\left(s-p_{2}\right) \cdots\left(s-p_{n-1}\right)\left(s-p_{n}\right)} .
$$
信号和系统代写
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS代考|ANALYTICAL DEVELOPMENT
在部分5.1, CTFT 对,X(吨)⟷ CTFT X(jω), 定义如下:
CTFT 合成方程X(吨)=12圆周率∫−∞∞X(jω)和jω吨 dω;
CTFT分析方程X(jω)=∫−∞∞X(吨)和−jω吨 d吨.
在方程式中。6.1和6.2, 的 CTFTX(吨)表示为X(jω), 而不是早期的符号X(ω), 强调 CTFT 是在虚数上计算的jω- 复 s 平面中的轴。对于 CT 信号X(吨), 双边拉普拉斯变换的表达式是通过考虑修改版本的 CTFT 导出的,X(吨)和−σ吨, 的信号。基于方程式。6.2, 修改后信号的 CTFTX(吨)和−σ吨是(谁)给的
$x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}$, of the signal. Based on Eq. (6.2), the CTFT of the modified signal $x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}$ is given by
$$
\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t} \mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{j} \omega t} \mathrm{~d} t
$$
which reduces to
$$
\begin{aligned}
\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right} &=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-(\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega) t} \mathrm{~d} t \
&=X(\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega) .
\end{aligned}
$$
Substituting $s=\sigma+\mathrm{j} \omega$ in Eq. (6.4) leads to the following definition for the bilateral Laplace transform: ${ }^{\dagger}$
Laplace analysis equation $\quad X(s)=\Im\left{x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-\sigma t}\right}=\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} x(t) \mathrm{e}^{-s t} \mathrm{~d} t$.
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS代考|UNILATERAL LAPLACE TRANSFORM
在 6.1 节中,我们介绍了用于分析因果和非因果 LTIC 系统的双边拉普拉斯变换。在信号处理中,大多数物理系统和信号都是因果的。应用因果关系条件,双边拉普拉斯变换简化为拉普拉斯变换的更简单版本。因果信号和系统的拉普拉斯变换称为单边拉普拉斯变换,定义如下:
X(s)=大号X(吨)=∫0−∞X(吨)和−s吨 d吨
其中系统的初始条件由下限合并(吨=0−). 在我们随后的讨论中,我们将主要使用单边拉普拉斯变换。为简单起见,我们将省略“单边”一词,因此拉普拉斯变换意味着单边拉普拉斯变换。当我们提到双边拉普拉斯变换时,将明确说明术语“双边”。为了进一步阐明单边和双边拉普拉斯变换之间的差异,我们总结了要点。
1单边拉普拉斯变换简化了因果 LTIC 系统的分析。但是,它不能直接分析非因果系统。由于大多数物理系统都是自然因果的,我们将在计算中使用单边拉普拉斯变换。双边变换将仅用于分析非因果系统。
2对于因果信号和系统,单边和双边拉普拉斯变换是相同的。
3用于计算单边拉普拉斯变换逆的合成方程与式(1)相同。6.7用于评估双边变换的逆。
信号代写|信号和系统作业代写SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS代考|INVERSE LAPLACE TRANSFORM
拉普拉斯逆变换的评估是 LTIC 系统分析中的一个重要步骤。拉普拉斯逆变换可以直接通过求解合成方程 Eq 中的复积分来计算。6.7. 这种方法涉及轮廓积分,这超出了本文的范围。在拉普拉斯变换采用以下有理形式的情况下:
X(s)=ñ(s)D(s)=b米s米+b米−1s米−1+b米−2s米−2+⋯+b1s+b0sn+一种n−1sn−1+一种n−2sn−2+⋯+一种1s+一种0
通常使用基于部分分数展开的替代方法。该方法消除了计算方程式的需要。6.7并由以下步骤组成。
1计算有理分数的特征方程的根,Eq。6.11. 特征方程由分母相等得到D(s)在等式。6.11为零,即
D(s)=sn+一种n−1sn−1+一种n−2sn−2+⋯+一种1s+一种0=0
为n三阶特征方程,将有n一阶根。取决于系数的值\left{b_{l}\right}, 0 \leq l \leq(n-1)\left{b_{l}\right}, 0 \leq l \leq(n-1), 根\left{p_{r}\right}, 1 \leq r \leq n\left{p_{r}\right}, 1 \leq r \leq n,特征方程的 ,可以是实值和/或复值。假设根是实值且不重复,拉普拉斯变换X(s)表示为
X(s)=ñ(s)(s−p1)(s−p2)⋯(s−pn−1)(s−pn).

信号代写|信号和系统作业代写signals and systems代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。