运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
作为专业的留学生服务机构,Assignmentexpert™多年来已为美国、英国、加拿大、澳洲等留学热门地的学生提供专业的学术服务,包括但不限于论文代写,A作业代写,Dissertation代写,Report代写,Paper代写,Presentation代写,网课代修等等。为涵盖高中,本科,研究生等海外留学生提供辅导服务,辅导学科包括数学,物理,统计,化学,金融,经济学,会计学等全球99%专业科目。写作团队既有专业英语母语作者,也有海外名校硕博留学生,每位写作老师都拥有过硬的语言能力,专业的学科背景和学术写作经验。我们承诺100%原创,100%专业,100%准时,100%满意。
my-assignmentexpert愿做同学们坚强的后盾,助同学们顺利完成学业,同学们如果在学业上遇到任何问题,请联系my-assignmentexpert™,我们随时为您服务!
运筹学代写
In previous sections, the theory, computation procedure, and indeed much of the technique, necessary for the detailed implementation of the simplex method have been established. In this section, we show how this procedure could be presented in a more intuitive and visible way, which is called the simplex method in tableau form.
As usual, let us assume that $\mathbf{B}$ consists of the first $m$ columns of $\mathbf{A}$. Then, the initial simplex tableau takes the form
$$
\left[\begin{array}{c:c}
\mathbf{A} & \mathbf{b} \
-\mathbf{c}^{T} & —
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c:c:c}
\mathbf{B} & \mathbf{D} & \mathbf{b} \
- & — & — \
\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} & \mathbf{c}{\mathbf{D}}^{T} & 0
\end{array}\right]
$$
If the matrix $\mathbf{B}$ is used as a basis, then the corresponding tableau can be equivalently rewritten as
$$
\mathbf{T}=\left[\begin{array}{c:c:c}
\mathbf{I} & \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{D} & \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b} \
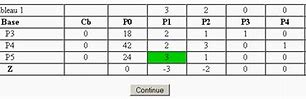
\hdashline- & —{-}^{T}-\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{D} & -\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b} \end{array}\right] $$ which is called the simplex canonical form corresponding to basis matrix $\mathbf{B}$. This transformation can be viewed as: (1) left-multiplying $\mathbf{B}^{-1}$ to the top blocks of the right original tableau, (2) then left-multiplying $\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T}$ to the resulting top blocks and subtracting them from the bottom row. In this canonical form, the constraint matrix corresponding to the current basis becomes the $m \times m$ identity matrix, where (defined in (4.4)), and the far-right column becomes $\overline{\mathbf{a}}{0}=\mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b}$ (defined in (4.3)). Furthermore, the row at the bottom consists of the relative cost coefficients and the negative of the current objective cost. In this section we assume that we begin with a basic feasible solution and that the tableau corresponding to $\mathbf{A x}=\mathbf{b}$ is in the canonical form for this solution. Methods for obtaining this first basic feasible solution, when one is not obvious, 4 The Simplex Method 94 \begin{tabular}{ccccccccccc} $\mathbf{a}{1}$ & $\mathbf{a}{2}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{m}$ & $\mathbf{a}{m+1}$ & $\mathbf{a}{m+2}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{n}$ & $\mathbf{b}$ \
\hline 1 & 0 & $\cdots$ & 0 & $\bar{a}{1(m+1)}$ & $\bar{a}{1(m+2)}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{1 j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{1 n}$ & $\bar{a}{10}$ \ 0 & 1 & & 0 & $\bar{a}{2(m+1)}$ & $\bar{a}{2(m+2)}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{2 j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{2 n}$ & $\bar{a}{10}$
\end{tabular}
在前面的章节中,已经建立了单纯形法详细实施所必需的理论、计算过程以及实际上的大部分技术。在本节中,我们将展示如何以更直观和可见的方式呈现此过程,这称为表格形式的单纯形法。
像往常一样,让我们假设 $\mathbf{B}$ 由 $\mathbf{A}$ 的前 $m$ 列组成。然后,初始单纯形表采用以下形式
$$
\left[\begin{数组}{c:c}
\mathbf{A} & \mathbf{b} \
-\mathbf{c}^{T} & —
\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{c:c:c}
\mathbf{B} & \mathbf{D} & \mathbf{b} \
- & — & — \
\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} & \mathbf{c}{\mathbf{D}}^{T} & 0
\end{数组}\right]
$$
如果以矩阵 $\mathbf{B}$ 为基,则对应的表格可以等价地改写为
$$
\mathbf{T}=\left[\begin{数组}{c:c:c}
\mathbf{I} & \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{D} & \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b} \
\hdashline- & —{-}^{T}-\mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{D} & -\ mathbf{c}{\mathbf{B}}^{T} \mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b} \end{数组}\right] $$ 称为与基矩阵 $\mathbf{B}$ 对应的单纯形规范形式。这种变换可以看成:(1) 将 $\mathbf{B}^{-1}$ 左乘到右侧原始画面的顶部块,(2) 然后左乘 $\mathbf{c}{ \mathbf{B}}^{T}$ 到结果顶部块并从底部行中减去它们。在这种规范形式下,当前基对应的约束矩阵变为$m\times m$单位矩阵,其中(定义在(4.4)中),最右边的列变为$\overline{\mathbf{a}} {0}=\mathbf{B}^{-1} \mathbf{b}$(在 (4.3) 中定义)。此外,底部的行由相对成本系数和当前目标成本的负数组成。 在本节中,我们假设我们从一个基本可行的解决方案开始,并且对应于 $\mathbf{A x}=\mathbf{b}$ 的表格是这个解决方案的规范形式。获得第一个基本可行解的方法,当一个不明显时, 4 单纯形法 94 \开始{表格}{ccccccccccc} $\mathbf{a}{1}$ & $\mathbf{a}{2}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{m}$ & $\mathbf{a}{m +1}$ & $\mathbf{a}{m+2}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\mathbf{a}{n }$ & $\mathbf{b}$ \
\hline 1 & 0 & $\cdots$ & 0 & $\bar{a}{1(m+1)}$ & $\bar{a}{1(m+2)}$ & $\cdots $ & $\bar{a}{1 j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{1 n}$ & $\bar{a}{10}$ \ 0 & 1 & & 0 & $\bar{a}{2(m+1)}$ & $\bar{a}{2(m+2)}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{ a}{2 j}$ & $\cdots$ & $\bar{a}{2 n}$ & $\bar{a}{10}$
\end{表格}
运筹学代考
什么是运筹学代写
运筹学(OR)是一种解决问题和决策的分析方法,在组织管理中很有用。在运筹学中,问题被分解为基本组成部分,然后通过数学分析按定义的步骤解决。
运筹学的过程大致可以分为以下几个步骤:
- 确定需要解决的问题。
- 围绕问题构建一个类似于现实世界和变量的模型。
- 使用模型得出问题的解决方案。
- 在模型上测试每个解决方案并分析其成功。
- 实施解决实际问题的方法。
与运筹学交叉的学科包括统计分析、管理科学、博弈论、优化理论、人工智能和复杂网络分析。所有这些学科的目标都是解决某一个现实中出现的复杂问题或者用数学的方法为决策提供指导。 运筹学的概念是在二战期间由参与战争的数学家们提出的。二战后,他们意识到在运筹学中使用的技术也可以被应用于解决商业、政府和社会中的问题。
运筹学代写的三个特点
所有运筹学解决实际问题的过程中都具有三个主要特征:
- 优化——运筹学的目的是在给定的条件下达到某一机器或者模型的最佳性能。优化还涉及比较不同选项和缩小潜在最佳选项的范围。
- 模拟—— 这涉及构建模型,以便在应用解决方案刀具体的复杂大规模问题之前之前尝试和测试简单模型的解决方案。
- 概率和统计——这包括使用数学算法和数据挖掘来发现有用的信息和潜在的风险,做出有效的预测并测试可能的解决方法。
运筹学领域提供了比普通软件和数据分析工具更强大的决策方法。此外,运筹学可以根据特定的业务流程或用例进行定制,以确定哪些技术最适合解决问题。
运筹学可以应用于各种活动,比如:计划和时间管理(Planning and Time Management),城乡规划(Urban and Rural Planning),企业资源计划(ERP)与供应链管理(Supply Chain Management)等等。 如有代写代考需求,欢迎同学们联系Assignmentexpert™,我们期待为你服务!