如果你也在 怎样代写光学Optics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。光学Optics始于古埃及人和美索不达米亚人对镜片的开发。最早的已知透镜由抛光的水晶制成,通常是石英,最早可追溯到公元前2000年的克里特岛(希腊赫拉克里翁考古博物馆)。罗德岛的镜片可追溯到公元前700年左右,亚述人的镜片也是如此,如尼姆鲁德的镜片。古代罗马人和希腊人将玻璃球装满水来制作透镜。在这些实践发展之后,古希腊和印度的哲学家们发展了关于光和视觉的理论,并在希腊-罗马世界中发展了几何光学。光学这个词来自古希腊词ὀπτική(optikē),意思是 “外观,看”。
光学Optics是研究光的行为和属性的物理学分支,包括它与物质的相互作用以及使用或探测它的仪器的构造。光学通常描述可见光、紫外光和红外光的行为。
my-assignmentexpert™ 光学Optics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的光学Optics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此光学Optics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理physics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的物理physics代写服务。我们的专家在光学Optics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种光学Optics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的光学Optics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 几何光学 Geometrical optics
几何光学,或称射线光学,是一种用射线来描述光的传播的光学模型。几何光学中的射线是一个抽象的概念,有助于近似地描述光线在某些情况下的传播路径。
- 波动光学
在物理学中,波动光学,或称波光学,是光学的一个分支,研究干涉、衍射、偏振和其他几何光学中的射线近似不成立的现象。
- 量子光学
量子光学是原子、分子和光学物理学的一个分支,处理单个光量子(称为光子)如何与原子和分子互动的问题。它包括研究光子的类似粒子的特性。
物理代写|光学作业代写Optics代考|resonant (micro-)cavity
It is pointed out by (Senellart et al. [28]) that a quantum dot “emits a cascade of photons and a single photon is obtained only through spectral filtering of one emission line”. “Bright sources have been obtained using micropillar cavities where the optical field is confined vertically by two distributed Bragg mirrors (DBR) and laterally by the high refractive index contrast. The mode volume is of the order of few $\lambda^{3}$ (wavelength $)^{3}$ and the quality factor can reach values of a few $10^{5} . “$ In micro-cavities, a spontaneously emitted photon can be reflected from DBR gratings and return to stimulate the emission of another photon $-$ thereby creating a small group of identical photons – even for several picoseconds-long exciting pulses.
A quantum dot (QD) placed in a high finesse micro-cavity of a few wavelengths long and excited with a picosecond pulse, can emit a photon spontaneously and be re-excited within the duration of the same pulse. If the photon was reflected towards the QD, stimulated emission may occur due to the small dimensions of the micro-cavity. This will result in two, or more, photons leaving the emitter simultaneously in a group, as well as a reduced lifetime of the excited state of the $\mathrm{QD}$, manifesting itself as a higher decay rate overshadowing the Purcell effect.
“Resonators with small mode volume and high-quality factors $(Q$ factors) enhance the light-matter coupling.” (R. Trivedi et al. [29]). However, a high $Q$-factor indicates a build-up of energy inside the cavity, i.e., a large number of photons do not leave the cavity after being emitted and reaching the output facet for the first time. The early photons emitted by a QD embedded in a resonant cavity of a dielectric structure of distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs), may be reflected towards the excited quantum dot and be amplified, thereby giving rise to time-varying spectral or intensity distributions which emerges from the “single-photon source” in the form of discrete pulses.
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|photons bouncing
The lifetime of the $\mathrm{QD}$ excited state for spontaneous emission inside a micro-cavity can be reduced by stimulated emission induced by resonant photons bouncing back and forth inside the cavity. As a result, temporarily discrete groups of monochromatic photons will build up and be partially emitted. These, however, will be mistaken for spontaneously emitted single photons because of the photodetector’s inability to resolve the number of photons.
Equally, the quantum Rayleigh stimulated emission in a dielectric medium – described in Chapter 2 and $3-$ can coalesce two counterpropagating photons into one group by having one photon excite a dipole, with the other photon capturing the absorbed photon into its radiation mode through stimulated emission.
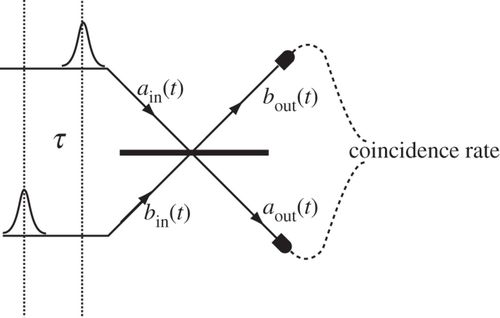
High-finesse optical cavities incorporated in an HBT measurement setup distort the temporally regular sequence of single photons because of multiple internal reflections. The emerging stream may contain groups of a few overlapping photons, e.g. five, which may be unevenly split by a beam splitter and reduced in number through quantum Rayleigh spontaneous emission, so as to generate no coincidence for a zero time-delay in an HBT measurement.
For atoms inside cavities with highly reflective mirrors, the emission rate of discrete photons is much lower than the laser pump rate, e.g., $3.6$ $\mathrm{MHz}$ versus $80 \mathrm{MHz}$ (Loredo et al. [30]). This can be explained by the synchronisation condition between the pumping time-interval $\Delta t_{p u m p}$ and the average exit time-interval of photons $\Delta t_{\text {photongroup }}$, which may be related by the following equality
$$
m \times \Delta t_{p h o t o n ~ g r o u p}=p \times \Delta t_{p u m p}+\tau_{e x}
$$
where $\tau_{e x}$ is the life time of the excited state that decays through stimulated emission. The integers $m$ and $p$ correspond to the respective number of intervals for synchronisation.
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|PHOTONS BOUNCING
A monochromatic pulse-like field profile, derived in Chapter 3 , is represented by a mixed time-frequency structure [19]. A spectral or interference filter may delay the photon’s exit from the output facet by
repeated internal reflections, thereby spreading out the exit times of photons from an input group.
A sequence of groups of photons (pulses containing a low number of monochromatic photons) temporarily separated, can be transformed into a quasi-continuous stream (or wave) of photons by means of interference filters. A high internal reflectivity will retain, repeatedly, more photons inside the cavity than those exiting, for additional round-trip propagations, which will spread out the initial monochromatic pulse. The higher the number of photons inside a dielectric cavity hosting a quantum dot, the more likely it is that the quantum Rayleigh coupling interactions will create larger groups of photons, even for counter – propagating photons. As a result, the triggered clicks at the detector will count a lower number of photon groups rather than individual photons.
When another group of photons enters the interference filter of the DBR, the relative phase will determine the direction of photon- coupling through the phase-dependent quantum Rayleigh conversion of photons (QRCP). As a result, an output continuous wave beam is generated which can serve as an unmodulated or reference wave for interference.
物理代写
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|RESONANT (MICRO-)CAVITY
指出小号和n和一世一世一种r吨和吨一种一世.[28]一个量子点“发射一串光子,一个光子只能通过一条发射线的光谱滤波得到”。“使用微柱腔获得了明亮的光源,其中光场由两个分布式布拉格镜垂直限制D乙R和横向的高折射率对比。模式音量为几λ3 $\lambda^{3}$ (wavelength) ${ }^{3}$ and the quality factor can reach values of a few $10^{5}$.” In micro-cavities, a spontaneously emitted photon can be reflected from DBR gratings and return to stimulate the emission of another photon – thereby creating a small group of identical photons – even for several picoseconds-long exciting pulses. 从而产生一小组相同的光子——即使是几个皮秒长的激发脉冲。
一个量子点问D放置在几个波长长的高精细微腔中并用皮秒脉冲激发,可以自发发射光子并在同一脉冲的持续时间内被重新激发。如果光子被反射到 QD,由于微腔的小尺寸,可能会发生受激发射。这将导致两个或更多光子同时离开发射器,并缩短激发态的寿命。问D,表现为更高的衰减率掩盖了珀塞尔效应。
“具有小模式体积和高质量因子的谐振器(问因素)增强光与物质的耦合。”R.吨r一世v和d一世和吨一种一世.[29]. 然而,一个高问-因子表示腔内能量的积累,即大量光子在发射并首次到达输出端面后不会离开腔。嵌入分布式布拉格反射器介电结构的谐振腔中的 QD 发射的早期光子D乙Rs,可能会被反射到激发的量子点并被放大,从而产生从“单光子源”以离散脉冲形式出现的随时间变化的光谱或强度分布。
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|PHOTONS BOUNCING
的寿命问D微腔内自发发射的激发态可以通过共振光子在腔内来回反弹所引起的受激发射来降低。结果,临时离散的单色光子组将累积并部分发射。然而,这些将被误认为是自发发射的单光子,因为光电探测器无法分辨光子的数量。
同样,介电介质中的量子瑞利受激发射——在第 2 章和3−可以通过让一个光子激发偶极子将两个反向传播的光子合并为一组,而另一个光子通过受激发射将吸收的光子捕获为其辐射模式。
由于多次内部反射,HBT 测量装置中包含的高精细光学腔会扭曲单光子的时间规则序列。出现的流可能包含几个重叠光子的组,例如五个,它们可能被分束器不均匀地分裂并通过量子瑞利自发发射减少数量,以便在 HBT 测量中产生零时延不发生巧合.
对于腔内具有高反射镜的原子,离散光子的发射率远低于激光泵浦率,例如,3.6 米H和相对80米H和 大号这r和d这和吨一种一世.[30]. 这可以通过泵送时间间隔之间的同步条件来解释Δ吨p你米p和光子的平均退出时间间隔Δ吨光子群 , 这可能与以下等式有关
米×Δ吨pH这吨这n Gr这你p=p×Δ吨p你米p+τ和X
在哪里τ和X是通过受激发射衰减的激发态的寿命。整数米和p对应于同步间隔的相应数量。
物理代写|光学作业代写OPTICS代考|PHOTONS BOUNCING
在第 3 章中推导出的单色脉冲类场分布由混合时频结构表示19. 光谱或干涉滤光片可能会延迟光子从输出面的退出时间
重复的内部反射,从而扩展光子从输入组的退出时间。
一系列光子组p你一世s和sC这n吨一种一世n一世nG一种一世这在n你米b和r这F米这n这CHr这米一种吨一世CpH这吨这ns暂时分离,可以转化为准连续流这r在一种v和光子通过干涉滤光片。高内部反射率将重复地保留腔内的光子多于退出的光子,用于额外的往返传播,这将分散初始单色脉冲。承载量子点的电介质腔内的光子数量越多,量子瑞利耦合相互作用就越有可能产生更大的光子群,即使对于反向传播的光子也是如此。因此,探测器上触发的咔嗒声将计数较少数量的光子组,而不是单个光子。
当另一组光子进入DBR的干涉滤光片时,相对相位将通过光子的相位相关量子瑞利转换决定光子耦合的方向问RC磷. 结果,产生了一个输出连续光束,该光束可以用作干扰的未调制波或参考波。

物理代写|光学作业代写Optics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。