如果你也在 怎样代写复分析complex analysis这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。复分析complex analysis传统上称为复变函数理论,是数学分析的一个分支,研究复数函数。它对数学的许多分支都有帮助,包括代数几何、数论、分析组合学、应用数学;以及物理学。数论、分析组合学、应用数学;以及物理学,包括流体力学、热力学,特别是量子力学等分支。推而广之,复数分析在工程领域也有应用,如核、航天、机械和电气工程。
复分析complex analysis复数分析的核心工具之一是线积分。正如Cauchy积分定理所指出的那样,在封闭路径所包围的区域内到处都是全形函数,其围绕封闭路径的线积分总是为零。这样一个全形函数在圆盘内的数值可以通过圆盘边界上的路径积分来计算(如考奇积分公式所示)。复平面内的路径积分经常被用来确定复杂的实积分,这里适用于残差理论等(。一个函数的 “极点”(或孤立的奇点)是指该函数的值变得无界,或 “爆炸 “的一个点。如果一个函数有这样一个极点,那么人们可以在那里计算函数的残差,这可以用来计算涉及该函数的路径积分;这就是强大的残差定理的内容。
my-assignmentexpert™ 复分析complex analysis作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的复分析complex analysis作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此复分析complex analysis作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的复分析complex analysis代写服务。我们的专家在数学mathematics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种复分析complex analysis相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的复分析complex analysis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
数学代写|复分析代写complex analysis代考|Möbius-type group.
The bilinear transforms set is a group with respect to the functions composition. This group is called Möbius-type group.
Proof. $T_{j}$ is a bilinear transform $\Leftrightarrow \operatorname{det}\left(\begin{array}{c}a_{j} b_{j} \ c_{j} d_{j}\end{array}\right) \neq 0$. The determinant of the $T_{1} \circ T_{2}$ corresponding matrix is det $T_{1} \cdot \operatorname{det} T_{2}$, hence the matrix of $T_{j}$ belongs to the group $G L_{2}(\mathbb{C})$. From this remark, we deduce that the set of all bilinear transforms represent a group with respect to the composition, which is a subgroup $G L_{2}(\mathbb{C})$. We call that the bilinear transformation group as it is the holomorphic image of $G L_{2}(\mathbb{C})$.
Remark 2.7.1. An arbitrary bilinear transform remains unchanged if we multiply all its coefficients by the same complex number $k, k \neq 0$. That is,
$$
\frac{a z+b}{c z+d}=\frac{\frac{a}{k} z+\frac{b}{k}}{\frac{c}{k} z+\frac{d}{k}}, \quad \forall z \in \mathbb{C} \backslash\left{-\frac{d}{c}\right} .
$$
The constant $k$ may be chosen such that $a d-b c=1$.
数学代写|复分析代写COMPLEX ANALYSIS代考|Those bilinear transforms
Those bilinear transforms with $a, b, c, d \in \mathbb{R}$ and $a d-b c=1$, represent the subgroup of the Möbius-type group that maps the upper half-plane into the upper half-plane.
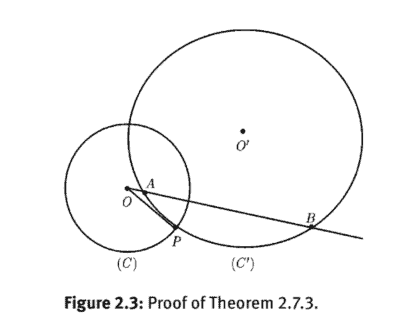
Proof. According to Theorem 2.6.5, if $a, b, c, d \in \mathbb{R}$ and $a d-b c>0$, the transform $T z=$ $\frac{a z+b}{c z+d}$ maps the upper half-plane into the upper half-plane. Dividing all its coefficients by $\sqrt{a d-b c}$, and changing the notation, we obtain $a d-b c=1$.
Conversely, suppose that $T$ maps the upper half-plane into the upper half-plane. Hence, we will deduce that $T z \in \mathbb{R}$ if $z \in \mathbb{R}$, so $T$ can be written in such a form that $a, b, c, d \in \mathbb{R}$.
Case I: $c d=0$
- If $d=0$, then $T z=\frac{a}{c}+\frac{b}{c z} \in \mathbb{R}$.
Further,
$$
z \in \mathbb{R}, \quad z \rightarrow \infty \Rightarrow \frac{a}{c} \in \mathbb{R} \quad \text { and } \quad z=1 \Rightarrow \frac{b}{c} \in \mathbb{R} .
$$ - If $c=0$, then $T z=\frac{a}{d} z+\frac{b}{d}$.
Further,
$$
z=0 \Rightarrow \frac{b}{d} \in \mathbb{R} \quad \text { and } \quad z=1 \Rightarrow \frac{a}{d} \in \mathbb{R} .
$$
Case II: $c d \neq 0$.
In this case, we obtain
$$
z \in \mathbb{R}, \quad z \rightarrow \infty \Rightarrow \frac{a}{c} \in \mathbb{R} \quad \text { and } \quad z=0 \Rightarrow \frac{b}{d} \in \mathbb{R},
$$
hence
$$
\frac{a}{c}-\frac{b}{d}=\frac{a d-b c}{c d} \in \mathbb{R}
$$
From here, we have
$$
T z=\frac{a}{c}+\frac{\frac{b c-a d}{c d}}{\frac{c}{d} z+1} \in \mathbb{R}, \quad \text { if } z \in \mathbb{R} \Rightarrow \frac{c}{d} z+1 \in \mathbb{R}, \quad \text { if } z \in \mathbb{R} \Rightarrow \frac{c}{d} \in \mathbb{R}
$$
Hence, if $T$ maps $\mathbb{R}$ into $\mathbb{R}$, the coefficients $a, b, c$ and $d$ may be chosen to be real numbers. From here, according to Theorem 2.6.5 we obtain that $a d-b c>0$.
复分析代写
数学代写|复分析代写COMPLEX ANALYSIS代考|MÖBIUS-TYPE GROUP.
双线性变换集是关于函数组合的一组。该群称为莫比乌斯群。
证明。吨j是双线性变换⇔这(一种jbj Cjdj)≠0. 的决定因素吨1∘吨2对应的矩阵是 det吨1⋅这吨2,因此矩阵吨j属于组G大号2(C). 从这句话中,我们推断出所有双线性变换的集合代表了一个关于组合的组,它是一个子组G大号2(C). 我们称其为双线性变换群,因为它是G大号2(C).
备注 2.7.1。如果我们将其所有系数乘以相同的复数,则任意双线性变换保持不变到,到≠0. 那是,
\frac{a z+b}{c z+d}=\frac{\frac{a}{k} z+\frac{b}{k}}{\frac{c}{k} z+\frac{d }{k}}, \quad \forall z \in \mathbb{C} \backslash\left{-\frac{d}{c}\right} 。\frac{a z+b}{c z+d}=\frac{\frac{a}{k} z+\frac{b}{k}}{\frac{c}{k} z+\frac{d }{k}}, \quad \forall z \in \mathbb{C} \backslash\left{-\frac{d}{c}\right} 。
常数到可以这样选择一种d−bC=1.
数学代写|复分析代写COMPLEX ANALYSIS代考|THOSE BILINEAR TRANSFORMS
那些双线性变换与一种,b,C,d∈R和一种d−bC=1, 表示将上半平面映射到上半平面的莫比乌斯型群的子群。
证明。根据定理 2.6.5,如果一种,b,C,d∈R和一种d−bC>0, 变换吨和= 一种和+bC和+d将上半平面映射到上半平面。将其所有系数除以一种d−bC,并改变符号,我们得到一种d−bC=1.
相反,假设吨将上半平面映射到上半平面。因此,我们将推断吨和∈R如果和∈R, 所以吨可以写成这样的形式一种,b,C,d∈R.
案例一:Cd=0
- 如果d=0, 然后吨和=一种C+bC和∈R.
更远,
和∈R,和→∞⇒一种C∈R 和 和=1⇒bC∈R. - 如果C=0, 然后吨和=一种d和+bd.
更远,
和=0⇒bd∈R 和 和=1⇒一种d∈R.
案例二:Cd≠0.
在这种情况下,我们得到
和∈R,和→∞⇒一种C∈R 和 和=0⇒bd∈R,
因此
一种C−bd=一种d−bCCd∈R
从这里,我们有
吨和=一种C+bC−一种dCdCd和+1∈R, 如果 和∈R⇒Cd和+1∈R, 如果 和∈R⇒Cd∈R
因此,如果吨地图R进入R, 系数一种,b,C和d可以选择为实数。从这里,根据定理 2.6.5 我们得到一种d−bC>0.

数学代写|复分析代写complex analysis代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。