如果你也在 怎样代写电动力学electrodynamics这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。电动力学electrodynamics是物理学的一个分支,涉及到对电磁力的研究,这是一种发生在带电粒子之间的物理作用。电磁力是由电场和磁场组成的电磁场所承载的,它是诸如光这样的电磁辐射的原因。它与强相互作用、弱相互作用和引力一起,是自然界的四种基本相互作用(通常称为力)之一。
电动力学electrodynamics电磁现象是以电磁力来定义的,有时也称为洛伦兹力,它包括电和磁,是同一现象的不同表现形式。电磁力在决定日常生活中遇到的大多数物体的内部属性方面起着重要作用。原子核和其轨道电子之间的电磁吸引力将原子固定在一起。电磁力负责原子之间形成分子的化学键,以及分子间的力量。电磁力支配着所有的化学过程,这些过程是由相邻原子的电子之间的相互作用产生的。电磁学在现代技术中应用非常广泛,电磁理论是电力工程和电子学包括数字技术的基础。
my-assignmentexpert™ 电动力学electrodynamics作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的电动力学electrodynamics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此电动力学electrodynamics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在物理physics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的电动力学electrodynamics代写服务。我们的专家在物理physics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种电动力学electrodynamics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的电动力学electrodynamics及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
物理代写|电动力学作业代electrodynamics代考|Electromagnetic Induction
Apart from being the first to introduce the concept of ‘magnetic field lines’, Michael Faraday conducted numerous experiments on the response of electrical circuits in presence of time-varying magnetic fields. The time-varying magnetic fields would be produced either by moving a magnet or abruptly turning off steady current in a wire or by moving a current carrying wire near a ‘pick-up’ coil. The transient response in the ‘pick-up’ coil would be detected by a galvanometer connected to the coil. Faraday observed that transient current flowed in the pick-up coil whenever there was a time-varying magnetic field either due to change of source current or due to relative motion between the sources producing non-uniform magnetic field (such as magnets or current carrying wires) and the pick-up coil. He concluded that the transient current flow was due to changing magnetic flux linked with the pick-up coil. More precisely, the time-varying magnetic flux generates an ‘electromotive force’ $\mathcal{E}$ (the line integral of the electric field around the coil circuit) which makes the current flow. Faraday’s conclusion can be neatly expressed using the following mathematical description:
$$
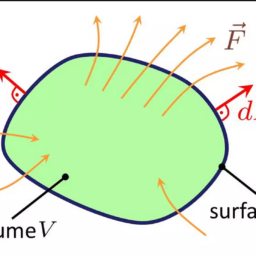
\mathcal{E}=\oint_{\mathcal{C}} \mathbf{E}^{\prime} \cdot \mathbf{d l}=-k \frac{d}{d t} \int_{\partial V} \mathbf{B} \cdot \hat{\mathbf{n}} d a
$$
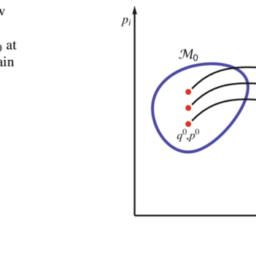
The left-hand side of the above equation is the electromotive force $\mathcal{E}$ expressed as the closed line integral around the pick-up coil $\oint_{\mathcal{C}} \mathbf{E}^{\prime} \cdot \mathbf{d l}$, while the right-hand side is the total time derivative of the magnetic flux through any open surface attached to the coil (Fig. 1.6). The minus sign is due to Lenz’s law which states that the induced current is in such a direction as to oppose the change of magnetic flux, while $k$ is a constant of proportionality depending on the choice of units.
物理代写|电动力学作业代electrodynamics代考|Energy Stored in Magnetic Field
A steady current distribution produces a magnetic field, according to Ampere’s law. On the other hand, Faraday’s law says that when a magnetic field is changed (or the current distribution which produces the magnetic field), it sets up an electromotive force that tries to oppose the change. Whenever a steady current is being set up, it has to go through a transient state starting from zero current to reach the final steady state. In the process, the source establishing the steady current has to do some work against the ‘induced’ electromotive force $\mathcal{E}$ (also called the back emf), which will be stored as energy in the steady current distribution, or, alternatively, in the magnetic field produced. The total energy stored in the magnetic field is the total work done to establish it.
The work done against the back emf to get a steady current $I$ going in a circuit is given by
$$
\frac{d W}{d t}=-\mathcal{E} I=\frac{I}{c} \frac{d \phi}{d t}
$$
Here, $\phi=\int_{\mathcal{S}} \mathbf{B} \cdot$ da is the magnetic flux linked with the circuit. The flux $\phi$ is proportional to the current so that $\phi=L I$. The constant of proportionality $L$ is called the self inductance, which depends solely on the geometry of the circuit. The total work done $W$, starting from zero initial current to final current $I$, is obtained on integrating Eq. (1.80)
$$
W=\frac{1}{2 c} L I^{2}
$$
Now let us generalize the expression dealing with a line current to surface and volume currents. We note that for line current $I$,
$$
\phi=L I=\int_{\mathcal{S}} \mathbf{B} \cdot \hat{\mathbf{n}} d a=\int_{\partial V} \nabla \times \mathbf{A} \cdot \hat{\mathbf{n}} d a=\oint \mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{d} \mathbf{l}
$$
Therefore,
$$
W=\frac{1}{2 c} I(L I)=\frac{1}{2 c} I \oint \mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{d} \mathbf{l}=\frac{1}{2 c} \oint(\mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{I}) d l
$$
The above expression readily generalizes to volume current $\mathbf{J}$ as
$$
W=\frac{1}{2 c} \int_{V}(\mathbf{A} \cdot \mathbf{J}) d^{3} x
$$
The integration is over the volume $V$ occupied by the current distribution. Now we replace $\mathbf{J}$ by magnetic field using Ampere’s law, $\nabla \times \mathbf{B}=\frac{4 \pi}{c} \mathbf{J}$.
$$
W=\frac{1}{8 \pi} \int_{V} \mathbf{A} \cdot(\nabla \times \mathbf{B}) d^{3} x
$$
电动力学代写
物理代写|电动力学作业代ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
除了第一个引入“磁场线”的概念外,迈克尔法拉第还对电路在时变磁场中的响应进行了许多实验。随时间变化的磁场可以通过移动磁铁或突然关闭电线中的稳定电流或通过移动“拾取”线圈附近的载流电线来产生。“拾取”线圈中的瞬态响应将由连接到线圈的检流计检测。法拉第观察到,每当由于源电流的变化或由于产生不均匀磁场的源之间的相对运动而产生随时间变化的磁场时,瞬态电流就会流入拾波线圈s你CH一种s米一种Gn和吨s这rC你rr和n吨C一种rr是一世nG在一世r和s和拾音线圈。他得出的结论是,瞬态电流是由于与拾波线圈相连的磁通量发生变化造成的。更准确地说,随时间变化的磁通量会产生“电动势”和 吨H和一世一世n和一世n吨和Gr一种一世这F吨H和和一世和C吨r一世CF一世和一世d一种r这你nd吨H和C这一世一世C一世rC你一世吨这使得电流流动。法拉第的结论可以用以下数学描述巧妙地表达:
和=∮C和′⋅d一世=−到dd吨∫∂五乙⋅n^d一种
上式左边是电动势和表示为拾波线圈周围的闭合线积分∮C和′⋅d一世,而右侧是通过连接到线圈的任何开放表面的磁通量的总时间导数F一世G.1.6. 负号是由于楞次定律,它指出感应电流的方向与磁通量的变化相反,而到是一个比例常数,取决于单位的选择。
物理代写|电动力学作业代ELECTRODYNAMICS代考|ENERGY STORED IN MAGNETIC FIELD
根据安培定律,稳定的电流分布会产生磁场。另一方面,法拉第定律说,当磁场改变时这r吨H和C你rr和n吨d一世s吨r一世b你吨一世这n在H一世CHpr这d你C和s吨H和米一种Gn和吨一世CF一世和一世d,它建立了一个试图反对变化的电动势。每当建立稳定电流时,它必须经历从零电流开始的瞬态才能达到最终稳定状态。在此过程中,建立稳定电流的源必须对“感应”电动势做一些工作和 一种一世s这C一种一世一世和d吨H和b一种C到和米F,它将作为能量存储在稳定的电流分布中,或者存储在产生的磁场中。存储在磁场中的总能量是建立它所做的总功。
对反电动势所做的工作以获得稳定的电流一世进入电路由下式给出
d在d吨=−和一世=一世Cdφd吨
这里,φ=∫小号乙⋅da 是与电路相连的磁通量。通量φ与电流成正比,因此φ=大号一世. 比例常数大号称为自感,它仅取决于电路的几何形状。完成的总工作在,从零初始电流开始到最终电流一世, 是通过积分方程获得的。1.80
在=12C大号一世2
现在让我们将处理线电流的表达式推广到表面和体积电流。我们注意到,对于线电流一世,
φ=大号一世=∫小号乙⋅n^d一种=∫∂五∇×一种⋅n^d一种=∮一种⋅d一世
所以,
在=12C一世(大号一世)=12C一世∮一种⋅d一世=12C∮(一种⋅一世)d一世
上面的表达式很容易推广到体积电流Ĵ作为
在=12C∫五(一种⋅Ĵ)d3X
整合超过音量五被电流分布占据。现在我们替换Ĵ通过使用安培定律的磁场,∇×乙=4圆周率CĴ

物理代写|电动力学作业代写electrodynamics代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。