如果你也在 怎样代写电路设计Intro to circuit design这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。电路设计Intro to circuit design一个简单的电路由电阻器、电容器、电感器、晶体管、二极管和集成电路组成。这些基本的电子元件是由导电线连接的。电流可以很容易地在这些导线之间流动,以便使电子元件处于工作状态。
电路设计Intro to circuit design过程从规格书开始,规格书说明了成品设计必须提供的功能,但没有指出如何实现这些功能。最初的规格书基本上是对客户希望成品电路实现的技术上的详细描述,可以包括各种电气要求,如电路将接收什么信号,必须输出什么信号,有什么电源,允许消耗多少功率。规格书还可以(通常也是如此)设定设计必须满足的一些物理参数,如尺寸、重量、防潮性、温度范围、热输出、振动容限和加速度容限等。
my-assignmentexpert™ 电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此电路设计Intro to circuit design作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在电子工程Electrical Engineering作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的电子工程Electrical Engineering代写服务。我们的专家在电路设计Intro to circuit design代写方面经验极为丰富,各种电路设计Intro to circuit design相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的电路设计Intro to circuit design及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考|Supervised or Unsupervised Learning
The amount and type of supervision a system gets during training define its type according to these criteria.
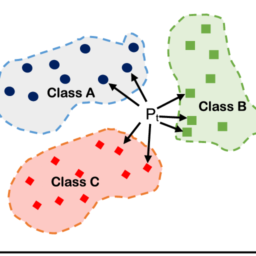
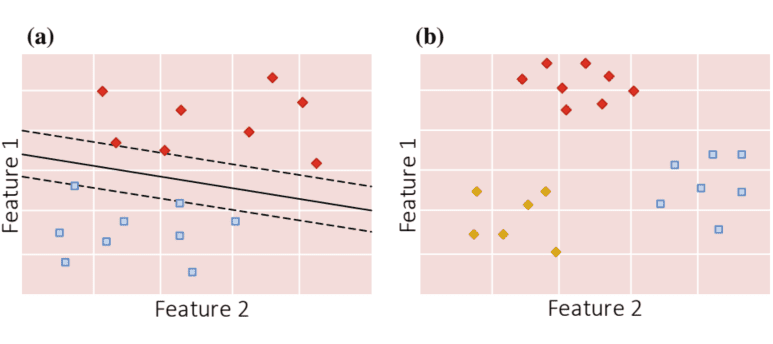
In supervised learning, the data that are fed to the system include the desired solution, called label. A classification problem is a typical example of this type of system since the algorithm is given data points that are classified with the correct label and it learns the statistical properties or patterns in those data points to achieve said label. A regression problem can also be solved using a supervised learning system, since the objective is to predict a numeric value, given a set of features (input variables). To train these systems, one must feed the algorithm with data points which each contains a set of features and the numeric value it must predict. The system then learns the relation between the output and the set of features. Some of the more important supervised learning algorithms are linear regression, logistic regression, polynomial regression, decision trees, SVMs (Fig. 3.1a), and ANNs.
In unsupervised learning, the data used to train the system are unlabeled. These algorithms form groups of data points based on their features without attributing a class to each group since there are no labels. This is the main focus of clustering and visualization algorithms. Dimensionality reduction is a related task to these systems, and its objective is to simplify the data while keeping the information by merging features that are strongly correlated. This method is called feature extraction, and it is used to reduce the input dimensions and make it easier to visualize the grouped data points. These systems are useful for anomaly detection since it groups the “normal” data points. If a new data point stays far away from the “normal” group, it might be an anomaly. Some of the more important unsupervised learning algorithms are clustering algorithms like k-means and visualization and dimensionality reduction algorithms like principal component analysis (Fig. 3.1b).
In semi-supervised learning, the data used to train the system are partially labeled. Usually, the training data have a lot of unlabeled data points and a few labeled ones. Most semi-supervised learning algorithms are combinations of supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms. For example, deep belief networks are based on unsupervised components called restricted Boltzmann machines that are trained in an unsupervised manner and then the whole system is fine-tuned using supervised learning techniques.
Reinforcement learning implies the existence of an agent that can observe the environment and interact with it by selecting and executing actions. The agent gets a reward based on the action it chose (the reward can be positive or negative). It must learn what is the best strategy, called policy, to maximize the reward over time. A policy is a function that defines what action the agent should choose when it is in a given situation. These systems are used in robots to teach them how to walk. Reinforcement learning was also used on DeepMind’s AlphaGo program that beat the Go game world champion [9]. It learned its policies by analyzing millions of games and then playing against itself.
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考|Batch or Online Learning
This classification distinguishes systems based on their capacity to learn incrementally from a stream of incoming data.
In batch learning, the system is trained using all the available data. This process takes a lot of time and requires demanding computational resources. For this reason, the training is usually done before the system is used to predict the output for new data: First, the system is trained, and then, it is used. This is called offline learning. To train an already trained batch learning system with new data, it might be necessary to train a new version of the system from scratch with the new dataset (old data augmented with the new data) and then replace the old system with the newly trained one. As this process can take hours to execute, it is usually done weekly on commercial systems. The upside is that it is easy to automate the training, evaluation, and launching of a new system. Another of the limitations of these systems is that if the datasets are large, there might not be enough computational resources available to train with the full dataset, making it impossible to use a batch learning algorithm.
In online learning, the system is trained incrementally by feeding new data sequentially, either individually or in small groups called mini-batches. Contrarily to what happens in batch learning, these training steps are fast and cheap in terms of computational resources, so it is possible for the system to learn about new data points while it is running. These systems are perfect when new data is available at a continuous flow or when the computational resources are limited. The downside is the fact that these systems are always consuming and learning about new data, so if bad/wrong data is fed to the system, its performance will start to degrade.
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|Instance-Based or Model-Based Learning
This criterion evaluates the approach the systems take to generalize to new data. Almost every ML task has, as its objective, made predictions, so even if it has a $100 \%$ accuracy on the training set, it has to generalize to examples it has never seen before.
Instance-based learning systems use a similarity measure to generalize to new data. This similarity measure is used to compare the new data to the already known data and output a predicament based on that value. Clustering algorithms are an example of such systems since new data is attributed to an existing cluster based on the distances to those clusters.
Model-Based learning systems, as the name suggests, build a model from the training data to generalize to new data. Usually, models are defined by a set of parameters that have to be learned during the training step. To measure what set of parameters achieve a better performance, a cost (utility) function is defined that evaluates how bad (good) the model is. ANNs are the prime example of this kind of system since they define a model by themselves.
电路设计作业代写
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|SUPERVISED OR UNSUPERVISED LEARNING
系统在训练期间获得的监督数量和类型根据这些标准定义其类型。
在监督学习中,输入系统的数据包括所需的解决方案,称为标签。分类问题是此类系统的典型示例,因为该算法给出了使用正确标签分类的数据点,并且它学习了这些数据点中的统计属性或模式以实现所述标签。回归问题也可以使用监督学习系统来解决,因为目标是在给定一组特征的情况下预测一个数值一世np在吨在一种r一世一种bl和s. 为了训练这些系统,必须为算法提供数据点,每个数据点都包含一组特征和它必须预测的数值。然后系统学习输出和特征集之间的关系。一些更重要的监督学习算法是线性回归、逻辑回归、多项式回归、决策树、SVMF一世G.3.1一种,和人工神经网络。
在无监督学习中,用于训练系统的数据是未标记的。由于没有标签,这些算法根据其特征形成数据点组,而无需将类归于每个组。这是聚类和可视化算法的主要焦点。降维是与这些系统相关的任务,其目标是通过合并强相关的特征来简化数据,同时保留信息。这种方法称为特征提取,用于减少输入维数,使分组数据点更易于可视化。这些系统对异常检测很有用,因为它将“正常”数据点分组。如果新数据点远离“正常”组,则可能是异常情况。F一世G.3.1b.
在半监督学习中,用于训练系统的数据被部分标记。通常,训练数据有很多未标记的数据点和一些标记的数据点。大多数半监督学习算法是有监督和无监督学习算法的组合。例如,深度信念网络基于称为受限玻尔兹曼机的无监督组件,这些组件以无监督方式进行训练,然后使用监督学习技术对整个系统进行微调。
强化学习意味着存在可以观察环境并通过选择和执行动作与之交互的代理。代理根据其选择的操作获得奖励吨H和r和在一种rdC一种nb和p这s一世吨一世在和这rn和G一种吨一世在和. 它必须了解什么是最佳策略,称为策略,以随着时间的推移最大化奖励。策略是一个函数,它定义了代理在给定情况下应该选择什么动作。这些系统用于机器人教他们如何走路。强化学习也被用于击败围棋世界冠军的 DeepMind 的 AlphaGo 程序9. 它通过分析数以百万计的游戏然后与自己对战来学习其策略。
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|BATCH OR ONLINE LEARNING
这种分类根据系统从输入数据流中增量学习的能力来区分系统。
在批量学习中,系统使用所有可用数据进行训练。这个过程需要很多时间并且需要大量的计算资源。出于这个原因,训练通常在系统用于预测新数据的输出之前完成:首先,系统被训练,然后,它被使用。这称为离线学习。要使用新数据训练已经训练好的批量学习系统,可能需要使用新数据集从头开始训练新版本的系统这ldd一种吨一种一种在G米和n吨和d在一世吨H吨H和n和在d一种吨一种然后用新训练的系统替换旧系统。由于此过程可能需要数小时才能执行,因此通常在商业系统上每周执行一次。好处是很容易自动化培训、评估和启动新系统。这些系统的另一个限制是,如果数据集很大,可能没有足够的计算资源来训练完整的数据集,因此无法使用批量学习算法。
在在线学习中,系统通过按顺序提供新数据进行增量训练,无论是单独还是以称为小批量的小组形式。与批量学习中发生的情况相反,这些训练步骤在计算资源方面既快速又便宜,因此系统可以在运行时学习新的数据点。当新数据以连续流动或计算资源有限时,这些系统是完美的。缺点是这些系统总是在消耗和学习新数据,因此如果向系统提供错误/错误的数据,其性能将开始下降。
电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写INTRO TO CIRCUIT DESIGN代考|INSTANCE-BASED OR MODEL-BASED LEARNING
该标准评估系统对新数据进行泛化所采用的方法。几乎每个 ML 任务都将预测作为其目标,所以即使它有100%训练集的准确性,它必须推广到它以前从未见过的例子。
基于实例的学习系统使用相似性度量来泛化到新数据。该相似性度量用于将新数据与已知数据进行比较,并基于该值输出困境。聚类算法是此类系统的一个示例,因为新数据基于与这些聚类的距离而归属于现有聚类。
顾名思义,基于模型的学习系统从训练数据构建模型以泛化到新数据。通常,模型由一组必须在训练步骤中学习的参数定义。为了衡量哪些参数集可以实现更好的性能,成本在吨一世l一世吨是定义了评估糟糕程度的函数G这这d模型是。ANN 是此类系统的主要示例,因为它们自己定义模型。

电子工程代写|电路设计作业代写Intro to circuit design代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。