如果你也在 怎样代写有机化学organic chemistry这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。有机化学organic chemistry是化学的一个分支,研究含有碳-碳共价键的有机化合物的结构、性质和反应。对性质的研究包括物理和化学性质,以及对化学反应性的评估,以了解其行为。有机反应的研究包括天然产品、药物和聚合物的化学合成,以及在实验室和通过理论(in silico)研究单个有机分子。
有机化学organic chemistry研究的化学品范围包括碳氢化合物(只含碳和氢的化合物)以及以碳为基础但也含有其他元素的化合物,特别是氧、氮、硫、磷(包括在许多生化制品中)和卤素。有机金属化学是研究含有碳-金属键的化合物。此外,当代研究的重点是涉及其他有机金属的有机化学,包括镧系元素,但特别是过渡金属锌、铜、钯、镍、钴、钛和铬。
my-assignmentexpert™ 有机化学organic chemistry作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的有机化学organic chemistry作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此有机化学organic chemistry作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在化学Chemical作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的化学Chemical代写服务。我们的专家在有机化学organic chemistry代写方面经验极为丰富,各种有机化学organic chemistry相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的有机化学organic chemistry及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考|A Cycloaddition Forming Three-Membered Rings
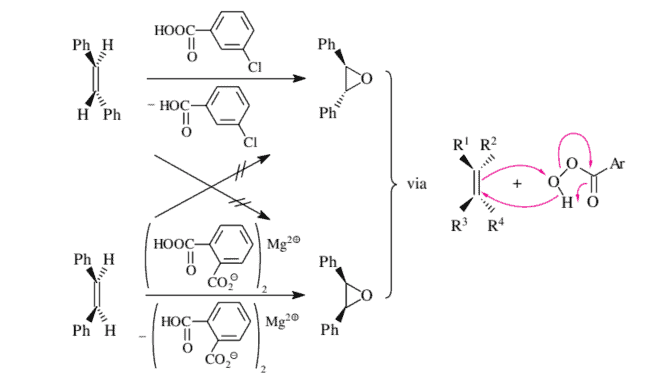
Cycloadditions are ring-forming addition reactions in which the product, the so-called cycloadduct, possesses an empirical formula that corresponds to the sum of the empirical formulas of the starting material and the reagent. All one-step cycloadditions take place with cis selectivity. Three-, four-, five-, or six-membered but not larger rings can be produced by cycloadditions to monoolefins (Figure 3.10).
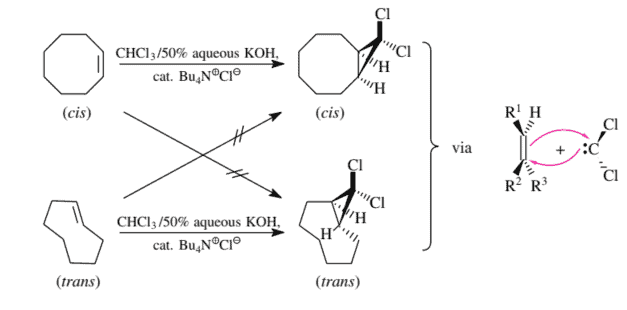
You will become familiar with selected cycloadditions that lead to four-, five-, or sixmembered rings in Chapter 12. Two more cycloadditions, which are also oxidations, will be examined in Chapter 14, which deals with oxidations and reductions: the ozonolysis reaction can be found in Section 14.3.2 (as well as in Section 12.5.5) and the cisvic dihydroxylation with $\mathrm{OsO}_{4}$ can be found in Section 14.3.2. Here we discuss only the addition of dichlorocarbene to olefins as an example of a cis addition of the cycloaddition type (Figure 3.11).
Dichlorocarbene cannot be isolated, but it can be produced in the presence of an olefin and then reacted with it immediately. The best dichlorocarbene precursor is the anion $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{C}^{-}$, which easily eliminates a chloride ion. This anion is obtained from $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{CH}$ and fairly strong bases. The $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ion is sufficiently basic for effecting this deprotonation provided that it comes into contact with the $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{CH}$ molecules. Consequently, when chloroform is stirred with potassium hydroxide solution, there is only moderate conversion into the anion $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{C}^{-}$. This is because $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{CH}$ and aqueous $\mathrm{KOH}$ are not miscible so that $\mathrm{KOH}$ cannot efficiently migrate from the aqueous phase into the $\mathrm{Cl}{3} \mathrm{CH}$. The solvation of the $\mathrm{K}^{+}$and $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ions in the organic phase would be far too low.
The transfer of only the $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ions into the chloroform, however, succeeds very well in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst. The most frequently used phase transfer catalysts are tetraalkylammonium chlorides or tetraalkylammonium hydrogensulfates. With a large excess of $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ions, they give the corresponding tetraalkylammonium hydroxides in an equilibrium reaction. These dissolve in chloroform because the cation is so large that it requires practically no solvation. Via the Coulomb attraction, these cations pull the nonsolvatable $\mathrm{OH}^{-}$ions with them into the chloroform phase.
化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考|Additions to C“C Double Bonds That Are Related to Cycloadditions and Form Three-Membered Rings, Too
In contrast to the dichlorocyclopropanations from Section 3.3.1, the reactions discussed in this section are not cycloadditions in a strict sense. The reason is that the empirical formula of the addition products presented here is not equal to the sum of the empirical formulas of the reaction partners. Accordingly, the reaction products here are not cycloadducts in the strict sense.
The addition of the Simmons-Smith reagent to olefins leads in a single step to chlorine-free cyclopropanes (Figure 3.12). This addition also runs stereoselectively and stereospecifically. A Simmons-Smith reagent can be produced from diiodomethane and $\mathrm{Zn} / \mathrm{Cu}$ couple, which in turn is produced from zinc dust and catalytic amounts of $\mathrm{CuSO}{4}, \mathrm{CuCl}{2}$, or $\mathrm{Cu}(\mathrm{OAc}){2}$. This Simmons-Smith reagent is usually assigned the structural formula $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI}$. This species, however, is subject to an equilibrium similar to the one that is known as the Schlenk equilibrium for Grignard compounds (cf. Figure 8.1):
$$
2 \mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{Zn}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{ZnI}{2}
$$
In the Simmons-Smith reaction, as formulated in Figure 3.12, it has seemingly been clarified that the attacking species is $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI}$ rather than $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{Zn}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{I}$, which is in equilibrium with it in small amounts. A reagent that has properties quite similar to those of the actual Simmons-Smith reagent (but is advantageously produced in a homogeneous reaction) results from a halogen/metal exchange between diiodomethane and $\mathrm{ZnEt}{2}$. It can be written as $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{ZnEt}$.
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|cis-Hydration of Olefins via the Hydroboration/Oxidation/Hydrolysis Reaction Sequence
In monoborane $\left(\mathrm{BH}{3}\right)$, monoalkylboranes $\mathrm{RBH}{2}$, or dialkylboranes $\mathrm{R}{2} \mathrm{BH}$ there is only an electron sextet at the boron atom. In comparison to the more stable electron octet, the boron atom thus lacks two valence electrons. It “obtains” them by bonding with a suitable electron pair donor. When no better donor is available, the bonding electron pair of the B-H bond of a second borane molecule acts as the donor so that a “twoelectron, three-center bond” is produced. Under these conditions, boranes are consequently present as dimers: ” $\mathrm{BH}{3}$,” for example, as $\mathrm{B}{2} \mathrm{H}{6}$. Still, small fractions of the monomers appear as minor components in the dissociation equilibrium of the dimer: $\mathrm{B}{2} \mathrm{H}{6}$, for example, thus contains some $\mathrm{BH}_{3}$.
The Lewis bases $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S}$ or THF are better electron pair donors than the boranes themselves. Therefore, they convert dimeric boranes into $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S}$ or THF complexes of the monomers such as $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S} \cdots \mathrm{BH}{3}$ or THF $\cdots \mathrm{BH}_{3}$. This type of complex also dissociates to a small extent and thus contains a small equilibrium concentration of free monomeric boranes.
有机化学代写
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|A CYCLOADDITION FORMING THREE-MEMBERED RINGS
环加成是形成环的加成反应,其中产物,即所谓的环加合物,具有对应于起始材料和试剂的经验公式之和的经验公式。所有一步环加成反应都以顺式选择性发生。三元、四元、五元或六元但不是更大的环可以通过对单烯烃的环加成产生F一世G在r和3.10.
您将在第 12 章熟悉导致四元环、五元环或六元环的选定环加成反应。另外两个环加成反应也是氧化反应,将在第 14 章讨论氧化和还原反应:臭氧分解反应可以见第 14.3.2 节一种s在和ll一种s一世n小号和C吨一世这n12.5.5和 cisvic 二羟基化这s这4可以在第 14.3.2 节中找到。这里我们仅讨论将二氯卡宾加成烯烃作为环加成型顺式加成的例子F一世G在r和3.11.
二氯卡宾不能分离,但可以在烯烃存在下生产,然后立即与之反应。最好的二氯卡宾前体是阴离子Cl3C−,这很容易消除氯离子。该阴离子来源于Cl3CH和相当强大的基础。这这H−只要它与Cl3CH分子。因此,当氯仿与氢氧化钾溶液一起搅拌时,只有适度的转化为阴离子Cl3C−. 这是因为Cl3CH和水ķ这H不混溶,因此ķ这H不能有效地从水相迁移到Cl3CH. 的解决方案ķ+和这H−有机相中的离子太低。
仅转让这H−然而,在相转移催化剂的存在下,离子进入氯仿非常成功。最常用的相转移催化剂是四烷基氯化铵或四烷基硫酸氢铵。随着大量过剩这H−离子,它们在平衡反应中产生相应的四烷基氢氧化铵。这些溶解在氯仿中,因为阳离子太大,几乎不需要溶剂化。通过库仑吸引力,这些阳离子拉动不可溶解的这H−离子与它们进入氯仿相。
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|ADDITIONS TO C“C DOUBLE BONDS THAT ARE RELATED TO CYCLOADDITIONS AND FORM THREE-MEMBERED RINGS, TOO
与第 3.3.1 节中的二氯环丙烷相比,本节讨论的反应不是严格意义上的环加成反应。原因是这里给出的加成产物的经验公式不等于反应伙伴经验公式的总和。因此,这里的反应产物不是严格意义上的环加合物。
将 Simmons-Smith 试剂添加到烯烃中,只需一步即可获得不含氯的环丙烷F一世G在r和3.12. 这种添加还具有立体选择性和立体特异性。Simmons-Smith 试剂可由二碘甲烷和从n/C在偶,而锌粉和催化量的 $\mathrm{Zn} / \mathrm{Cu}$ couple, which in turn is produced from zinc dust and catalytic amounts of $\mathrm{CuSO}{4}, \mathrm{CuCl}{2}$, or $\mathrm{Cu}(\mathrm{OAc}){2}$. This Simmons-Smith reagent is usually assigned the structural formula $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI}$. This species, however, is subject to an equilibrium similar to the one that is known as the Schlenk equilibrium for Grignard compounds (cf. Figure 8.1):
$$
2 \mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{Zn}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{I}+\mathrm{ZnI}{2}
$$
在 Simmons-Smith 反应中,如图 3.12 所示,似乎已经阐明了攻击物种是 $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{ZnI}$ rather than $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{Zn}-\mathrm{CH}{2}-\mathrm{I}$, which is in equilibrium with it in small amounts. A reagent that has properties quite similar to those of the actual Simmons-Smith reagent (but is advantageously produced in a homogeneous reaction) results from a halogen/metal exchange between diiodomethane and $\mathrm{ZnEt}{2}$. It can be written as $\mathrm{I}-\mathrm{CH}_{2}-\mathrm{ZnEt}$.
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|CIS-HYDRATION OF OLEFINS VIA THE HYDROBORATION/OXIDATION/HYDROLYSIS REACTION SEQUENCE
在单硼烷中$\left(\mathrm{BH}{3}\right)$, monoalkylboranes $\mathrm{RBH}{2}$, or dialkylboranes $\mathrm{R}{2} \mathrm{BH}$ there is only an electron sextet at the boron atom. In comparison to the more stable electron octet, the boron atom thus lacks two valence electrons. It “obtains” them by bonding with a suitable electron pair donor. When no better donor is available, the bonding electron pair of the B-H bond of a second borane molecule acts as the donor so that a “twoelectron, three-center bond” is produced. Under these conditions, boranes are consequently present as dimers: ” $\mathrm{BH}{3}$,” for example, as $\mathrm{B}{2} \mathrm{H}{6}$. Still, small fractions of the monomers appear as minor components in the dissociation equilibrium of the dimer: $\mathrm{B}{2} \mathrm{H}{6}$, for example, thus contains some $\mathrm{BH}_{3}$.
刘易斯底 $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S}$ or THF are better electron pair donors than the boranes themselves. Therefore, they convert dimeric boranes into $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S}$ or THF complexes of the monomers such as $\mathrm{Me}{2} \mathrm{~S} \cdots \mathrm{BH}{3}$ or THF $\cdots \mathrm{BH}_{3}$.。这种类型的复合物也有少量解离,因此含有少量平衡浓度的游离单体硼烷。

化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。