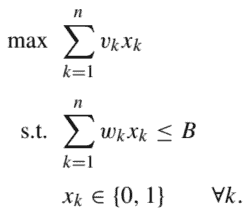如果你也在 怎样代写matlab这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。matlab全世界有数百万工程师和科学家将MATLAB用于工业和学术界的一系列应用,包括深度学习和机器学习、信号处理和通信、图像和视频处理、控制系统、测试和测量、计算金融以及计算生物学。
matlab是一个专门为工程师和科学家设计的编程平台,用于分析和设计改变我们世界的系统和产品。MATLAB的核心是MATLAB语言,这是一种基于矩阵的语言,允许计算数学的最自然表达。
my-assignmentexpert™matlab代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的matlab作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此matlab作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在matlab代写方面经验极为丰富,各种matlab相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的matlab及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:

数学代写|matlab代写|Deterministic Lead Time
The standard state equation
$$
I_{t+1}=I_{t}+x_{t}-d_{t+1}
$$
assumes that what is ordered at time instant $t$ is immediately available to satisfy demand during the following time interval $t+1$. This assumption of zero delivery lead time may be well questionable, but it may make sense in some settings. For instance, imagine a retail store which is closed during Sundays. If orders are issued on Saturdays and transportation is fast enough, what is ordered on a Saturday evening will be available on the shelves on the next Monday morning. While lead time is not really zero, it is negligible from a modeling viewpoint. However, in many settings a non-negligible lead time is an issue. As a result, what we order now will be available after a delay. Let us assume that the lead time is not subject to any uncertainty and that it is an integer number $L T \geq 1$ of time intervals. In this setting, we need to introduce state variables keeping track of what was ordered in the past and is still in the transportation pipeline. Let us denote these state variables by $z_{t, \tau}$, the amount that will be delivered $\tau$ time intervals after the current time $t$, where $\tau=0,1,2, \ldots, \mathrm{LT}-1$. Hence, $z_{t, 0}$ represents what is immediately available at the current time instant $t$, and it is involved in the state transition equation for on-hand inventory:
$$
I_{t+1}=I_{t}+z_{t, 0}-d_{t+1}
$$
if we disregard demand uncertainty. What we order at time instant $t$, represented by decision variable $x_{t}$, will be available LT time intervals after $t$. Hence, at the next time instant $t+1$, the amount $x_{t}$ will be $\mathrm{LT}-1$ time intervals from delivery. We may therefore relate the decision $x_{t}$ to the additional state variable corresponding to $\tau=\mathrm{LT}-1$ as follows:
$$
z_{t+1, \mathrm{LT}-1}=x_{t} .
$$
数学代写|matlab代写|Perishable Items
Let us consider the case of a perishable item with a deterministic shelf-life. In this case, we must introduce an array of state variables $I_{t, \tau}$, representing the amount of on-hand inventory at time $t$ with an age of $\tau$ time periods. We assume again that delivery lead time is zero, and that items have age $\tau=0$ when delivered at the beginning of a time interval. Note, however, that they will have age $\tau=1$ when we update state variables at the end of that time interval. Therefore, if the maximum shelf-life of the item is $L$, we will hold inventory at age levels $\tau=1, \ldots, L$. Items that have age $L$ at time instant $t$ will have to be scrapped at time instant $t+1$, if they are not sold during the next time interval $t+1$. The amount of fresh items ordered and immediately delivered at time instant $t$ is denoted by $x_{t}$. The process of ageing inventory is modeled by a time shift, much like Eq. (3.15). However, here we must also account for inventory issuing to satisfy demand. From the retailer’s viewpoint, the best mechanism is FIFO (first-in-first-out), as this helps clearing oldest items first. ${ }^{6}$ The opposite LIFO (last-in-first-out) case is less convenient, as it may result in increased scrap; consumers preferring fresh items will collect stock under this scheme, if allowed to do so. Let us write down the state equations for the FIFO case, under the additional assumption that unsatisfied demand results in lost sales (no backlog).
To figure out the state transition equations, let us consider the inventory level $I_{(t+1){-}, \tau}$, of age $\tau$, after meeting demand $d{t+1}$, but before updating age [which is why we use the subscript $\left.(t+1){-}\right]$. This will be $$ I{(t+1){-}, \tau}=\max \left{0, \quad I{t, \tau}-U_{\tau+1}\right}
$$
i.e., the maximum between zero (the case in which demand is larger than the sum of inventory of age $\tau$ or older) and the difference between available inventory $I_{t, \tau}$ and the unmet demand $U_{\tau+1}$ after using inventory of age $\tau+1$ or older,
$$
U_{\tau+1} \doteq \max \left{0, \quad d_{t+1}-\sum_{j=\tau+1}^{L} I_{t, j}\right}
$$
matlab代写
数学代写|MATLAB代写|DETERMINISTIC LEAD TIME
标准状态方程
一世吨+1=一世吨+X吨−d吨+1
假设在瞬间订购的东西吨在接下来的时间间隔内可以立即满足需求吨+1. 这种零交货提前期的假设可能很值得怀疑,但在某些情况下可能是有道理的。例如,想象一家零售店在周日不营业。如果周六下单,而且运输速度够快,周六晚上下的单,下周一早上就能上架。虽然交货时间并不是真正的零,但从建模的角度来看可以忽略不计。然而,在许多情况下,不可忽略的交货时间是一个问题。因此,我们现在订购的产品将在延迟后可用。让我们假设提前期不受任何不确定性的影响,并且它是一个整数大号吨≥1的时间间隔。在这种情况下,我们需要引入状态变量来跟踪过去订购的内容并且仍在运输管道中。让我们将这些状态变量表示为和吨,τ, 将交付的金额τ当前时间之后的时间间隔吨, 在哪里τ=0,1,2,…,大号吨−1. 因此,和吨,0表示在当前时刻立即可用的内容吨,并且它涉及到现有库存的状态转移方程:
一世吨+1=一世吨+和吨,0−d吨+1
如果我们忽略需求的不确定性。我们在瞬间订购的东西吨,由决策变量表示X吨, 之后将可用 LT 时间间隔吨. 因此,在下一个瞬间吨+1, 数量X吨将会大号吨−1从交货的时间间隔。因此,我们可以将决定联系起来X吨到对应的附加状态变量τ=大号吨−1如下:
和吨+1,大号吨−1=X吨.
数学代写|MATLAB代写|PERISHABLE ITEMS
让我们考虑具有确定保质期的易腐烂物品的情况。在这种情况下,我们必须引入一个状态变量数组一世吨,τ,表示当时的现有库存量吨年龄为τ时间段。我们再次假设交货提前期为零,并且物品有年龄τ=0在时间间隔开始时交付。但是请注意,他们将有年龄τ=1当我们在该时间间隔结束时更新状态变量时。因此,如果物品的最长保质期是大号,我们将按年龄级别持有库存τ=1,…,大号. 有年龄的物品大号在瞬间吨必须及时报废吨+1, 如果它们在下一个时间间隔内没有售出吨+1. 即时订购并立即交付的生鲜商品数量吨表示为X吨. 库存老化的过程是通过时间偏移来建模的,很像方程。3.15. 但是,在这里我们还必须考虑库存发放以满足需求。从零售商的角度来看,最好的机制是先进先出F一世rs吨−一世n−F一世rs吨−这在吨,因为这有助于首先清除最旧的项目。6相反的LIFOl一种s吨−一世n−F一世rs吨−这在吨案例不太方便,因为它可能导致废品增加;如果允许,喜欢新鲜商品的消费者将根据该计划收集库存。让我们写下 FIFO 案例的状态方程,假设不满足的需求会导致销售损失n这b一种Cķl这G.
为了找出状态转移方程,让我们考虑库存水平 $I_{(t+1){-}, \tau}$, of age $\tau$, after meeting demand $d{t+1}$, but before updating age [which is why we use the subscript $\left.(t+1){-}\right]$. This will be $$ I{(t+1){-}, \tau}=\max \left{0, \quad I{t, \tau}-U_{\tau+1}\right}
$$
i.e., the maximum between zero (the case in which demand is larger than the sum of inventory of age $\tau$ or older) and the difference between available inventory $I_{t, \tau}$ and the unmet demand $U_{\tau+1}$ after using inventory of age $\tau+1$ or older,
$$
U_{\tau+1} \doteq \max \left{0, \quad d_{t+1}-\sum_{j=\tau+1}^{L} I_{t, j}\right}
$$

数学代写|matlab代写 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。