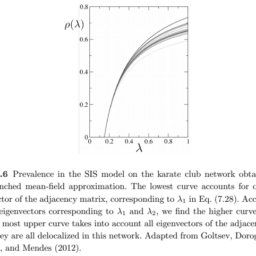
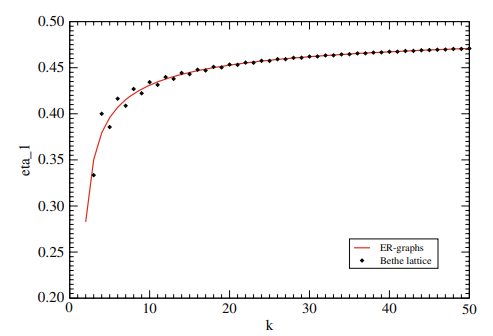
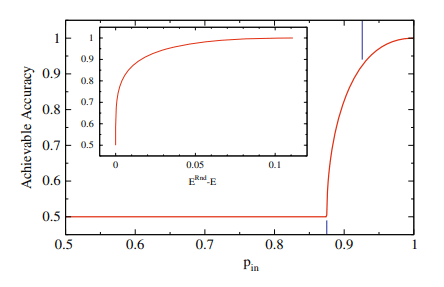
如果你也在 怎样代写复杂网络Complex Network 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。复杂网络Complex Network在网络理论的背景下,复杂网络是指具有非微观拓扑特征的图(网络)–这些特征在简单的网络(如格子或随机图)中不会出现,但在代表真实系统的网络中经常出现。复杂网络的研究是一个年轻而活跃的科学研究领域(自2000年以来),主要受到现实世界网络的经验发现的启发,如计算机网络、生物网络、技术网络、大脑网络、气候网络和社会网络。
复杂网络Complex Network大多数社会、生物和技术网络显示出实质性的非微观拓扑特征,其元素之间的连接模式既不是纯粹的规则也不是纯粹的随机。这些特征包括学位分布的重尾、高聚类系数、顶点之间的同态性或异态性、社区结构和层次结构。在有向网络的情况下,这些特征还包括互惠性、三联体重要性概况和其他特征。相比之下,过去研究的许多网络的数学模型,如格子和随机图,并没有显示这些特征。最复杂的结构可以由具有中等数量相互作用的网络实现。这与中等概率获得最大信息含量(熵)的事实相对应。
复杂网络Complex Network代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。最高质量的复杂网络Complex Network作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此复杂网络Complex Network作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
数据科学代写|复杂网络代写Complex Network代考|Methodology
Although many network-based measures have been proposed for weighted networks, few of them can process those networks made up of edges with similarity weight, just like GIVCN model. On the one hand, from the view of the network, all edges have a strength naturally associated with them that differentiates the number of intermediate goods, which has been operationalized as weight. On the other hand, based on IO theory, Leontief and Ghosh models are widely used to quantify the length or position of production networks .
In this section, we propose a network-based framework that relies on the first principle to detect inter-industry relevance. In detail, the information of sector’s function and inter-industry relative position on the GVC is already embedded in the topological structure of GIVCN model, so the first thing is to redefine the optimal path to reflect the propagation process of intermediate goods on the premise of considering the properties of the economic system.
Both Betweenness and Closeness Centrality rely on identifying optimal paths, which in the case of binary data can be unproblematically identified as shortest paths. But if the edges are weighted, there are a variety of possibilities in assessing the optimality of a path . In other words, there is no one-size-fits-all generalization for weighted networks, and it all depends on what kinds of network processes we are studying.
For many researchers studying ICIO networks, the most common style they used is to binarize the weighted edges and run the traditional Breadth-First-Search $(\boldsymbol{B F S})$ algorithms, in consideration of the computational intension. Besides, someone defined the optimal path as the maximum shortest path length between any two pairs, and took the minimum shortest path length based on taking the reciprocal of weights. They did so in part because they wanted to obtain the metric of consecutive paths, which is inappropriate.
In network science, path plays a central role, and many network-based indicators are developed around it. The Shortest Path between nodes $i$ and $j$, also known as Distance or Geodesic Path, is the path with the fewest edges linking to them, as denoted by $d_{i j}$. If there is no such path between them, it means $d_{i j}=\infty$. Besides, multiple shortest paths of the same length $d_{i j}$ are possible to be found. In general, Floyd-Warshall Algorithm (FWA) as a classical BFS algorithm is used to find all inter-node shortest paths in a recursive way, which means it compares all possible paths through the network between each pair of nodes by incrementally improving an estimate on the shortest path until the estimate is optimal [16]. The core formula of FWA is:
$$
d_{i j}^{(k)}=\min {i, j, k \in{1,2, \ldots, N}}\left{d{i j}^{(k-1)}, d_{i k}^{(k-1)}+d_{k j}^{(k-1)}\right}(i \neq j)
$$
Equation (3.1) works by first computing $d_{i j}^{(k)}$ for all pairs of source-to-sink nodes for $k=1$, then $k=2$, etc. This process continues until $k=N$, and we have found the shortest path using any intermediate nodes.
数据科学代写|复杂网络代写Complex Network代考|Theoretical Basis of SRPL in GIVCN Model
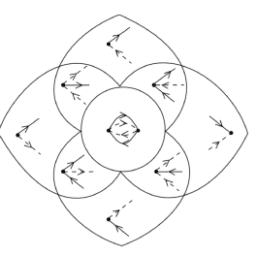
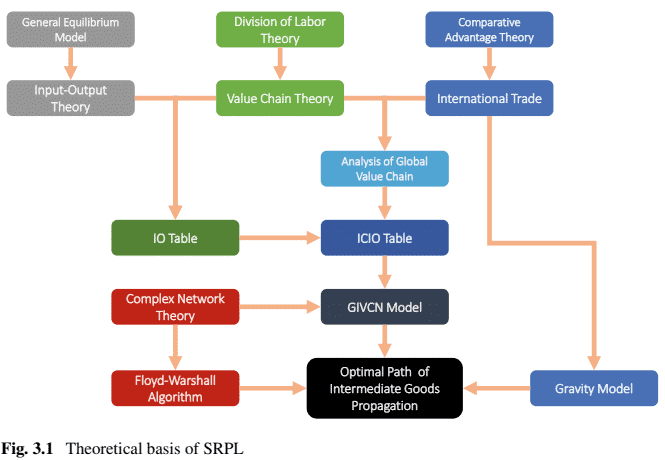
By Porter’s definition in 1985, an IVC is a physical representation of the various processes in producing goods (and services), starting with raw materials and ending with the delivered product. It is based on the notion of value-added at the stage of production. Wasilly Leontief’s IO table, published in the 1950s, estimated the relative importance of every individual link in industry-level value chains. In recent decades, in pursuit of better efficiency and profits, multinational enterprises locate a lot of activities, such as research, development, design, assembly, production of parts, marketing and branding, in different countries around the globe. It is the epitome of comparative advantage in the context of globalization, so here comes the concept of GVC. Furthermore, analytical tools stemming from complex networks have been proven to be very effective in the analysis of GVC, so the SRPL is proposed to find the optimal path for intermediate goods propagation based on theories and models as shown in Fig. 3.1.
It should be noted that the RFWA uses the experience of gravity model in the field of international economics for reference. Gravity models are often used in social science to predict and describe certain behaviors that mimic gravitational interaction as described in Isaac Newton’s law of gravity. Generally, the models employed in social science contain some elements of mass and distance, which leads them to the metaphor of physical gravity. A gravity model can help estimate the volume of flows of, for example, goods, services, or people between locations. This can be the population movement between cities or the volume of trade between countries [18].
The gravity model of international trade in international economics, first introduced in world economics by Walter Isard in 1954 [19], can predict, in its traditional form, bilateral trade flows based on economic sizes and distance between two units. The basic model for trade between two countries $i$ and $j$ takes the form of
$$
T_{i j}=\frac{A \times Y_i \times Y_j}{D_{i j}}
$$
where $A$ is the constant, $T_{i j}$ stands for trade flow, $D_{i j}$ the distance, and $Y_i$, as well as $Y_j$, stands for the economic dimensions of the countries that are being measured, often using GDP as a measure.
In econometric applications, this model is customary to specify
$$
T_{i j}=\frac{A \times Y_i^a \times Y_j^b}{D_{i j}^c}
$$
where $a, b$ and $c$ as adjustable parameters are used to optimize the approximation estimation of the model.
复杂网络代写
数据科学代写|复杂网络代写COMPLEX NETWORK代考|METHODOLOGY
尽管已经为加权网络提出了许多基于网络的措施,但很少有措施能够处理那些由具有相似权重的边组成的网络,就像 GIVCN 模型一样。一方面, 从网络的角度来看,所有边都有一个与它们自然相关的强度,可以区分中间商品的数量,这些中间商品已经被操作为权重。另一方面,基于 10 理 论,Leontief 和 Ghosh 模型被广泛用于量化生产网络的长度或位置。
在本节中,我们提出了一个基于网络的框架,该框架依赖于第一原则来检测行业间相关性。具体来说,GIVCN模型的拓扑结构中已经嵌入了部门功 能和产业间相对位置在GVC上的信息,因此首先要在考虑经济系统的特性。
Betweenness 和 Closeness Centrality 都依赖于识别最佳路径,在二进制数据的情况下,可以毫无问题地将其识别为最短路径。但是如果对边进行加 权,则在评估一条路径的最优性时会有多种可能性。换句话说,加权网络没有放之四海而皆准的泛化,这完全取决于我们研究的是哪种网络过 程。
对于许多研究 ICIO 网络的研究人员来说,他们使用的最常见的方式是将加权边二值化并运行传统的广度优先搜索 $(\boldsymbol{B F S})$ 算法,考虑到计算强度。 此外,有人将最优路径定义为任意两对之间的最大最短路径长度,并根据取权重的倒数取最小的最短路径长度。他们这样做的部分原因是他们想 获得连续路径的度量,这是不合适的。
在网络科学中,路径起着核心作用,许多基于网络的指标都是围绕它发展起来的。节点之间的最短路径 $i$ 和 $j$ ,也称为距离或测地线路径,是链接 到它们的边最少的路径,如表示为 $d_{i j}$. 如果它们之间没有这样的路径,则意味着 $d_{i j}=\infty$. 此外,多个相同长度的最短路径 $d_{i j}$ 有可能被发现。一般 来说,Floyd-Warshall 算法 $F W A$ 因为经典的 BFS 算法用于以递归方式找到所有节点间的最短路径,这意味着它通过递增地改进对最短路径的估计 直到估计是最优的来比较每对节点之间通过网络的所有可能路径
16
. FWA的核心公式是:
方程3.1通过首先计算工作 $d_{i j}^{(k)}$ 对于所有源到汇节点对 $k=1$ ,然后 $k=2$ 等。这个过程一直持续到 $k=N$ ,并且我们找到了使用任何中间节点的最 短路径。
数据科学代写|复杂网络代写COMPLEX NETWORK代考|THEORETICAL BASIS OF SRPL IN GIVCN MODEL
根据 Porter 在 1985 年的定义,IVC 是生产商品的各种过程的物理表示andservices,从原材料开始,到交付的产品结束。它基于生产阶段增值的 概念。Wasilly Leontief 于 1950 年代发布的 10 表估计了行业级价值链中每个环节的相对重要性。近几十年来,为了追求更好的效率和利润,跨国企 业将大量活动,如研发、设计、组装、零部件生产、营销和品牌推广,设在全球不同国家。它是全球化背景下比较优势的缩影,因此产生了全球 价值链的概念。此外,源自复杂网络的分析工具已被证明在分析全球价值链方面非常有效,
需要说明的是,RFWA借鉴了国际经济学领域引力模型的经验。重力模型通常用于社会科学,以预测和描述某些模仿艾萨克牛顿万有引力定律中描 述的重力相互作用的行为。通常,社会科学中使用的模型包含一些质量和距离的元素,这导致它们成为物理引力的隐喻。引力模型可以帮助估算 不同地点之间的商品、服务或人员的流动量。这可以是城市之间的人口流动或国家之间的贸易量
18
国际经济学中国际贸易的引力模型,1954年由Walter Isard首次引入世界经济学
19
可以根据经济规模和两个单位之间的距离以传统形式预测双边贸易流量。两国贸易的基本模型 $i$ 和 $j$ 采取的形式
$$
T_{i j}=\frac{A \times Y_i \times Y_j}{D_{i j}}
$$
在哪里 $A$ 是常数, $T_{i j}$ 代表贸易流量, $D_{i j}$ 距离,和 $Y_i$ ,也 $Y_j$, 代表被衡量国家的经济规模,通常使用 GDP 作为衡量标准。 在计量经济学应用中,该模型习惯于指定
$$
T_{i j}=\frac{A \times Y_i^a \times Y_j^b}{D_{i j}^c}
$$
在哪里 $a, b$ 和 $c$ 作为可调参数用于优化模型的近似估计。

数据科学代写|复杂网络代写Complex Network代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。