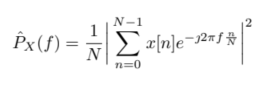如果你也在 怎样代写信号处理signal processing这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。信号处理signal processing是一个电气工程的子领域,主要是分析、修改和合成信号,如声音、图像和科学测量。信号处理技术可用于提高传输、存储效率和主观质量,也可用于强调或检测测量信号中感兴趣的成分。
代写连续时间信号处理signal processing
连续时间信号处理是针对随着连续域的变化而变化的信号(不考虑一些单独的中断点)。 函数和确定性信号的连续时间过滤
代写离散时间信号处理signal processing
离散时间信号处理是针对采样信号的,只定义在离散的时间点上,因此在时间上是量化的,但在幅度上不是。(见下文),并且仍被用于千兆赫兹信号的高级处理。
代写数字信号处理signal processing
主文章。数字信号处理(FFT),有限脉冲响应(FIR)滤波器,无限脉冲响应(IIR)滤波器,以及自适应滤波器,如维纳和卡尔曼滤波器。
In comparison, the output viewpoint examines how a single point in the output signal is determined by the various values from the input signal. Just as with discrete signals, each instantaneous value in the output signal is affected by a section of the input signal, weighted by the impulse response flipped left-for-right. In the discrete case, the signals are multiplied and summed. In the continuous case, the signals are multiplied and integrated. In equation form:
$$
y(t)=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} x(\tau) h(t-\tau) d \tau
$$
The convolution integral. This equation defines the meaning of: $y(t)=x(t) * h(t)$.
This equation is called the convolution integral, and is the twin of the convolution sum ) used with discrete signals.shows how this equation can be understood. The goal is to find an expression for calculating the value of the output signal at an arbitrary time, $t$. The first step is to change the independent variable used to move through the input signal and the impulse response. That is, we replace $t$ with $\tau$ (a lower case Greek tau). This makes $x(t)$ and $h(t)$ become $x(\tau)$ and $h(\tau)$, respectively. This change of variable names is needed because $t$ is already being used to represent the point in the output signal being calculated. The next step is to flip the impulse response left-for-right, turning it into $h(-\tau)$. Shifting the flipped impulse response to the location $t$, results in the expression becoming $h(t-\tau)$. The input signal is then weighted by the flipped and shifted impulse response by multiplying the two, i.e., $x(\tau) h(t-\tau)$. The value of the output signal is then found by integrating this weighted input signal from negative to positive infinity.
my-assignmentexpert™ 信号处理signal processing作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的信号处理signal processing作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此信号处理signal processing作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在信号处理signal processing作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计Statistics代写服务。我们的专家在信号处理signal processing代写方面经验极为丰富,各种信号处理signal processing相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的信号处理signal processing及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 微分方程 Differential equations
- 递归关系 Recurrence relations
- 变换理论 Time-frequency analysis – for dealing with non-stationary signals [14]
- 时频分析 Transformation theory Time-frequency analysis – for dealing with non-stationary signals
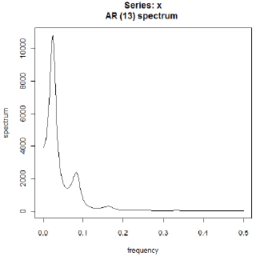
- 频谱估计 Spectral estimation – for determining the spectral content
- 统计信号处理 Statistical signal processing – for analyzing and extracting information based on the stochastic properties of signals and noise
- 线性时不变系统理论和变换理论 Linear time-invariant systems theory and transformation theory
- 多项式信号处理 Polynomial signal processing – analysis of systems related to inputs and outputs using polynomials
数学代写|信号处理代考|Random signals and stochastic processes
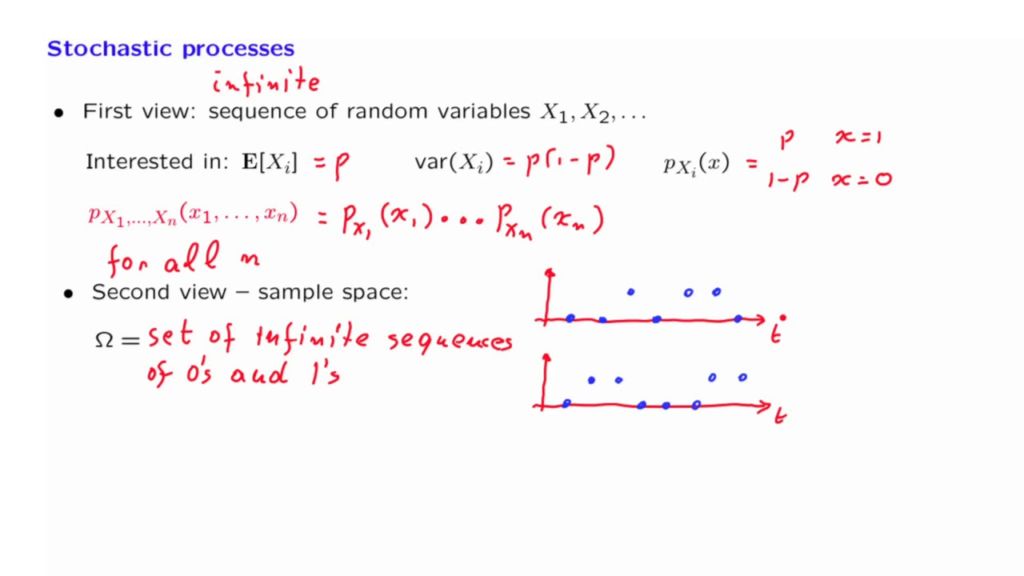
Using the MATLAB command rand, generate a 1000 -sample vector $\mathrm{x}=[x[1], x[2], \ldots, x[1000]]^{T}$ where each sample $x[n]$ is a realisation of a uniform random variable $X \sim \mathcal{U}(0,1)$ at time instant $n$. Plot the result and observe that despite its stochastic nature, $x$ exhibits a degree of uniformity due to its time-invariant statistical properties, since the different samples $x[n], x[m]$ have been drawn from the same distribution. Such signals are referred to as statistically stationary.
The vector $\mathbf{x}$ can be considered as a 1000 -sample realisation of a stationary stochastic process $X_{n}$, whereby $X_{n} \sim$ $\mathcal{U}(0,1), \forall n$.
- Calculate the expected value of $X$, denoted by $m=\mathbb{E}{X}$, also known as the theoretical mean. Using your [5] 1000 -sample realisation $\mathbf{x}$, also compute the sample mean using the MATLAB function mean, calculated as
$$
\widehat{m}=\frac{1}{N} \sum_{n=1}^{N} x[n]
$$
where the circumflex denotes an estimate. Comment on the accuracy of the sample mean as an estimator. - Repeat the analysis for the standard deviation: calculate the theoretical value $\sigma=\sqrt{\mathbb{E}{X-\mathbb{E}{X}}^{2}}$ and also its sample estimate from data $\mathbf{x}$ using the MATLAB function std which computes the sample standard deviation as $^{1}$
$$
\widehat{\sigma}=\sqrt{\frac{1}{N-1} \sum_{n=1}^{N}(x[n]-\hat{m})^{2}}
$$
Comment on the accuracy of $\widehat{\sigma}$.
[5]
Comment on the accuracy of $\hat{\sigma}$. - The bias of the sample mean estimation is given by $B=\mathbb{E}{X}-\widehat{m}$. Generate an ensemble of ten 1000 -sample realisations of $X$, denoted by $\mathbf{x}{1: 10}$, and calculate the sample means $\widehat{m}{1: 10}$ and standard deviations $\widehat{\sigma}_{1: 10}$ for each realisation. Plot these estimates of mean and standard deviation and comment on their bias, by showing how they cluster about their theoretical values.
Note: In general, when plotting quantities that are not indexed by time stamps (as in this case, where the index is the ‘realisation’) there is no reason to connect the plotted points. - The mean and standard deviation describe second order statistical properties of a random variable, however, to
[5] obtain a complete statistical description it is necessary to examine the probability density function (pdf) from which the samples are drawn. Approximate the pdf of $X$ by showing in the same plot the histogram of $\mathbf{x}$ (see hist), normalised by the number of samples considered, and the theoretical pdf. Comment upon the result, in particular, on whether the estimate appears to converge as the number of generated samples increases, and how the number of histogram bins considered affects the analysis.
Note: As mentioned above, the theoretical pdf of $X$ is $\mathcal{U}(0,1)$. - Repeat Part 1-Part 4 using the MATLAB function randn to generate zero-mean, unit standard deviation, Gaussian
[20] random variables.
信号处理代写
数学代写|信号处理代考|RANDOM SIGNALS AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES
使用 MATLAB 命令 rand,生成 1000 个样本向量X=[X[1],X[2],…,X[1000]]吨其中每个样本X[n]是一个均匀随机变量的实现X∼ü(0,1)在瞬间n. 绘制结果并观察尽管它具有随机性,X由于其时不变的统计特性,表现出一定程度的均匀性,因为不同的样本X[n],X[米]来自同一个分布。这样的信号被称为统计稳定的。
向量X可以被认为是平稳随机过程的 1000 个样本实现Xn,由此Xn∼ ü(0,1),∀n.
- 计算期望值X,表示为米=和X,也称为理论平均值。使用您的51000个样本实现X,还使用 MATLAB 函数 mean 计算样本均值,计算为
米^=1ñ∑n=1ñX[n]
其中抑扬符表示估计值。评论作为估计量的样本均值的准确性。 - 对标准差重复分析:计算理论值σ=和X−和X2以及它的数据样本估计X使用 MATLAB 函数 std 计算样本标准偏差为1
σ^=1ñ−1∑n=1ñ(X[n]−米^)2
评论准确性σ^.
5
评论准确性σ^. - 样本均值估计的偏差由下式给出乙=和X−米^. 生成 10 个 1000 个样本实现的集合X,记为 $\mathbf{x} {1: 10},一种ndC一种一世C你一世一种吨和吨H和s一种米p一世和米和一种ns\widehat{m} {1:10}一种nds吨一种nd一种rdd和v一世一种吨一世○ns\widehat{\sigma}_{1: 10}$ 为每个实现。绘制这些均值和标准差的估计值,并通过显示它们如何围绕其理论值进行聚类来评论它们的偏差。
注意:通常,在绘制未按时间戳索引的数量时一种s一世n吨H一世sC一种s和,在H和r和吨H和一世nd和X一世s吨H和‘r和一种一世一世s一种吨一世○n′没有理由连接绘制的点。 - 然而,均值和标准差描述了随机变量的二阶统计特性
5获得完整的统计描述 有必要检查概率密度函数pdF从中抽取样本。近似的pdfX通过在同一图中显示直方图X s和和H一世s吨,通过考虑的样本数量和理论 pdf 进行归一化。评论结果,特别是估计是否随着生成的样本数量的增加而收敛,以及所考虑的直方图箱的数量如何影响分析。
注意:如上所述,理论pdfX是ü(0,1). - 使用 MATLAB 函数 randn 重复第 1 部分至第 4 部分以生成零均值、单位标准差、高斯
20随机变量。

信号处理代写signal processing代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
统计代考
统计是汉语中的“统计”原有合计或汇总计算的意思。 英语中的“统计”(Statistics)一词来源于拉丁语status,是指各种现象的状态或状况。
数论代考
数论(number theory ),是纯粹数学的分支之一,主要研究整数的性质。 整数可以是方程式的解(丢番图方程)。 有些解析函数(像黎曼ζ函数)中包括了一些整数、质数的性质,透过这些函数也可以了解一些数论的问题。 透过数论也可以建立实数和有理数之间的关系,并且用有理数来逼近实数(丢番图逼近)
数值分析代考
数值分析(Numerical Analysis),又名“计算方法”,是研究分析用计算机求解数学计算问题的数值计算方法及其理论的学科。 它以数字计算机求解数学问题的理论和方法为研究对象,为计算数学的主体部分。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。