如果你也在 怎样统计计算Statistical Computing这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。统计计算Statistical Computing是统计学和计算机科学之间的纽带。它意味着通过使用计算方法来实现的统计方法。它是统计学的数学科学所特有的计算科学(或科学计算)的领域。这一领域也在迅速发展,导致人们呼吁应将更广泛的计算概念作为普通统计教育的一部分。与传统统计学一样,其目标是将原始数据转化为知识,[2]但重点在于计算机密集型统计方法,例如具有非常大的样本量和非同质数据集的情况。
许多统计建模和数据分析技术可能难以掌握和应用,因此往往需要使用计算机软件来帮助实施大型数据集并获得有用的结果。S-Plus是公认的最强大和最灵活的统计软件包之一,它使用户能够应用许多统计方法,从简单的回归到时间序列或多变量分析。该文本广泛涵盖了许多基本的和更高级的统计方法,集中于图形检查,并具有逐步说明的特点,以帮助非统计学家充分理解方法。
my-assignmentexpert™统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在统计计算Statistical Computing作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的统计计算Statistical Computing代写服务。我们的专家在统计计算Statistical Computing代写方面经验极为丰富,各种统计计算Statistical Computing相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的统计计算Statistical Computing及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 随机微积分 Stochastic calculus
- 随机分析 Stochastic analysis
- 随机控制理论 Stochastic control theory
- 微观经济学 Microeconomics
- 数量经济学 Quantitative Economics
- 宏观经济学 Macroeconomics
- 经济统计学 Economic Statistics
- 经济学理论 Economic Theory
- 计量经济学 Econometrics
统计代写
数学代写|统计计算作业代写Statistical Computing代考|Discrete state space
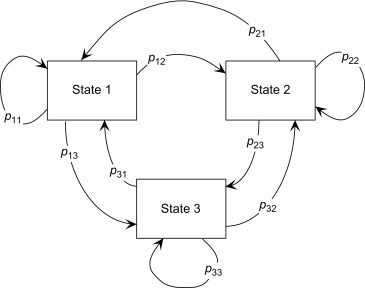
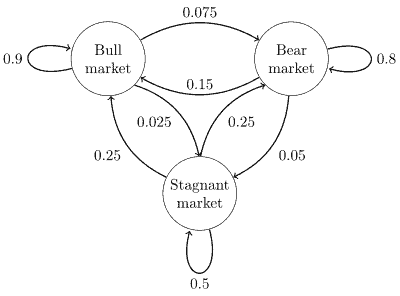
If the state space $S$ is finite, for example $S={1,2, \ldots, N}$, then the transition probabilities $P\left(X_{n} \in A_{n} \mid X_{n-1} \in A_{n-1}\right)$ in (2.2) can be described by giving the probabilities
$$
p_{x y}=P\left(X_{j}=y \mid X_{j-1}=x\right)
$$
of the transitions between all pairs of elements $x, y \in S$. The resulting matrix $P=$ $\left(p_{x y}\right)_{x, y \in S}$ is called the transition matrix of the Markov chain $X$.
When considering transition matrices, it is often convenient to label the rows and columns of the matrix $P$ using elements of $S$ instead of using the usual indices ${1,2, \ldots, n}$. Thus, if $S$ is the alphabet $S={\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}, \ldots, \mathrm{Z}}$ we write $p_{\mathrm{AZ}}$ instead of $p_{1,26}$ to denote the probability of transitions from A to $Z$. We write $\mathbb{R}^{S \times S}$ for the set of all matrices where the columns and rows are indexed by elements of $S$. Similarly, for vectors consisting of probability weights for the elements of $S$, for example the initial distribution of a Markov chain, it is convenient to label the components of the vector by elements of $S$. We write $\mathbb{R}^{S}$ for the set of all such vectors.
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|Continuous state space
In this section we will briefly discuss Markov chains with continuous state space. Markov chains can be considered on very general state spaces, but here we restrict ourselves to the case $S=\mathbb{R}^{d}$. Most of the results from the previous section formally carry over to the case of continuous state space, with only changes in notation.
The concept of transition matrices in the case of continuous state space is replaced by transition kernels, as given in the following definition.
Definition 2.27 A transition kernel is a map $P(\cdot, \cdot)$ such that:
(a) $P(x, A) \geq 0$ for all $x \in \mathbb{R}^{d}$ and all $A \subseteq \mathbb{R}^{d}$; and
(b) $P(x, \cdot)$ is a probability distribution on $\mathbb{R}^{d}$ for all $x \in \mathbb{R}^{d}$.
This definition hides some of the technical complications associated with the study of Markov chains on a continuous state space. If full mathematical rigour is required, an additional condition, relating to ‘measurability’, must be included.
The idea in this definition is that $x$ takes the rôle of the current state of the Markov chain and, for given $x$, the map $A \mapsto P(x, A)$ is the distribution of the next value of the Markov chain. Thus, the transition kernel of a time-homogeneous Markov chain is defined by
$$
P(x, A)=P\left(X_{j} \in A \mid X_{j-1}=x\right)
$$
Often, the conditional distribution of $X_{j}$, given $X_{j-1}=x$, has a density. In this case, instead of giving a transition kernel, we can describe the transitions of a Markov chain by giving a transition density. In analogy to lemma $2.19$, a transition density is defined in the following.
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|DISCRETE STATE SPACE
如果状态空间小号是有限的,例如小号=1,2,…,ñ, 那么转移概率磷(Xn∈一种n∣Xn−1∈一种n−1)在2.2可以通过给出概率来描述
pX和=磷(Xj=和∣Xj−1=X)
所有元素对之间的转换X,和∈小号. 结果矩阵磷= (pX和)X,和∈小号称为马尔可夫链的转移矩阵X.
在考虑转移矩阵时,通常方便标记矩阵的行和列磷使用元素小号而不是使用通常的索引1,2,…,n. 因此,如果小号是字母表小号=一种,乙,…,和我们写p一种和代替p1,26表示从 A 到和. 我们写R小号×小号对于列和行由元素索引的所有矩阵的集合小号. 类似地,对于由以下元素的概率权重组成的向量小号,例如马尔可夫链的初始分布,可以方便地通过元素标记向量的分量小号. 我们写R小号对于所有此类向量的集合。
数学代写|统计计算作业代写STATISTICAL COMPUTING代考|CONTINUOUS STATE SPACE
在本节中,我们将简要讨论具有连续状态空间的马尔可夫链。可以在非常一般的状态空间上考虑马尔可夫链,但在这里我们仅限于这种情况小号=Rd. 上一节的大部分结果都正式延续到连续状态空间的情况,只是符号有所变化。
在连续状态空间的情况下,转移矩阵的概念被转移核所取代,如下面的定义所示。
定义 2.27 转换核是一个映射磷(⋅,⋅)这样:
一种 磷(X,一种)≥0对所有人X∈Rd和所有一种⊆Rd; 和
b 磷(X,⋅)是一个概率分布Rd对所有人X∈Rd.
这个定义隐藏了一些与在连续状态空间上研究马尔可夫链相关的技术复杂性。如果需要完全的数学严谨性,则必须包括与“可测量性”相关的附加条件。
这个定义中的想法是X扮演马尔可夫链当前状态的角色,并且,对于给定X, 地图一种↦磷(X,一种)是马尔可夫链下一个值的分布。因此,时间齐次马尔可夫链的转移核定义为
磷(X,一种)=磷(Xj∈一种∣Xj−1=X)
通常,条件分布Xj, 给定Xj−1=X, 有密度。在这种情况下,我们可以通过给出转移密度来描述马尔可夫链的转移,而不是给出转移核。类似于引理2.19,过渡密度定义如下。

计量经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
微观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写
宏观经济学代写请认准my-assignmentexpert™ Economics 经济学作业代写