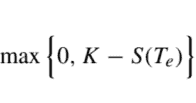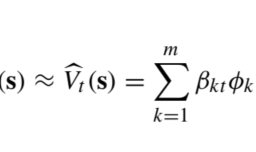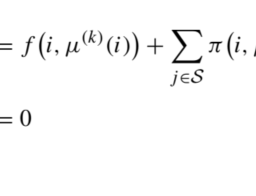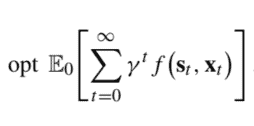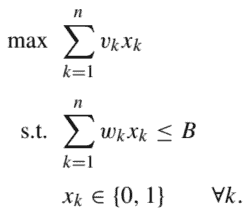如果你也在为遇到的matlab相关的难题发愁,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。MATLAB®将为迭代分析和设计过程而调整的桌面环境与直接表达矩阵和阵列数学的编程语言相结合。它包括用于创建脚本的实时编辑器,这些脚本将代码、输出和格式化文本结合在可执行的笔记本中。
- 专业构建
MATLAB工具箱是专业开发的,经过严格的测试,并有完整的文件记录。 - 拥有互动式应用程序
MATLAB应用程序让您看到不同的算法是如何与您的数据一起工作的。迭代直到您得到您想要的结果,然后自动生成一个MATLAB程序来重现或自动完成您的工作。 - 以及扩展的能力
只需稍加修改代码,就可以将您的分析扩展到集群、GPU和云上运行。不需要重写你的代码或学习大数据编程和内存外技术。
my-assignmentexpert™ matlab作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的matlab作业代写作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此matlab作业代写作业代写的价格不固定。通常在matlab专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在matlab作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在matlab作业代写方面经验极为丰富,各种matlab作业代写相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的matlab作业代写及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 数据分析
- 数值与符号计算
- 工程与科学绘图
- 控制系统设计
- 航天工业
- 汽车工业
- 生物医学工程
- 语音处理
运筹学代写
数学代写|matlab作业代写|finite-horizon problem
When dealing with a finite-horizon problem, we may build a sequence of value functions iteratively, starting from a boundary condition, since everything is given in explicit form. On the contrary, when we tackle an infinite-horizon MDP, the value function is implicitly given by equations like
$$
V(i)=\underset{a \in \mathcal{A}(i)}{\operatorname{opt}}\left{f(i, a)+\gamma \sum_{j} \pi(i, a, j) V(j)\right}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
or
$$
V(i)=\underset{a \in \mathcal{A}(i)}{\operatorname{opt}} \sum_{j \in \mathcal{S}} \pi(i, a, j){h(i, a, j)+\gamma V(j)}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
We recall that these two formulations are equivalent in principle, if both the transition probabilities $\pi(i, a, j)$ and the random immediate contributions $h(i, a, j)$ are known. In this chapter, where we apply standard numerical methods (or model-based DP, if you prefer, in contrast to model-free approaches typical of reinforcement learning), we assume that this is the case. Thus, we may choose either form as a matter of modeling convenience.
Since we deal with finite MDPs, the state space may be identified with a finite set of integer numbers, $\mathcal{S} \equiv{1, \ldots, n}$ and the value function $V: \mathcal{S} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ is a vector in $\mathbb{R}^{n}$, which we will denote by $\mathbf{V}$, with components $V(i), i \in \mathcal{S}$. Hence, the above DP recursions are actually a system of nonlinear equations with unknown variables $V(i)$. A closer look shows that the equations are, in a sense, piecewise linear, since we take the minimum or the maximum of a finite set of linear (better, affine) functions of the state values: each linear piece corresponds to a feasible action. In general, systems of nonlinear equations are solved by iterative methods. By the same token, there are two basic strategies for solving the above equations numerically and find the optimal policy: ${ }^{2}$
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|policy iteration
In principle, both value and policy iteration will yield an optimal policy, even though they are rather different in nature. Value iteration relies on computationally cheap iterations, but the optimal value function is only obtained in the limit. On the contrary, policy iteration requires more expensive iterations, but it will converge in finite time for a finite MDP, since there is a finite number of policies. When the computational effort is too large, we may adopt heuristic variants of the two basic strategies. It turns out that, for both analyzing the strategies in their exact form and understanding their heuristic variants, it is convenient to define the following two operators:
- Given a generic value function represented by vector $\tilde{\mathbf{V}}$, not necessarily the optimal one, we define the operator $\mathcal{T}$ :
$$
\mathcal{T} \tilde{\mathbf{V}}=\operatorname{opt}{a \in \mathcal{A}(i)} \sum{j \in \mathcal{S}} \pi(i, a, j){h(i, a, j)+\gamma \tilde{V}(j)}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
Note that $\mathcal{T} \tilde{\mathbf{V}}$ is itself a function over $\mathcal{S}$, in this case just another vector. - Given a generic value function $\tilde{\mathbf{V}}$ and a generic stationary policy $\mu$, not necessarily optimal, we define the operator $\mathcal{T}{\mu}$ as follows: $$ \left\mathcal{T}{\mu} \tilde{\mathbf{V}}\right=\sum_{j \in \mathcal{S}} \pi(i, \mu(i), j){h(i, \mu(i), j)+\gamma \widetilde{V}(j)}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
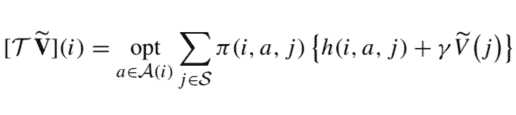
matlab代写
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|FINITE-HORIZON PROBLEM
在处理有限范围问题时,我们可以从边界条件开始迭代地构建一系列值函数,因为一切都是以显式形式给出的。相反,当我们处理无限范围的 MDP 时,值函数由如下等式隐含地给出
V(i)=\underset{a \in \mathcal{A}(i)}{\operatorname{opt}}\left{f(i, a)+\gamma \sum_{j} \pi(i, a , j) V(j)\right}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}V(i)=\underset{a \in \mathcal{A}(i)}{\operatorname{opt}}\left{f(i, a)+\gamma \sum_{j} \pi(i, a , j) V(j)\right}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
要么
五(一世)=选择一种∈一种(一世)∑j∈小号圆周率(一世,一种,j)H(一世,一种,j)+C五(j),一世∈小号
我们记得这两个公式原则上是等价的,如果两个转移概率圆周率(一世,一种,j)和随机的直接贡献H(一世,一种,j)是已知的。在本章中,我们应用标准数值方法○r米○d和一世−b一种s和dD磷,一世F和○你pr和F和r,一世nC○n吨r一种s吨吨○米○d和一世−Fr和和一种ppr○一种CH和s吨和p一世C一种一世○Fr和一世nF○rC和米和n吨一世和一种rn一世nG,我们假设是这种情况。因此,出于建模方便的考虑,我们可以选择任何一种形式。
由于我们处理有限的 MDP,状态空间可以用一组有限的整数来标识,小号≡1,…,n和价值函数五:小号→R是一个向量Rn,我们将表示为五, 有组件五(一世),一世∈小号. 因此,上述DP递归实际上是一个具有未知变量的非线性方程组五(一世). 仔细观察会发现,这些方程在某种意义上是分段线性的,因为我们取有限线性集的最小值或最大值b和吨吨和r,一种FF一世n和状态值的函数:每个线性片段对应一个可行的动作。通常,非线性方程组通过迭代方法求解。同理,有两种基本策略可用于数值求解上述方程并找到最优策略:2
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|POLICY ITERATION
原则上,价值迭代和策略迭代都会产生最优策略,即使它们本质上完全不同。值迭代依赖于计算成本低的迭代,但最优值函数只能在极限中获得。相反,策略迭代需要更昂贵的迭代,但对于有限的 MDP,它将在有限的时间内收敛,因为策略的数量是有限的。当计算量太大时,我们可以采用两种基本策略的启发式变体。事实证明,为了分析策略的确切形式和理解它们的启发式变体,定义以下两个运算符很方便:
- 给定一个由向量表示的通用值函数五~,不一定是最优的,我们定义算子吨:
$$
\mathcal{T} \tilde{\mathbf{V}} =\operatorname{opt} {a \in \mathcal{A}一世} \sum {j \in \mathcal{S}} \pi一世,一种,j{H一世,一种,j+ \ gamma \ 波浪号 {V}j}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
注意吨五~本身就是一个函数小号,在这种情况下只是另一个向量。 - 给定一个通用的价值函数五~和一个通用的固定策略μ,不一定是最优的,我们定义算子 $\mathcal{T} {\mu}一种sF○一世一世○在s:$ \left \mathcal{T} {\mu} \tilde{\mathbf{V}}\right =\sum_{j \in \mathcal{S}} \pi一世,μ(一世, j){h一世,μ(一世, j)+\gamma \widetilde{V}j}, \quad i \in \mathcal{S}
$$
统计代考
统计是汉语中的“统计”原有合计或汇总计算的意思。 英语中的“统计”(Statistics)一词来源于拉丁语status,是指各种现象的状态或状况。
数论代考
数论(number theory ),是纯粹数学的分支之一,主要研究整数的性质。 整数可以是方程式的解(丢番图方程)。 有些解析函数(像黎曼ζ函数)中包括了一些整数、质数的性质,透过这些函数也可以了解一些数论的问题。 透过数论也可以建立实数和有理数之间的关系,并且用有理数来逼近实数(丢番图逼近)
数值分析代考
数值分析NumericalAnalysis,又名“计算方法”,是研究分析用计算机求解数学计算问题的数值计算方法及其理论的学科。 它以数字计算机求解数学问题的理论和方法为研究对象,为计算数学的主体部分。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。