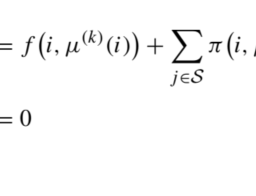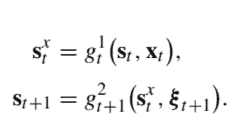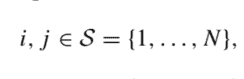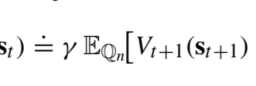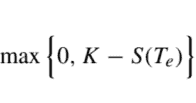如果你也在为遇到的matlab相关的难题发愁,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。MATLAB®将为迭代分析和设计过程而调整的桌面环境与直接表达矩阵和阵列数学的编程语言相结合。它包括用于创建脚本的实时编辑器,这些脚本将代码、输出和格式化文本结合在可执行的笔记本中。
- 专业构建
MATLAB工具箱是专业开发的,经过严格的测试,并有完整的文件记录。 - 拥有互动式应用程序
MATLAB应用程序让您看到不同的算法是如何与您的数据一起工作的。迭代直到您得到您想要的结果,然后自动生成一个MATLAB程序来重现或自动完成您的工作。 - 以及扩展的能力
只需稍加修改代码,就可以将您的分析扩展到集群、GPU和云上运行。不需要重写你的代码或学习大数据编程和内存外技术。
my-assignmentexpert™ matlab作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的matlab作业代写作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此matlab作业代写作业代写的价格不固定。通常在matlab专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在matlab作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在matlab作业代写方面经验极为丰富,各种matlab作业代写相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的matlab作业代写及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 数据分析
- 数值与符号计算
- 工程与科学绘图
- 控制系统设计
- 航天工业
- 汽车工业
- 生物医学工程
- 语音处理
运筹学代写
数学代写|matlab作业代写|Static Model with Perfect Demand Segmentation
This is the simplest model, where demand for classes occurs sequentially, $D_{n}$ first, and no customer is willing to switch to another class. To build a DP recursion, we may associate decision stages with classes, rather than time. Accordingly, the sequence of stages is indexed in decreasing order of $j: j=n, n-1, \ldots, 2,1$. We have to decide at each stage $j$ how much of the remaining capacity is offered to class $j$. The natural state variable is $s_{j}$, the integer number representing the residual capacity at the beginning of stage $j$; the initial state is $s_{n}=C$, the number of available seats on the aircraft. The overall objective is to find the maximum expected revenue that we may collect by selling the $C$ available seats to the $n$ classes, denoted by $V_{n}(C)$. To this aim, we need to find a sequence of value functions $V_{j}\left(s_{j}\right)$. If, at the end of the decision process (at aircraft takeoff), we still have a residual capacity $s_{0}>0$, this terminal state corresponds to unsold seats with no value. Thus, we apply the boundary condition
$$
V_{0}\left(s_{0}\right)=0, \quad s_{0}=0,1, \ldots, C,
$$
in order to initialize the DP recursion. We also assume that demands for different classes are independent random variables. Otherwise, we should apply a more complicated DP recursion, possibly accounting for learning effects. ${ }^{11}$
A rather surprising finding is that we may build the DP recursion by assuming the following event sequence, for each class $j$ :
- First, we observe demand $D_{j}$ for class $j$.
- Then, we decide how many requests for class $j$ to accept, a decision represented by the integer number $x_{j}$.
- Then, we collect revenue $p_{j} x_{j}$ and proceed to stage $j-1$, with the updated state variable $s_{j-1}=s_{j}-x_{j}$.
This does not seem plausible, as we are supposed to make decisions before observing demand. However, we shall prove below that the decision $x_{j}$ does not rely on the probability distribution of $D_{j}$. The intuition is that we do not really need to declare $x_{j}$ beforehand. We may observe each individual request for class $j$ sequentially, and each time we decide whether to accept it or not. If we reject a request, then we declare class $j$ closed.
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|Dynamic Model with Perfect Demand Segmentation
In this section we relax the assumption that demand for classes occur sequentially over disjoint time intervals, but we still assume a rigid market segmentation. This reintroduces time into the DP recursion, and we have to model a possibly timevarying customer arrival process. A simple model is obtained if we assume that time intervals are small enough that we may observe at most one arrival per time interval. ${ }^{12}$ Let us denote by $\lambda_{j}(t)$ the probability of an arrival for class $j$ during time interval $t, t=1, \ldots, T$. Since we assume a perfectly segmented market, these probabilities refer to independent events and must satisfy the consistency constraint:
$$
\sum_{j=1}^{n} \lambda_{j}(t) \leq 1, \quad \forall t
$$
The DP recursion in this case aims at finding value functions $V_{t}(s)$, where $s$ is residual capacity, subject to the boundary conditions
$$
\begin{aligned}
V_{t}(0) &=0, & t &=1, \ldots, T, \
V_{T+1}(s) &=0, & s &=0,1, \ldots, C,
\end{aligned}
$$
where $T+1$ denotes the end of the time horizon (when the aircraft takes off). We may denote by $R(t)$ the available revenue at time $t$, which is a random variable taking value $p_{j}$ when an arrival of class $j$ occurs, 0 otherwise. Whenever there is an arrival, we have to decide whether we accept the request or not, a decision that may be denoted by the binary decision variable $x$. As in the static model, we do not need to make a decision in advance, since we just need to react to a request. Hence, the DP recursion takes again the “swapped” form
$$
V_{t}(s)=\mathbb{E}\left{\max {x \in{0,1}}\left[R(t) x+V{t+1}(s-x)\right]\right}
$$
Using expected marginal values of capacity again, a policy in terms of protection levels may be devised. In this case, however, protection levels may be time-varying.
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|Dynamic Model with Customer Choice
In this last model, we also relax the assumption of perfectly segmented markets. This radically changes the approach, and we must define a model of customer choice. One way of doing so is to partition the market into segments and to estimate the fraction of passengers belonging to each segment, as well as the probability that a class will be purchased by a passenger of each segment, if she is offered that class.
The control decision, at each time instant $t$, is the subset of classes that we offer. Let $\mathcal{N}$ be the set of available classes, indexed by $j$ and associated with revenue $p_{j}$. It is convenient to introduce $p_{0}=0$, the zero revenue earned when there is a passenger willing to fly but, given the subset of classes currently offered, she decides not to purchase any ticket. Formally, a potential passenger request arrives at time $t$ with probability $\lambda$ and, given the offered subset of classes $\mathcal{S}{t} \subseteq \mathcal{N}={1, \ldots, n}$, she will make a choice. Let $P{j}\left(\mathcal{S}{t}\right)$ be the probability that the customer chooses class $j$, as a function of the offered set, where we include the probability $P{0}\left(\mathcal{S}{t}\right)$ of no-purchase. These probabilities may be estimated, based on the aforementioned market segmentation model, ${ }^{13}$ and they are subject to the natural constraints $$ \begin{array}{ll} P{j}(\mathcal{S}) \geq 0, & \mathcal{S} \subseteq \mathcal{N}, j \in \mathcal{S} \cup{0} \
\sum_{j \in \mathcal{S}} P_{j}(\mathcal{S})+P_{0}(\mathcal{S})=1, & \mathcal{S} \subseteq \mathcal{N}
\end{array}
$$
In this model, the decision variable is actually a set, i.e., the subset $\mathcal{S}{t}$ of classes offered at time $t$. The decision-dependent purchase probabilities at time $t$ are $$ \begin{array}{ll} \lambda P{j}\left(\mathcal{S}{t}\right), & j=1, \ldots, n \ (1-\lambda)+\lambda P{0}\left(\mathcal{S}_{t}\right), & j=0
\end{array}
$$
matlab代写
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|STATIC MODEL WITH PERFECT DEMAND SEGMENTATION
这是最简单的模型,对课程的需求是按顺序发生的,Dn首先,没有客户愿意换其他班。为了构建 DP 递归,我们可以将决策阶段与类相关联,而不是时间。因此,阶段的顺序按降序索引j:j=n,n−1,…,2,1. 我们必须在每个阶段做出决定j有多少剩余容量提供给班级j. 自然状态变量为sj, 表示阶段开始时剩余容量的整数j; 初始状态是sn=C, 飞机上的可用座位数。总体目标是找到我们可以通过出售C可用座位n类,表示为五n(C). 为此,我们需要找到一系列价值函数五j(sj). 如果,在决策过程结束时一种吨一种一世rCr一种F吨吨一种到和○FF,我们还有剩余容量s0>0,此最终状态对应于没有价值的未售出席位。因此,我们应用边界条件
五0(s0)=0,s0=0,1,…,C,
为了初始化DP递归。我们还假设不同类别的需求是独立的随机变量。否则,我们应该应用更复杂的 DP 递归,可能会考虑学习效果。11
一个相当令人惊讶的发现是,对于每个类,我们可以通过假设以下事件序列来构建 DP 递归j:
- 首先,我们观察需求Dj上课j.
- 然后,我们决定有多少类请求j接受,由整数表示的决定Xj.
- 然后,我们收集收入pjXj并进入舞台j−1, 更新后的状态变量sj−1=sj−Xj.
这似乎不太合理,因为我们应该在观察需求之前做出决定。但是,我们将在下面证明该决定Xj不依赖于概率分布Dj. 直觉是我们并不真的需要声明Xj预先。我们可能会观察每个单独的课程请求j依次,每次我们决定是否接受它。如果我们拒绝一个请求,那么我们声明类j关闭。
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|DYNAMIC MODEL WITH PERFECT DEMAND SEGMENTATION
在本节中,我们放宽了对类别的需求在不相交的时间间隔内顺序发生的假设,但我们仍然假设严格的市场细分。这将时间重新引入 DP 递归,我们必须对可能随时间变化的客户到达过程进行建模。如果我们假设时间间隔足够小,以至于每个时间间隔最多可以观察到一次到达,则可以得到一个简单的模型。12让我们用λj(吨)上课到达的概率j在时间间隔内吨,吨=1,…,吨. 由于我们假设一个完全分割的市场,这些概率指的是独立事件并且必须满足一致性约束:
∑j=1nλj(吨)≤1,∀吨
这种情况下的 DP 递归旨在找到价值函数五吨(s), 在哪里s是剩余容量,受边界条件约束
五吨(0)=0,吨=1,…,吨, 五吨+1(s)=0,s=0,1,…,C,
在哪里吨+1表示时间范围的结束在H和n吨H和一种一世rCr一种F吨吨一种到和s○FF. 我们可以表示为R(吨)当时的可用收入吨,这是一个随机变量取值pj下课时j发生,否则为 0。每当有到达时,我们必须决定是否接受请求,这个决定可以用二元决策变量表示X. 与静态模型一样,我们不需要提前做出决定,因为我们只需要对请求做出反应。因此,DP 递归再次采用“交换”形式
$$
V_{t}s=\mathbb{E}\left{\max {x \in{0,1}}\left[R吨x+V {t+1}s−X\right]\right}
$$
再次使用容量的预期边际值,可以设计保护级别方面的策略。然而,在这种情况下,保护级别可能会随时间变化。
数学代写|MATLAB作业代写|DYNAMIC MODEL WITH CUSTOMER CHOICE
在最后一个模型中,我们还放宽了完美细分市场的假设。这从根本上改变了方法,我们必须定义一个客户选择模型。这样做的一种方法是将市场划分为多个部分,并估计属于每个部分的乘客的比例,以及如果为每个部分的乘客提供该类,则该类将被购买的概率。
控制决策,在每个时刻吨, 是我们提供的类的子集。让ñ是可用类的集合,由j并与收入相关pj. 方便介绍p0=0,当有乘客愿意飞行时获得的零收入,但鉴于目前提供的舱位子集,她决定不购买任何机票。正式地,潜在的乘客请求准时到达吨有概率λ并且,给定所提供的类子集 $p_{j}$. It is convenient to introduce $p_{0}=0$, the zero revenue earned when there is a passenger willing to fly but, given the subset of classes currently offered, she decides not to purchase any ticket. Formally, a potential passenger request arrives at time $t$ with probability $\lambda$ and, given the offered subset of classes $\mathcal{S}{t} \subseteq \mathcal{N}={1, \ldots, n}$, she will make a choice. Let $P{j}\left(\mathcal{S}{t}\right)$ be the probability that the customer chooses class $j$, as a function of the offered set, where we include the probability $P{0}\left(\mathcal{S}_{t}\right)$ of no-purchase. These probabilities may be estimated, based on the aforementioned market segmentation model, ${ }^{13}$ and they are subject to the natural constraints
在这个模型中,决策变量实际上是一个集合,即子集
\begin{array}{ll}
\lambda P_{j}\left(\mathcal{S}{t}\right), & j=1, \ldots, n \ (1-\lambda)+\lambda P{0}\left(\mathcal{S}_{t}\right), & j=0
\end{array}
统计代考
统计是汉语中的“统计”原有合计或汇总计算的意思。 英语中的“统计”(Statistics)一词来源于拉丁语status,是指各种现象的状态或状况。
数论代考
数论(number theory ),是纯粹数学的分支之一,主要研究整数的性质。 整数可以是方程式的解(丢番图方程)。 有些解析函数(像黎曼ζ函数)中包括了一些整数、质数的性质,透过这些函数也可以了解一些数论的问题。 透过数论也可以建立实数和有理数之间的关系,并且用有理数来逼近实数(丢番图逼近)
数值分析代考
数值分析NumericalAnalysis,又名“计算方法”,是研究分析用计算机求解数学计算问题的数值计算方法及其理论的学科。 它以数字计算机求解数学问题的理论和方法为研究对象,为计算数学的主体部分。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
MATLAB代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。