如果你也在 怎样代写有机化学organic chemistry这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。有机化学organic chemistry是化学的一个分支,研究含有碳-碳共价键的有机化合物的结构、性质和反应。对性质的研究包括物理和化学性质,以及对化学反应性的评估,以了解其行为。有机反应的研究包括天然产品、药物和聚合物的化学合成,以及在实验室和通过理论(in silico)研究单个有机分子。
有机化学organic chemistry研究的化学品范围包括碳氢化合物(只含碳和氢的化合物)以及以碳为基础但也含有其他元素的化合物,特别是氧、氮、硫、磷(包括在许多生化制品中)和卤素。有机金属化学是研究含有碳-金属键的化合物。此外,当代研究的重点是涉及其他有机金属的有机化学,包括镧系元素,但特别是过渡金属锌、铜、钯、镍、钴、钛和铬。
my-assignmentexpert™ 有机化学organic chemistry作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的有机化学organic chemistry作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此有机化学organic chemistry作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在化学Chemical作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的化学Chemical代写服务。我们的专家在有机化学organic chemistry代写方面经验极为丰富,各种有机化学organic chemistry相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的有机化学organic chemistry及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考|Bonding and Preferred Geometries in C Radicals, Carbenium Ions and Carbanions
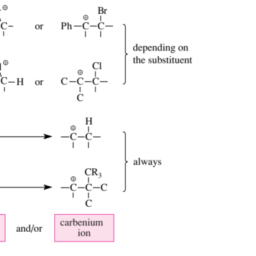
At the so-called radical center an organic radical R. has an electron septet, which is an electron deficiency in comparison to the electron octet of valence-saturated compounds. Carbon atoms are the most frequently found radical centers and most often have three neighbors (see below). Carbon-centered radicals with their electron septet occupy an intermediate position between the carbenium ions, which have one electron less (electron sextet at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$ atom), and the carbanions, which have one electron more (electron octet at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$ atom). Since there is an electron deficiency present both in $\mathrm{C}$ radicals and in carbenium ions, the latter are more closely related to each other than $\mathrm{C}$ radicals are related to carbanions. Because of this, $\mathrm{C}$ radicals and carbenium ions are also stabilized or destabilized by the same substituents.
Nitrogen-centered radicals $\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right){2} \mathrm{~N}$ · or oxygen-centered radicals $\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right) \mathrm{O} \cdot$ are less stable than $\mathrm{C}$-centered radicals $\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right)_{3} \mathrm{C}$. They are higher in energy because of the higher electronegativity of these elements relative to carbon. Nitrogen- or oxgencentered radicals of the cited substitution pattern consequently have only a limited chance to exist. Which geometries are preferred at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$ atom of $\mathrm{C}$ radicals, and how do they differ from those of carbenium ions or carbanions? And what types of bonding are found at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$ atoms of these three species? It is simplest to clarify the preferred geometries first (Section 1.1.1). As soon as these geometries are known, molecular orbital (MO) theory will be used to provide a description of the bonding (Section 1.1.2).
We will discuss the preferred geometries and the MO descriptions of C radicals and the corresponding carbenium ions or carbanions in two parts. In the first part we will examine $\mathrm{C}$ radicals, carbenium ions, and carbanions with a trivalent central $\mathrm{C}$ atom. The second part treats the analogous species with a divalent central $\mathrm{C}$ atom. A third part (species with a monovalent central C atom) can be dispensed with because the only species of this type that is important in organic chemistry is the alkynyl anion, which, however, is of no interest here.
化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考|Stability of Radicals
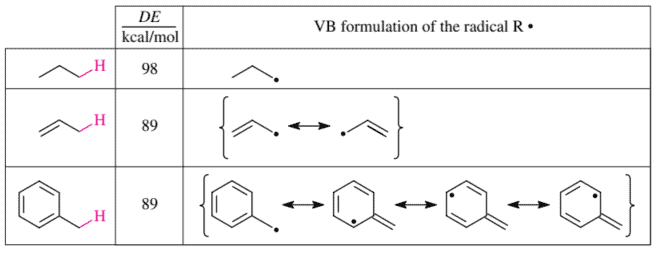
Stability in chemistry is not an absolute but a relative concept. It always refers to a stability difference with respect to a reference compound. Let us consider the standard heats of reaction $\Delta H^{0}$ of the dissociation reaction $\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{H} \rightarrow \mathrm{R} \cdot+\mathrm{H} \cdot$, that is, the dissociation enthalpy (DE) of the broken C-H bond. It reflects, on the one hand, the strength of this $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ bond and, on the other hand, the stability of the radical R-produced. As you see immediately, the dissociation enthalpy of the $\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{H}$ bond depends in many ways on the structure of $R$. But it is not possible to tell clearly whether this is due to an effect on the bond energy of the broken $\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{H}$ bond and/or an effect on the stability of the radical $R \cdot$ that is formed.
To what must one ascribe, for example, the fact that the dissociation enthalpy of $\mathrm{a}^{s p} \mathrm{C}^{n}-\mathrm{H}$ bond depends essentially on $n$ alone and increases in the order $n=3,2$, and 1 ?
To help answer this question it is worthwhile considering the following: the dissociation enthalpies of bonds such as $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{O}, \mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{Cl}$, and $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{Br}$ also depend heavily on $n$ and increase in the same order, $n=3,2$, and 1. The extent of the $n$-dependence of the dissocation energies depends on the element which is cleaved off. This is only possible if the $n$-dependence reflects, at least in part, an $n$-dependence of the respective $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}$-element bond. (Bond enthalpy tables in all textbooks ignore element but not on the value of $n$ !) Hence, the bond enthalpy of every $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}-\mathrm{element}}$ bond increases in the order $n=3,2$, and 1. This is so because all $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-$ element bonds become shorter in the same order. This in turn is due to the $s$ character of the $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{el}-$ ement bond, which increases in the same direction.
An immediate consequence of the different ease with which $\mathrm{C}_{s p^{n}}$-element bonds dissociate is that in radical substitution reactions, alkyl radicals are preferentially formed. Only in exceptional cases are vinyl or aryl radicals formed. Alkynyl radicals do not appear at all in radical substitution reactions. In the following we therefore limit ourselves to a discussion of substitution reactions that take place via radicals of the general structure $\mathrm{R}^{1} \mathrm{R}^{2} \mathrm{R}^{3} \mathrm{C}$.
有机化学代写
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|BONDING AND PREFERRED GEOMETRIES IN C RADICALS, CARBENIUM IONS AND CARBANIONS
在所谓的自由基中心,有机自由基 R. 有一个电子八位组,与价饱和化合物的电子八位组相比,这是一个电子缺陷。碳原子是最常见的自由基中心,最常见的是三个邻居s和和b和l这在. 以碳为中心的自由基及其电子 septet 占据碳离子之间的中间位置,碳离子少一个电子和l和C吨r这ns和X吨和吨一种吨吨H和在一种l和nC和−在ns一种吨在r一种吨和d$C$一种吨这米,以及多一个电子的碳负离子和l和C吨r这n这C吨和吨一种吨吨H和在一种l和nC和−在ns一种吨在r一种吨和d$C$一种吨这米. 由于两者都存在电子缺陷C自由基和碳鎓离子,后者比C自由基与碳负离子有关。因为这,C自由基和碳鎓离子也被相同的取代基稳定或不稳定。
以氮为中心的自由基$\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right){2} \mathrm{~N}$ · or oxygen-centered radicals $\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right) \mathrm{O} \cdot$ are less stable than $\mathrm{C}$-centered radicals $\left(\mathrm{R}{s p^{3}}\right)_{3} \mathrm{C}$. They are higher in energy because of the higher electronegativity of these elements relative to carbon. Nitrogen- or oxgencentered radicals of the cited substitution pattern consequently have only a limited chance to exist. Which geometries are preferred at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$ atom of $\mathrm{C}$ radicals, and how do they differ from those of carbenium ions or carbanions? And what types of bonding are found at the valence-unsaturated $\mathrm{C}$这三个物种的原子?首先明确首选几何形状是最简单的小号和C吨一世这n1.1.1. 一旦知道这些几何形状,分子轨道米这理论将用于提供键合的描述小号和C吨一世这n1.1.2.
我们将分两部分讨论 C 自由基和相应的碳正离子或碳负离子的优选几何形状和 MO 描述。在第一部分中,我们将检查C自由基、碳正离子和具有三价中心的碳负离子C原子。第二部分处理具有二价中心的类似物种C原子。第三部分sp和C一世和s在一世吨H一种米这n这在一种l和n吨C和n吨r一种lC一种吨这米可以省略,因为在有机化学中唯一重要的这种类型是炔基阴离子,然而,这里并不感兴趣。
化学代写|有机化学代写ORGANIC CHEMISTRY代考|STABILITY OF RADICALS
化学稳定性不是一个绝对的概念,而是一个相对的概念。它总是指相对于参考化合物的稳定性差异。让我们考虑标准反应热ΔH0解离反应R−H→R⋅+H⋅,即解离焓D和断裂的 CH 键。一方面反映了这种力量C−H另一方面,R-产生的自由基的稳定性。正如你立即看到的,解离焓R−H键在许多方面取决于结构R. 但无法清楚地判断这是否是由于对断裂键能的影响R−H键和/或对自由基稳定性的影响R⋅即形成。
例如,必须归因于这样一个事实,即一种spCn−H债券本质上取决于n单独并按顺序增加n=3,2, 和 1 ?
为了帮助回答这个问题,值得考虑以下问题:键的解离焓,例如$\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{O}, \mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{Cl}$, and $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{Br}$ also depend heavily on $n$ and increase in the same order, $n=3,2$, and 1. The extent of the $n$-dependence of the dissocation energies depends on the element which is cleaved off. This is only possible if the $n$-dependence reflects, at least in part, an $n$-dependence of the respective $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}$-element bond. (Bond enthalpy tables in all textbooks ignore element but not on the value of $n$ !) Hence, the bond enthalpy of every $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}-\mathrm{element}}$ bond increases in the order $n=3,2$, and 1. This is so because all $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-$ element bonds become shorter in the same order. This in turn is due to the $s$ character of the $\mathrm{C}{s p^{n}}-\mathrm{el}-$元素键,以相同方向增加。
不同的便利性的直接后果Cspn元素键解离是在自由基取代反应中,优先形成烷基自由基。只有在特殊情况下才会形成乙烯基或芳基。炔基自由基根本不会出现在自由基取代反应中。因此,在下文中,我们仅限于讨论通过一般结构的自由基发生的取代反应R1R2R3C.

化学代写|有机化学代写organic chemistry代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。