如果你也在 怎样代写金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics是使用统计方法来发展理论或检验经济学或金融学的现有假设。计量经济学依靠的是回归模型和无效假设检验等技术。计量经济学也可用于尝试预测未来的经济或金融趋势。
金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics的一个基本工具是多元线性回归模型。计量经济学理论使用统计理论和数理统计来评估和发展计量经济学方法。计量经济学家试图找到具有理想统计特性的估计器,包括无偏性、效率和一致性。应用计量经济学使用理论计量经济学和现实世界的数据来评估经济理论,开发计量经济学模型,分析经济历史和预测。
金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics 免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此金融计量经济学Financial Econometrics作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在经济Economy代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的经济Economy代写服务。我们的专家在微观经济学Microeconomics代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微观经济学Microeconomics相关的作业也就用不着 说。
经济代写|计量经济学代写Introduction to Econometrics代考|Motivation
The European Central Bank (ECB) seems to have been successful anchoring inflation expectations since the launching of the euro up to the Great Recession (GR). However, one can ask if this has been just as a result of good luck or good policy. To reach its final target in terms of inflation, the ECB monitors and controls some intermediate variables that work as medium targets. The ECB’s approach to organizing, evaluating and cross-checking the information relevant for assessing the risks to price stability is based on two analytical perspectives, referred to as the “two pillars”: economic analysis and monetary analysis. The historical importance of money growth on inflation changes has been well established in the literature (Friedman and Schwartz 1963; Crowder 1998; Haug and Dewald 2012). This is the reason why the study of the stability of the money demand function is of such a great importance. Nevertheless, for this function to be stable, the velocity of circulation of money should not change or, at least, its deviations from its long-run value should not be permanent.
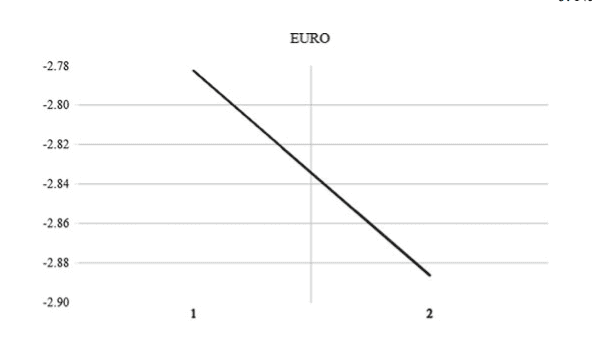
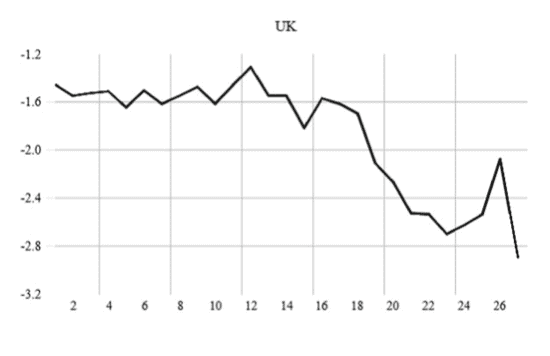
In the euro area (EA), the decoupling between interest rates, money supply and inflation started from the very first moment of its creation. However, recent developments in M3 velocity in the EA have seriously questioned the reliability of M3 growth as a pillar of the ECB’s monetary policy strategy. In fact, since 2001, M3 growth has systematically exceeded its reference value without a clear effect on inflation. Thus, the ECB has actually been an inflation targeter in deeds and a monetary targeter in words only. Overall, inflation has not diverged much from its $2 \%$ target, if anything, has been below and currently is struggling to return to $2 \%$. Since 2000 2001 , the income velocity of M3 has declined at a stable rate, close to $3.5 \%$, and this fall has accelerated from 2015 with the more recent enhanced asset purchase programs (APPs). These results tend to show that fundamental changes in M3 velocity trends relative to its historical patterns have occurred and we argue that this should be made explicit in the derivation of the reference value. During the mid-70s and mid80s, the key challenge for central banks in OECD countries was very high inflation, not too low. Since then, countries that progressively adopted an inflation-targeting strategy experienced a reduction in the level of inflation that was accompanied by a decline in the volatility of inflation together with an improved anchoring of inflation expectations. However, after the global financial crisis, this approach has received criticism.
经济代写|计量经济学代写Introduction to Econometrics代考|The Inflation Puzzle and Money Velocity in the EA: Theoretical and Empirical Issues
The quantity theory of money (QTM) predicts a positive relationship between monetary growth and inflation. However, even if inflation truly were a monetary phenomenon in the long run, as stated in Friedman (1963) seminal book, a conventional vector cointegration approach does not necessarily identify the long-run relation between money and prices correctly, because it neglects the structural development of the velocity of money. Since excess supply and demand of money are captured by transitory movements of velocity in a world where real and nominal rigidities prevail, the identification of excess liquidity that endangers price stability is tied to the identification of equilibrium velocity.
In general, evidence from cross-country studies strongly supports the one-to-one correlation of average money growth and average inflation. However, the impact of money on prices is hard to identify within one country. De Grauwe and Polan (2005) have argued that the long-run link between nominal money growth and inflation might be much looser than commonly assumed in countries which have operated in moderate inflation environments as it is the case of the EA.
Flexible inflation targeting implies that the central bank attempts to reach the target gradually in the medium term and not in the immediate period. As recently stressed by Cochrane (2017), existing theories of inflation make straight predictions. The Keynesian school argues that velocity is a highly fluctuating variable which is significantly affected by economic policies. As a result, changes in velocity could nullify the effects of monetary policy. They stress that the velocity of money is severely affected by demand management policies; hence, it is a non-stationary variable. Furthermore, they argue that the movements of velocity are the opposite of the movement of money supply. Interest rate is also regarded as one of the variables influencing velocity. The opposite forecast is made by monetarist models, who predict that, as provided the velocity is “stable” in the long run, a massive increase in reserves must lead to galloping inflation. Yet, none of these predictions have proved right. This issue was already central to the debates of the 1950 s and 1960 s between Keynesians and monetarists. Keynesians thought that at the zero rates of the Great Depression, money and bonds were perfect substitutes, so monetary policy could do nothing, and advocated fiscal stimulus instead. On the contrary, monetarists held that additional money, even at zero rates, would be stimulative; therefore, the failure to provide additional money was the big monetary policy mistake of that time. The view that inflation is always a monetary phenomenon has a long tradition based on the quantity theory of money. In its simplest form, the QTM states that changes in money supply growth are followed by equal changes in the inflation rate and, through the force of the Fisher effect, in the nominal interest rate.
计量经济学代写
经济代写|计量经济学代写Introduction to Econometrics代考|Motivation
欧洲中央银行(ECB)似乎已经成功地锚定了通胀预期,从推出欧元到大衰退(GR)。然而,有人会问,这是否只是运气好或政策好。为了达到通胀的最终目标,欧洲央行监测和控制了一些中间变量,这些变量起到了中间目标的作用。欧洲央行组织、评估和交叉核查与评估价格稳定风险相关的信息的方法是基于两种分析视角,即“两大支柱”:经济分析和货币分析。货币增长对通货膨胀变化的历史重要性已经在文献中得到了很好的证实(Friedman and Schwartz 1963;克劳德1998;Haug and Dewald 2012)。这就是为什么研究货币需求函数的稳定性具有如此重要的意义。然而,为了使这一功能稳定,货币的流通速度不应该改变,或者至少,货币对其长期价值的偏离不应该是永久性的。
在欧元区(EA),利率、货币供应和通货膨胀之间的脱钩从创立之初就开始了。然而,欧洲央行最近M3速度的发展严重质疑了M3增长作为欧洲央行货币政策战略支柱的可靠性。事实上,自2001年以来,M3增长系统性地超过了参考值,但对通胀没有明显影响。因此,欧洲央行实际上是一个实际的通胀目标,而只是口头上的货币目标。总体而言,通胀并没有偏离2%的目标太远,如果有的话,那就是一直低于2%,目前正在努力重返2%。自2000年至2001年以来,M3的收入速度以稳定的速度下降,接近3.5%,并且随着最近加强的资产购买计划(app),这种下降从2015年开始加速。这些结果倾向于表明M3速度趋势相对于其历史模式已经发生了根本性的变化,我们认为这应该在参考值的推导中明确说明。在70年代中期和80年代中期,经合组织国家央行面临的主要挑战是非常高的通胀,而不是过低的通胀。从那时起,逐步采用通胀目标制战略的国家经历了通胀水平的下降,伴随着通胀波动性的下降,以及通胀预期锚定的改善。然而,在全球金融危机之后,这种方法受到了批评。
经济代写|计量经济学代写Introduction to Econometrics代考|The Inflation Puzzle and Money Velocity in the EA: Theoretical and Empirical Issues
货币数量理论(QTM)预测货币增长与通货膨胀呈正相关。然而,即使通货膨胀确实是一种长期的货币现象,正如弗里德曼(1963)的影响深远的著作所述,传统的矢量协整方法也不一定能正确地识别货币与价格之间的长期关系,因为它忽略了货币流通速度的结构性发展。由于在一个实际刚性和名义刚性占主导地位的世界里,货币的过剩供给和需求被短暂的流通速度运动所捕捉,因此,识别危及价格稳定的过剩流动性与识别均衡流通速度是联系在一起的。
总的来说,来自跨国研究的证据强烈支持平均货币增长和平均通货膨胀之间的一对一相关性。然而,货币对价格的影响很难在一个国家内确定。De Grauwe和Polan(2005)认为,名义货币增长和通胀之间的长期联系可能比在温和通胀环境下运行的国家(如EA的情况)通常假设的要宽松得多。
灵活的通胀目标制意味着央行试图在中期逐步达到目标,而不是在近期。正如科克伦(2017)最近强调的那样,现有的通货膨胀理论做出了直接的预测。凯恩斯学派认为,流通速度是一个高度波动的变量,受经济政策的显著影响。因此,流通速度的变化可能会抵消货币政策的影响。他们强调,货币流通速度受到需求管理政策的严重影响;因此,它是一个非平稳变量。此外,他们认为流通速度的变动与货币供给的变动是相反的。利率也被认为是影响速度的变量之一。货币主义模型做出了相反的预测,他们预测,如果从长远来看,流通速度是“稳定的”,那么大量增加的外汇储备必然会导致通货膨胀。然而,这些预测都没有被证明是正确的。这个问题已经成为上世纪五六十年代凯恩斯主义者和货币主义者之间辩论的核心。凯恩斯主义者认为,在大萧条时期的零利率下,货币和债券是完美的替代品,因此货币政策无能为力,并主张财政刺激。相反,货币主义者认为,即使在零利率的情况下,增加货币供应量也会起到刺激作用;因此,未能提供额外资金是当时重大的货币政策错误。基于货币数量理论的通货膨胀始终是一种货币现象的观点有着悠久的传统。在其最简单的形式中,QTM指出,货币供应增长的变化之后,通货膨胀率和名义利率的变化是相等的,通过费雪效应的力量。
经济代写|计量经济学代考ECONOMETRICS代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。