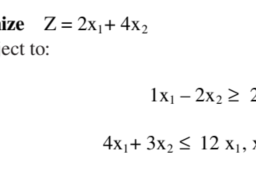如果你也在 怎样代写运筹学Operations Research这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。假设检验Hypothesis是假设检验是统计学中的一种行为,分析者据此检验有关人口参数的假设。分析师采用的方法取决于所用数据的性质和分析的原因。假设检验是通过使用样本数据来评估假设的合理性。
运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
二战中运筹学的应用
在二战时期,作战研究被定义为 “一种科学方法,为执行部门提供有关其控制的行动的决策的量化依据”。它的其他名称包括作战分析(英国国防部从1962年开始)和定量管理。
在第二次世界大战期间,英国有近1000名男女从事作战研究。大约有200名作战研究科学家为英国军队工作。
帕特里克-布莱克特在战争期间为几个不同的组织工作。战争初期,在为皇家飞机研究所(RAE)工作时,他建立了一个被称为 “马戏团 “的团队,帮助减少了击落一架敌机所需的防空炮弹数量,从不列颠战役开始时的平均超过20,000发减少到1941年的4,000发。
my-assignmentexpert™ 运筹学Operations Research作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在运筹学Operations Research作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的假设检验Hypothesis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 商业分析 Business Analysis
- 计算机科学 Computer Science
- 数据挖掘/数据科学/大数据 Data Mining / Data Science / Big Data
- 决策分析 Decision Analytics
- 金融工程 Financial Engineering
- 数据预测 Data Forecasting
- 博弈论 Game Theory
- 地理/地理信息科学 Geography/Geographic Information Science
- 图论 Graph Theory
- 工业工程 Industrial Engineering
- 库存控制 Inventory control
- 数学建模 Mathematical Modeling
- 数学优化 Mathematical Optimization
- 概率和统计 Probability and statistics
- 排队论 Queueing theory
- 社交网络/交通预测模型 Social network/traffic prediction modeling
- 随机过程 Stochastic processes
- 供应链管理 Supply chain management
运筹学代写
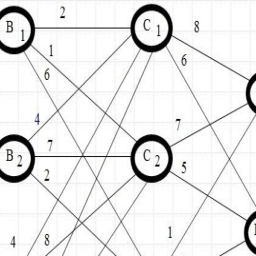
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|Least Cost Method
This method involves the following steps:
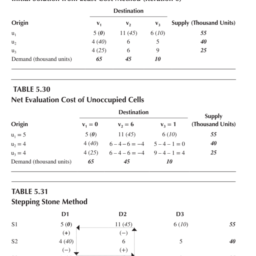
i. Find the least cost cell in entire cost matrix. In Table 5.3, routes $\mathrm{S} 2-\mathrm{D} 1$ and $\mathrm{S} 3$ – D1 each qualifies for minimum cost condition. Both have a transportation cost of $\$ 4$ per unit. In case of situation of tie, the cell with the maximum allocation is selected. For route $S 2$ – D1, the allocation of number of units
would be 40 , whereas that of S3-D1 would be 25 . The concept is that the maximum number of units should be transported at least possible cost. Thus, cell $\mathrm{a}{21}$ implying cost per unit of route $\mathrm{S} 2$ – D1 is selected. Allocate the number of units required or available. If demand is more than supply, assign the number of available units and if supply is more than demand, assign the number of units required. Supply centre $S 2$ can produce a fixed quantity of 40 units whereas demand of D1 centre is fixed quantity of 65 units. So Southfield manufacturing facility can provide only this much of products to Marysville plant. The remaining demand of 25 units of D1 is yet to be fulfilled. But production capacity is fully utilized. So any resource that is fully utilized and becomes zero should be struck off as shown in Table 5.4. ii. The next minimum cost cell is $\mathrm{a}{31}$ indicating transportation cost of Rs. 4 per unit through route $\mathrm{S} 3$ – D1. As demand is of only 25 units from available 25 units so 25 units would be allocated and column D1 as well as row S3 would be struck off.
iii. Cell $\mathrm{a}{12}$ indicating route $\mathrm{S} 1-\mathrm{D} 2$ is allocated 45 units. iv. Cell $\mathrm{a}{13}$ indicating route $\mathrm{S} 1-\mathrm{D} 3$ is allocated 10 units.
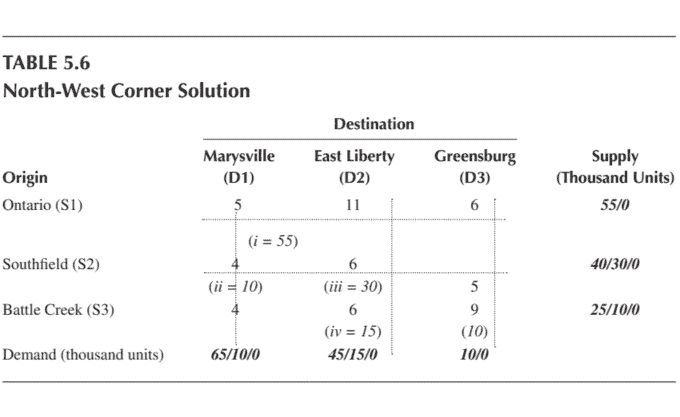
Summary of least cost method findings in sequential form and calculation of total cost is shown in Table 5.5.
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|North-West Corner Method
This method involves the following steps:
i. As the name suggests begin allocation of units from North-West cell of cost matrix, which is $\mathrm{a}_{11}$ cell.
ii. Allocate the number of units required or available, i.e.
- If demand is more than supply set, the cell equal to supply and proceed vertically.
- If demand is less than supply set, the cell equal to demand and proceed horizontally.
- If demand is equal to supply, proceed diagonally.
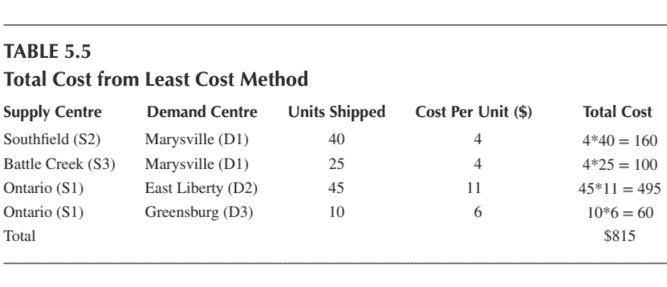
These steps are detailed as under (Table 5.6) by using same example shown in Table 5.3.
iii. Starting from first cell i.e. $\mathrm{a}{11}$ indicating route $\mathrm{S} 1-\mathrm{D} 1$ supply is 55 units and demand is 65 units. As requirement is more than available so only 55 units are allocated to this cell. Remaining demand of 10 units needs to be satisfied from other sources. This allocation finishes supply of S1 so row 1 is eliminated shown by dashed line. Next allocation would be done to cell following rule of that if demand is more than supply so proceed vertically. So allocation would be done to cell $\mathrm{a}{21}$.
iv. The remaining demand of D1 of 10 units is allocated to cell $\mathrm{a}{21}$ indicating route S2 – D1. S2 is left with 30 units. As demand is less than supply so next allocation would be done to the cell by moving horizontally. Therefore, the allocation would be done to cell $\mathrm{a}{22}$.
v. Demand of demand centre D2 is 45 units and available are 30 from S2. So 30 units are allocated to cell $\mathrm{a}_{22}$.
运筹学代考
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|LEAST COST METHOD
该方法包括以下步骤:
i.在整个成本矩阵中找到成本最低的单元格。在表 5.3 中,路线小号2−D1和小号3– D1 每个都符合最低成本条件。两者的运输成本为$4每单位。在平局的情况下,选择分配最大的小区。对于路线小号2– D1,分配单元数
iii. Cell a12 indicating route S1 – D2 is allocated 45 units.
iv. Cell a13 indicating route S1 – D3 is allocated 10 units.
被分配了 10 个单位。
表 5.5 以顺序形式总结了最低成本方法的结果和总成本的计算。
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|NORTH-WEST CORNER METHOD
该方法包括以下步骤:
i.顾名思义,从成本矩阵的西北单元开始分配单位,即一种11细胞。
ii. 分配所需或可用的单位数量,即
- 如果需求大于供给集合,则单元格等于供给并垂直进行。
- 如果需求小于供给集合,则单元格等于需求并水平进行。
- 如果需求等于供给,则沿对角线进行。
这些步骤详细如下吨一种b一世和5.6使用表 5.3 中所示的相同示例。
iii. 从第一个单元格开始,
iii. Starting from first cell i.e. $\mathrm{a}{11}$ indicating route $\mathrm{Sl}$ – Dl supply is 55 units and demand is 65 units. As requirement is more than available so only 55 units are allocated to this cell. Remaining demand of 10 units needs to be satisfied from other sources. This allocation finishes supply of Sl so row I is eliminated shown by dashed line. Next allocation would be done to cell following rule of that if demand is more than supply so proceed vertically. So allocation would be done to cell $\mathrm{a}{21}$.
iv. The remaining demand of Dl of 10 units is allocated to cell $a_{21}$ indicating route S2 – D1. S2 is left with 30 units. As demand is less than supply so next allocation would be done to the cell by moving horizontally. Therefore, the allocation would be done to cell $\mathrm{a}{22}$. v. Demand of demand centre D2 is 45 units and available are 30 from S2.