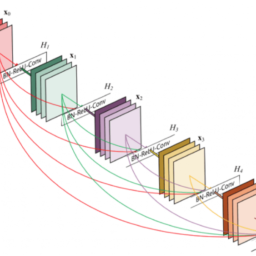
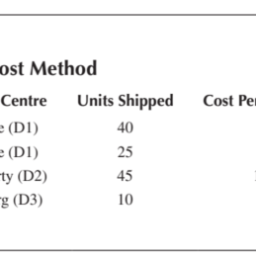
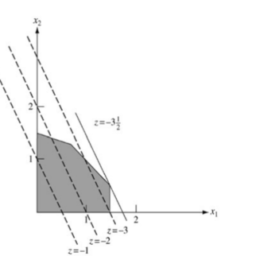
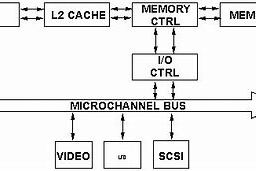
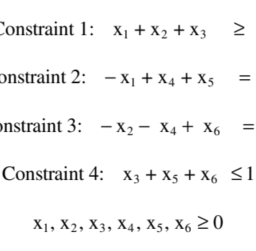如果你也在 怎样代写运筹学Operations Research这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。假设检验Hypothesis是假设检验是统计学中的一种行为,分析者据此检验有关人口参数的假设。分析师采用的方法取决于所用数据的性质和分析的原因。假设检验是通过使用样本数据来评估假设的合理性。
运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
二战中运筹学的应用
在二战时期,作战研究被定义为 “一种科学方法,为执行部门提供有关其控制的行动的决策的量化依据”。它的其他名称包括作战分析(英国国防部从1962年开始)和定量管理。
在第二次世界大战期间,英国有近1000名男女从事作战研究。大约有200名作战研究科学家为英国军队工作。
帕特里克-布莱克特在战争期间为几个不同的组织工作。战争初期,在为皇家飞机研究所(RAE)工作时,他建立了一个被称为 “马戏团 “的团队,帮助减少了击落一架敌机所需的防空炮弹数量,从不列颠战役开始时的平均超过20,000发减少到1941年的4,000发。
my-assignmentexpert™ 运筹学Operations Research作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在运筹学Operations Research作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的假设检验Hypothesis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 商业分析 Business Analysis
- 计算机科学 Computer Science
- 数据挖掘/数据科学/大数据 Data Mining / Data Science / Big Data
- 决策分析 Decision Analytics
- 金融工程 Financial Engineering
- 数据预测 Data Forecasting
- 博弈论 Game Theory
- 地理/地理信息科学 Geography/Geographic Information Science
- 图论 Graph Theory
- 工业工程 Industrial Engineering
- 库存控制 Inventory control
- 数学建模 Mathematical Modeling
- 数学优化 Mathematical Optimization
- 概率和统计 Probability and statistics
- 排队论 Queueing theory
- 社交网络/交通预测模型 Social network/traffic prediction modeling
- 随机过程 Stochastic processes
- 供应链管理 Supply chain management
运筹学代写
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|Properties and complexity
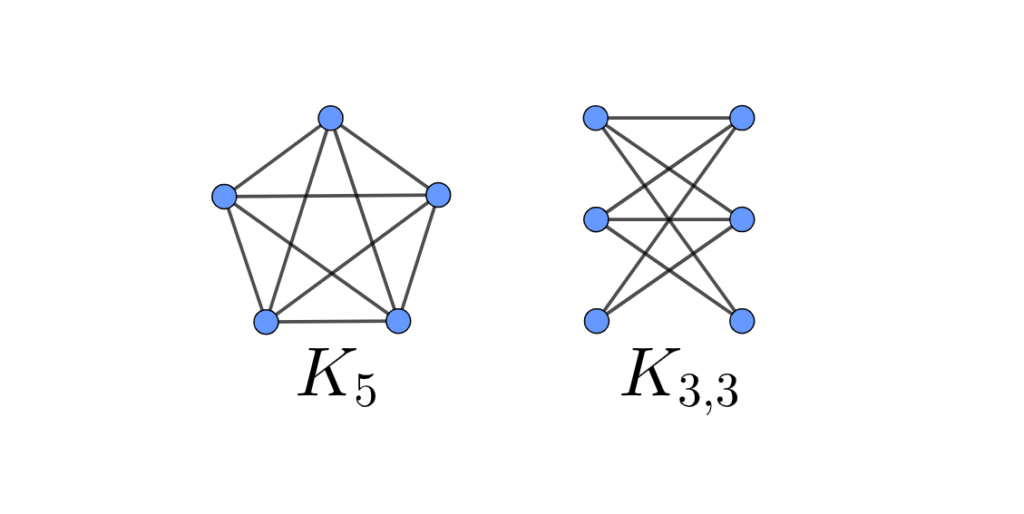
Liu and Geldmacher (1976) have shown that, any graph with no subgraph homomorphic to $K_{4}$ can be recursively transformed, by applying four transformation rules (see Definition $2.7$ below), to a single vertex. They have further devised a linear time algorithm that can decide whether a graph has a subgraph homomorphic to $K_{4}$ (Liu and Geldmacher 1980).
Definition 2.7 Let $G^{\prime}$ be the resultant graph after applying four transformation rules $T_{1}, T_{2}, T_{3}$ and $T_{4}$ to a graph $G$ until none of the rules can be further applied, where
$T_{1}:$ Replace a loop vv with a vertex $v$.
$T_{2}$ : Replace a dangling edge uv with a vertex $u$.
$T_{3}$ : Replace a pair of series edges $u v$ and vw with an edge uw.
$T_{4}$ : Replace a pair of parallel edges uv and uv with an edge $u v$.
If $G^{\prime}$ consists of only one single vertex, then we say $G$ is reducible. Otherwise, we say $G$ is nonreducible.
Note that in the definition above we follow Liu and Geldmacher (1976) to use the terminology “reducible”, which is different from the terminology “reducible” used in the NP-completeness analysis (see Section 3.2).
The following two properties are established in Liu and Geldmacher $(1976)$.
Property 2.1 If $T_{1}, T_{2}, T_{3}$ and $T_{4}$ are applied to a graph until no longer possible, then a unique graph results, independent of the sequence of application of $T_{1}, T_{2}, T_{3}$ and $T_{4}$.
Property 2.2 A graph $G$ is nonreducible if and only if it contains a subgraph homomorphic to $K_{4}$.
Corresponding to the concept of reducible graph, we define the terminology of “reducible network” as follows.
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|An exact algorithm
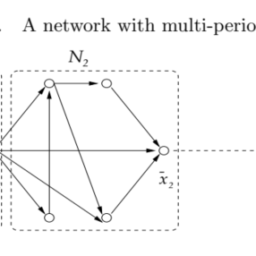
Recall that we consider time-varying networks with no parallel arcs, that is, there do not exist two arcs of the same direction between two vertices. It is possible to have, however, two arcs of opposite directions between two vertices. To simplify the presentation in figures, in this section we will use a link to indicate a single arc or a pair of opposite arcs between two vertices.
Let us first examine the following two special cases.
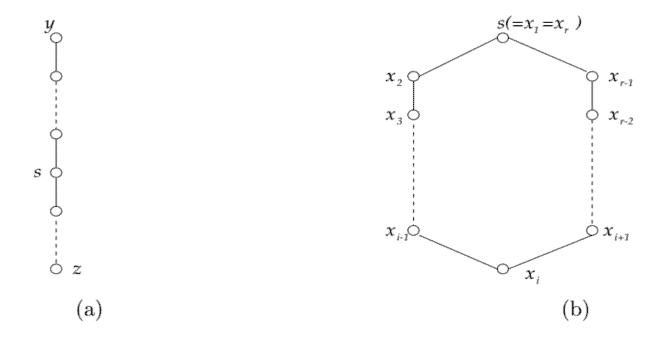
Case I. The network $N$ under consideration is shown in Figure 2.7(a), where $s$ is the source vertex. By Definition $2.5, d_{s, x}\left(x, t_{s}, t\right)$ is the cost of a shortest path from $s$ to $x$ within the time duration $\left[t_{s}, t\right]$ (Note that if such a path does not exist, then $\left.d_{s, x}\left(x, t_{s}, t\right)=\infty\right)$. Then, we can easily see that
$$
\zeta(T(\kappa))=d_{s, y}(y, 0, \kappa)+d_{s, z}(z, 0, \kappa)
$$
where $\zeta(T(\kappa))$ is the minimum cost of the spanning tree of $N$ within the time limit $\kappa$.
运筹学代考
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|PROPERTIES AND COMPLEXITY
刘和格尔德马赫1976已经证明,任何没有子图同态的图到4可以通过应用四个转换规则进行递归转换s和和D和F一世n一世吨一世这n$2.7$b和一世这在, 到单个顶点。他们进一步设计了一种线性时间算法,可以决定一个图是否具有同态的子图到4 大号一世你一种ndG和一世d米一种CH和r1980.
定义 2.7 让G′是应用四个变换规则后的结果图吨1,吨2,吨3和吨4到图G直到无法进一步应用任何规则,其中
吨1:用顶点替换循环 vvv.
吨2: 用顶点替换悬垂边 uv你.
吨3:替换一对系列边你v和带有边缘uw的大众。
吨4: 用一条边替换一对平行边 uv 和 uv你v.
如果G′只包含一个顶点,那么我们说G是可还原的。否则,我们说G是不可约的。
请注意,在上面的定义中,我们遵循 Liu 和 Geldmacher1976使用术语“reducible”,这与 NP-completeness 分析中使用的术语“reducible”不同s和和小号和C吨一世这n3.2.
在 Liu 和 Geldmacher 中建立了以下两个属性(1976).
属性 2.1 如果吨1,吨2,吨3和吨4被应用到一个图直到不再可能,然后一个唯一的图结果,独立于应用的顺序吨1,吨2,吨3和吨4.
属性 2.2 图表G不可约当且仅当它包含同态的子图到4.
对应于可约图的概念,我们将“可约网络”的术语定义如下。
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|AN EXACT ALGORITHM
回想一下,我们考虑了没有平行弧的时变网络,也就是说,两个顶点之间不存在两条相同方向的弧。然而,两个顶点之间可能有两条方向相反的弧。为了简化图中的表示,在本节中,我们将使用链接来指示两个顶点之间的单个弧或一对相反的弧。
让我们首先研究以下两种特殊情况。
案例一、网络ñ正在考虑的如图 2.7 所示一种, 在哪里s是源顶点。按定义2.5,ds,X(X,吨s,吨)是最短路径的成本s到X在持续时间内[吨s,吨] 请注意,如果这样的路径不存在,则 $\left.d_{s, x}\left(x, t_{s}, t\right请注意,如果这样的路径不存在,则
$$
\zeta(T(\kappa))=d_{s, y}(y, 0, \kappa)+d_{s, z}(z, 0, \kappa)
$$
where $\zeta(T(\kappa))$ is the minimum cost of the spanning tree of $N$ within the time limit $\kappa$.