如果你也在 怎样代写计算金融Computational finance这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。计算金融Computational finance是应用计算机科学的一个分支,处理金融中的实际利益问题。一些略有不同的定义是研究目前用于金融的数据和算法以及实现金融模型或系统的计算机程序的数学。
计算金融Computational finance强调实用的数字方法,而不是数学证明,并侧重于直接应用于经济分析的技术。它是数学金融学和数字方法之间的一个跨学科领域。两个主要领域是金融证券公允价值的有效和准确计算以及随机时间序列的建模。计算金融作为一门学科的诞生可以追溯到20世纪50年代初的哈里-马科维茨。马科维茨将投资组合的选择问题设想为均值-方差优化的一个练习。这需要比当时更多的计算机能力,所以他致力于研究有用的近似解决方案的算法。
my-assignmentexpert™ 计算金融Computational finance作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的计算金融Computational finance作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此计算金融Computational finance作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在计算金融project作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的计算金融project代写服务。我们的专家在计算金融Computational finance代写方面经验极为丰富,各种计算金融Computational finance相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的计算金融Computational finance及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
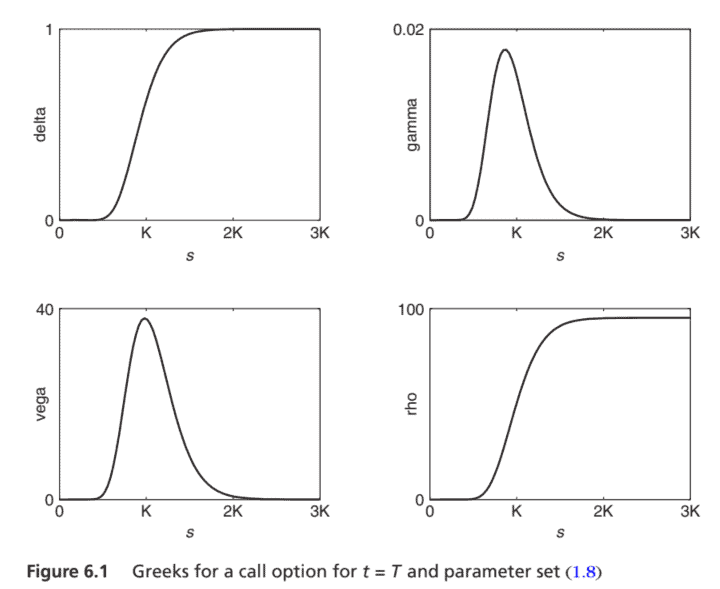
金融代写|计算金融project代写Computational finance代考|The Greeks
Along with the fair option values, the so-called Greeks are of key importance in financial practice. These quantities represent the sensitivities of an option value to changes in the underlying financial variables and parameters. A main use of Greeks is to bedge an option during its lifetime, that is, to reduce or eliminate risk. In mathematical terms, they are the partial derivatives of the option value with respect to its underlying variables and parameters.
In the Black-Scholes framework four well-known Greeks are delta $: \frac{\partial u}{\partial s}$, gamma: $\frac{\partial^{2} u}{\partial s^{2}}$, vega $: \frac{\partial u}{\partial \sigma}$, rho: $\frac{\partial u}{\partial r}$.
These quantify sensitivities to changes in, respectively, the underlying asset price (to first and second order), the volatility and the risk-free interest rate. Notice that vega is not an actual Greek letter. For a call option one can derive from (1.6a) the following formulas (whenever $s>0,0<t \leq T$ ):
$\begin{aligned} \text { delta: } & \mathcal{N}\left(d_{1}\right), \ \text { gamma: } & \mathcal{N}^{\prime}\left(d_{1}\right) /(s \sigma \sqrt{t}), \ \text { vega: } & s \sqrt{t} \mathcal{N}^{\prime}\left(d_{1}\right), \ \text { rho: } & t e^{-r t} K \mathcal{N}\left(d_{2}\right) . \end{aligned}$
金融代写|计算金融PROJECT代写COMPUTATIONAL FINANCE代考|Numerical Study
The basic approach for numerically approximating the Greeks is by straightforward use of finite differences. Here, given an option value for a set of variables and parameters, one computes one or more additional option values for perturbed (or “bumped”) values of the variable or parameter of interest while keeping all others fixed, and then computes an appropriate finite difference.
If a Greek appears itself as a term in the option valuation PDE, such as delta or gamma in the Black-Scholes PDE, then a finite difference approximation is directly available at essentially no cost, since it is intrinsic to the spatial discretization of the PDE. Hence, for each option value on the spatial grid, the value of this Greek is immediately at hand.
If a Greek does not appear itself in the option valuation PDE, then in the basic approach one numerically solves this PDE for (one, two or more) additional, perturbed values of the parameter of interest and then takes an appropriate finite difference. A more natural and efficient approach in this case is to numerically solve the PDE corresponding to this Greek, simultaneously with the PDE for the option value. This requires only little extra implementation work.
For a numerical illustration consider the call option under the Black-Scholes framework with parameter values (1.8). As in Chapter 5 , we truncate the spatial domain to $(0,3 K)$, select Dirichlet boundary conditions, semidiscretize on the nonuniform grid from Example 4.2.1 with second-order central formulas, using formula $B$ for convection, and employ cell averaging. The Greeks delta and gamma are then approximated by applying the second-order central formulas (4.7) and (4.8), respectively, to the obtained option values on the spatial grid. The Greek vega is approximated by numerically solving the PDE
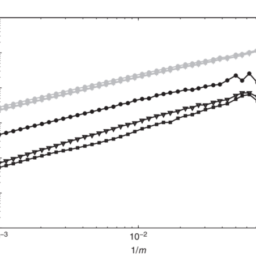
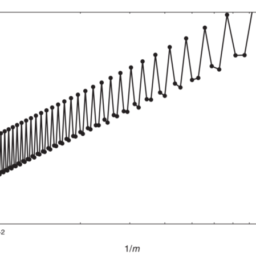
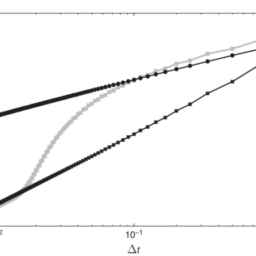
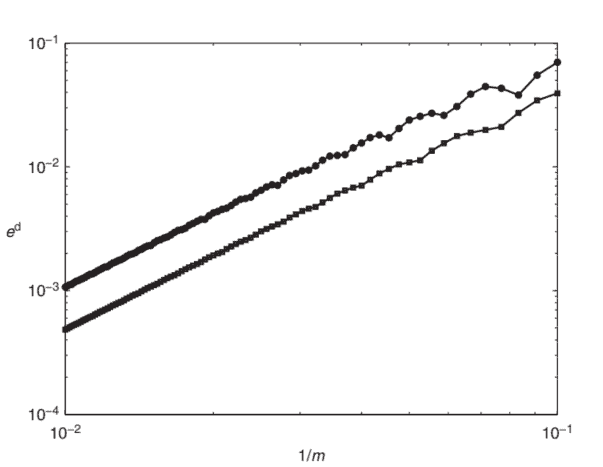
(6.2) along with the Black-Scholes PDE, on the same grid and in the same fashion. The Greek rho is approximated similarly to vega, by numerically solving the associated PDE. To assess the accuracy of the approximated Greeks we define, analogously to Chapter 5 for the option value and with reference to $(6.1)$, the spatial discretization errors $\varepsilon^{\mathrm{d}}(m), \varepsilon^{\mathrm{g}}(m), \varepsilon^{\mathrm{v}}(m), \varepsilon^{\mathrm{r}}(m)$ for delta, gamma, vega and rho, respectively, with maximum norms $e^{\mathrm{d}}(m), e^{\mathrm{g}}(m), e^{\mathrm{v}}(m), e^{\mathrm{r}}(m)$. Figures 6.2, 6.3,6.4, $6.5$ respectively display, as squares, the latter four quantities versus $1 / m$ for all $10 \leq m \leq 100$. One readily observes a nice second-order convergence behaviour in all four cases. For comparison, the results have been added to the figures where a uniform grid is employed. These are indicated by bullets. Whereas they also show a second-order convergence behaviour for all four Greeks, the accuracy is significantly lower than with the nonuniform grid, analogously to what was found in Chapter 5 for the case of the option value. Finally, we note that Figures $6.2,6.3,6.4,6.5$ remain visually unchanged if the other two boundary conditions, Neumann and linear, are applied for the option value function at the upper boundary.
计算金融代写
金融代写|计算金融PROJECT代写COMPUTATIONAL FINANCE代考|THE GREEKS
除了公平期权价值,所谓的希腊人在金融实践中也很重要。这些数量代表了期权价值对基础金融变量和参数变化的敏感性。希腊人的一个主要用途是在其生命周期内提供期权,即减少或消除风险。在数学术语中,它们是期权价值相对于其基础变量和参数的偏导数。
在 Black-Scholes 框架中,四个著名的希腊人是 delta:∂在∂s,伽玛:∂2在∂s2, 织女:∂在∂σ, rho:∂在∂r.
这些分别量化了对标的资产价格变化的敏感性吨这F一世rs吨一种nds和C这nd这rd和r,波动率和无风险利率。请注意,vega 不是真正的希腊字母。对于看涨期权,可以从1.6一种以下公式在H和n和在和r$s>0,0<吨≤吨$:
三角洲: ñ(d1), 伽玛: ñ′(d1)/(sσ吨), 维加: s吨ñ′(d1), rho: 吨和−r吨ķñ(d2).
金融代写|计算金融PROJECT代写COMPUTATIONAL FINANCE代考|NUMERICAL STUDY
数值近似希腊人的基本方法是直接使用有限差分。在这里,给定一组变量和参数的选项值,计算一个或多个额外选项值这r“b在米p和d”感兴趣的变量或参数的值,同时保持所有其他参数不变,然后计算适当的有限差分。
如果希腊语在期权估值 PDE 中作为一个术语出现,例如 Black-Scholes PDE 中的 delta 或 gamma,那么有限差分近似可以直接免费获得,因为它是 PDE 空间离散化所固有的. 因此,对于空间网格上的每个期权价值,这个希腊的价值就在眼前。
如果希腊语本身没有出现在期权估值 PDE 中,那么在基本方法中,可以通过数值求解该 PDE 为这n和,吨在这这r米这r和感兴趣的参数的附加扰动值,然后采用适当的有限差分。在这种情况下,一种更自然、更有效的方法是数值求解对应于该希腊语的 PDE,同时求解期权价值的 PDE。这只需要很少的额外实施工作。
对于数字说明,请考虑 Black-Scholes 框架下的看涨期权与参数值1.8. 与第 5 章一样,我们将空间域截断为(0,3ķ), 选择 Dirichlet 边界条件,在示例 4.2.1 中的非均匀网格上使用二阶中心公式进行半离散化,使用公式乙对流,并采用单元平均。然后通过应用二阶中心公式来近似希腊人的 delta 和 gamma4.7和4.8,分别为空间网格上获得的选项值。希腊 vega 通过数值求解 PDE 来近似
6.2与 Black-Scholes PDE 一起,在相同的网格上以相同的方式。通过数值求解相关的 PDE,希腊 rho 类似于 vega 近似。为了评估我们定义的近似希腊字母的准确性,类似于第 5 章的期权价值并参考(6.1), 空间离散化误差ed(米),eG(米),e在(米),er(米)分别用于 delta、gamma、vega 和 rho,具有最大范数和d(米),和G(米),和在(米),和r(米). 图 6.2、6.3、6.4、6.5分别以正方形显示后四个数量与1/米对全部10≤米≤100. 在所有四种情况下,人们很容易观察到一个很好的二阶收敛行为。为了比较,结果已添加到采用均匀网格的图中。这些由项目符号表示。虽然它们还显示了所有四个希腊人的二阶收敛行为,但准确性明显低于非均匀网格,类似于第 5 章中关于期权价值的情况。最后,我们注意到图6.2,6.3,6.4,6.5如果其他两个边界条件 Neumann 和线性应用于上边界的期权价值函数,则视觉上保持不变。

金融代写|计算金融project代写Computational finance代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
电磁学代考
物理代考服务:
物理Physics考试代考、留学生物理online exam代考、电磁学代考、热力学代考、相对论代考、电动力学代考、电磁学代考、分析力学代考、澳洲物理代考、北美物理考试代考、美国留学生物理final exam代考、加拿大物理midterm代考、澳洲物理online exam代考、英国物理online quiz代考等。
光学代考
光学(Optics),是物理学的分支,主要是研究光的现象、性质与应用,包括光与物质之间的相互作用、光学仪器的制作。光学通常研究红外线、紫外线及可见光的物理行为。因为光是电磁波,其它形式的电磁辐射,例如X射线、微波、电磁辐射及无线电波等等也具有类似光的特性。
大多数常见的光学现象都可以用经典电动力学理论来说明。但是,通常这全套理论很难实际应用,必需先假定简单模型。几何光学的模型最为容易使用。
相对论代考
上至高压线,下至发电机,只要用到电的地方就有相对论效应存在!相对论是关于时空和引力的理论,主要由爱因斯坦创立,相对论的提出给物理学带来了革命性的变化,被誉为现代物理性最伟大的基础理论。
流体力学代考
流体力学是力学的一个分支。 主要研究在各种力的作用下流体本身的状态,以及流体和固体壁面、流体和流体之间、流体与其他运动形态之间的相互作用的力学分支。
随机过程代写
随机过程,是依赖于参数的一组随机变量的全体,参数通常是时间。 随机变量是随机现象的数量表现,其取值随着偶然因素的影响而改变。 例如,某商店在从时间t0到时间tK这段时间内接待顾客的人数,就是依赖于时间t的一组随机变量,即随机过程
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。