如果你也在 怎样代写机器学习Machine Learning 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。机器学习Machine Learning令人兴奋。这是有趣的,具有挑战性的,创造性的,和智力刺激。它还为公司赚钱,自主处理大量任务,并从那些宁愿做其他事情的人那里消除单调工作的繁重任务。
机器学习Machine Learning也非常复杂。从数千种算法、数百种开放源码包,以及需要具备从数据工程(DE)到高级统计分析和可视化等各种技能的专业实践者,ML专业实践者所需的工作确实令人生畏。增加这种复杂性的是,需要能够与广泛的专家、主题专家(sme)和业务单元组进行跨功能工作——就正在解决的问题的性质和ml支持的解决方案的输出进行沟通和协作。
机器学习Machine Learning代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的机器学习Machine Learning作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此机器学习Machine Learning作业代写的价格不固定。通常在专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
计算机代写|机器学习代写Machine Learning代考|Cold-start woes
For certain types of ML projects, model prediction failures are not only frequent, but also expected. For solutions that require a historical context of existing data to function properly, the absence of historical data prevents the model from making a prediction. The data simply isn’t available to pass through the model. Known as the cold-start problem, this is a critical aspect of solution design and architecture for any project dealing with temporally associated data.
As an example, let’s imagine that we run a dog-grooming business. Our fleets of mobile bathing stations scour the suburbs of North America, offering all manner of services to dogs at their homes. Appointments and service selection is handled through an app interface. When booking a visit, the clients select from hundreds of options and prepay for the services through the app no later than a day before the visit.
To increase our customers’ satisfaction (and increase our revenue), we employ a service recommendation interface on the app. This model queries the customer’s historical visits, finds products that might be relevant for them, and indicates additional services that the dog might enjoy. For this recommender to function correctly, the historical services history needs to be present during service selection.
This isn’t much of a stretch for anyone to conceptualize. A model without data to process isn’t particularly useful. With no history available, the model clearly has no data in which to infer additional services that could be recommended for bundling into the appointment.
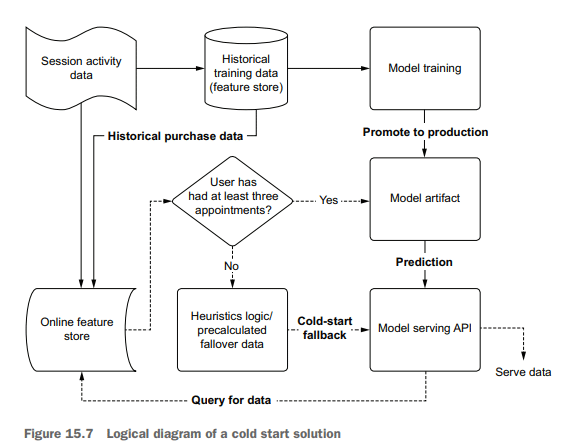
What’s needed to serve something to the end user is a cold-start solution. An easy implementation for this use case is to generate a collection of the most frequently ordered services globally. If the model doesn’t have enough data to provide a prediction, this popularity-based services aggregation can be served in its place. At that point, the app IFrame element will at least have something in it (instead of showing an empty collection) and the user experience won’t be broken by seeing an empty box.
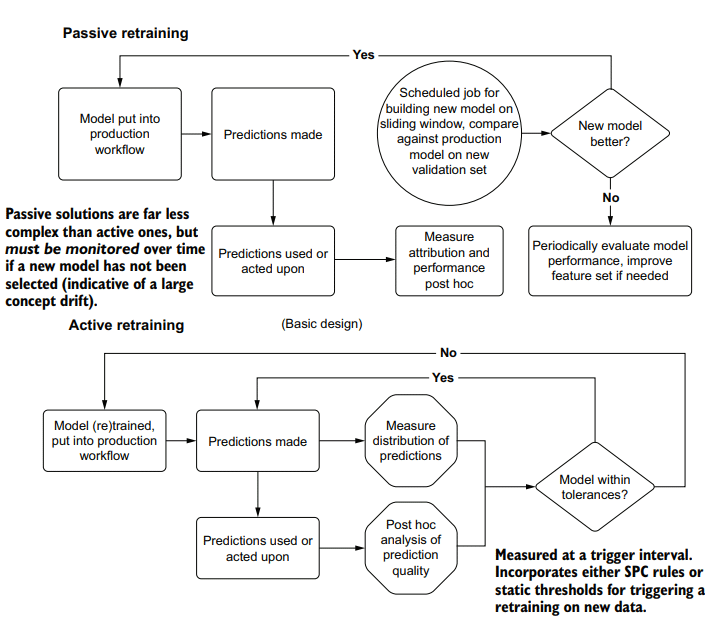
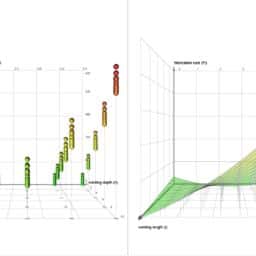
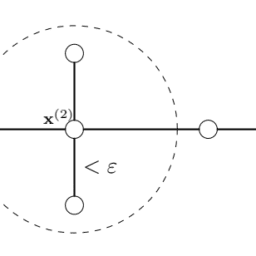
More-sophisticated implementations can be made, upgrading a global popularity ranking to one with more fine-grained cold-start pre-generated data. At a bare minimum, the geographic region can be used as a grouped aggregation to calculate popularity of services to create a pseudo-personalized failover condition. More-sophisticated grouping assignments can be made if additional data is available for the end user, referencing those aggregated data points across the user base for grouping conditions, ensuring that more refined and granular recommendations are served. A cold-start-enabled architecture is shown in figure 15.7.
计算机代写|机器学习代写Machine Learning代考|End user vs. internal use testing
Releasing a project to production once the end-to-end functionality is confirmed to be working is incredibly tempting. After so much work, effort, and metrics-based quantitative quality checks, it’s only natural to assume that the solution is ready to be sent out into the world for use. Resisting this urge to sprint the last mile to release is difficult, although it is absolutely critical.
The primary reasons it’s so ill-advised to simply release a project based solely on the internal evaluations of the DS team, as we covered in part 1, are as follows:
” The DS team members are biased. This is their baby. No one wants to admit to having created an ugly baby.
- Quantitative metrics do not always guarantee qualitative traits.
- The most important influence over quality predictions may be data that is not collected.
These reasons harken back to the concept of correlation not implying causality, as well as creator bias. While the model’s validation and quantitative metrics may perform remarkably well, precious few projects will have all of the causal factors captured within a feature vector.
What a thorough testing or QA process can help us do is assign a qualitative assessment of our solution. We can accomplish this in multiple ways.
Let’s imagine that we work at a music streaming service. We have an initiative to increase customer engagement by way of providing highly relevant song choices to follow along after a queued listening session.
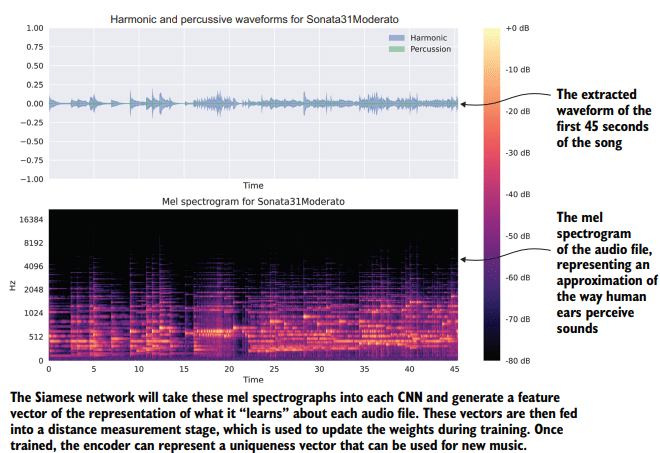
Instead of using a collaborative filtering approach that would find similar songs listened to by other users, we want to find songs that are similar based on how the human ear would interpret a song. We use a Fourier transformation of the audio file to get a frequency distribution and then map that distribution to a mel scale (a linear cosine transformation of the log power spectrum of an audio signal that closely approximates how the human ear perceives sound). With this transformation of the data and a plot, we arrive at a visual representation of the characteristics of each song. We then, in an offline manner, calculate similarities of all songs to all other songs through the use of a tuned tri-branch Siamese Network. The feature vector that comes out of this system, augmented by additional tagged features to each song, is used to calculate both a Euclidean and a Cosine distance from one song to another. We save these relationships among all songs in a NoSQL database that tracks the 1,000 most similar songs to all others for our serving layer.
机器学习代写
计算机代写|机器学习代写Machine Learning代考|Cold-start woes
对于某些类型的ML项目,模型预测失败不仅频繁,而且是意料之中的。对于需要现有数据的历史上下文才能正常工作的解决方案,缺少历史数据会阻止模型进行预测。数据根本无法通过模型。这被称为冷启动问题,对于任何处理临时关联数据的项目来说,这是解决方案设计和体系结构的一个关键方面。
举个例子,假设我们经营一家狗狗美容公司。我们的移动洗浴站遍布北美郊区,为狗狗提供各种上门服务。约会和服务选择是通过应用程序界面处理的。当预约参观时,客户可以从数百个选项中进行选择,并在参观前一天通过应用程序预付服务费用。
为了提高客户的满意度(并增加我们的收入),我们在应用程序上使用了一个服务推荐界面。这个模型会查询客户的历史访问记录,找到可能与他们相关的产品,并指出狗可能喜欢的其他服务。要使此推荐程序正确运行,在服务选择期间需要提供历史服务历史。
这对任何人来说都不是很容易理解的。没有数据要处理的模型并不是特别有用。由于没有可用的历史记录,该模型显然没有数据来推断可以推荐绑定到约会中的其他服务。
为最终用户提供服务所需要的是冷启动解决方案。此用例的一个简单实现是生成全局最频繁订购的服务的集合。如果模型没有足够的数据来提供预测,则可以使用这种基于流行度的服务聚合。在这一点上,应用程序的IFrame元素至少会有一些东西在里面(而不是显示一个空的集合),用户体验不会因为看到一个空框而被破坏。
可以制作更复杂的实现,将全球流行度排名升级为具有更细粒度冷启动预生成数据的排名。至少,可以将地理区域用作分组聚合,以计算服务的流行程度,从而创建伪个性化故障转移条件。如果最终用户可以获得额外的数据,则可以进行更复杂的分组分配,在用户群中引用这些聚合的数据点以进行分组条件,确保提供更精细和更细粒度的建议。启用冷启动的体系结构如图15.7所示。
计算机代写|机器学习代写Machine Learning代考|End user vs. internal use testing
一旦端到端功能被确认可以正常工作,就将项目发布到生产环境中是非常诱人的。经过这么多的工作、努力和基于度量的定量质量检查,很自然地假设解决方案已经准备好投入使用了。抵制这种冲刺最后一英里的冲动是很困难的,尽管这是绝对关键的。
就像我们在第1部分中所提到的,仅仅基于DS团队的内部评估去发行一个项目是不明智的主要原因是:
“DS团队成员有偏见。这是他们的孩子。没人愿意承认自己造了一个丑宝宝。
定量指标并不总是保证质量特征。
对质量预测最重要的影响可能是未收集的数据。
这些原因可以追溯到不意味着因果关系的相关性概念,以及创造者偏见。虽然模型的验证和定量度量可能执行得非常好,但很少有项目能够在特征向量中捕获所有的因果因素。
彻底的测试或QA过程可以帮助我们对解决方案进行定性评估。我们可以通过多种方式做到这一点。
让我们想象一下,我们在一家音乐流媒体服务公司工作。我们有一项倡议,通过提供高度相关的歌曲选择来提高客户的参与度,以便在排队聆听之后跟进。
我们希望根据人耳对歌曲的理解方式来查找相似的歌曲,而不是使用协作过滤方法来查找其他用户听过的相似歌曲。我们使用音频文件的傅里叶变换来获得频率分布,然后将该分布映射到mel尺度(音频信号的对数功率谱的线性余弦变换,非常接近人耳感知声音的方式)。通过数据和情节的转换,我们得到了每首歌特征的视觉表示。然后,我们以离线的方式,通过使用调谐的三分支暹罗网络来计算所有歌曲与所有其他歌曲的相似性。从这个系统中得到的特征向量,加上每首歌的附加标记特征,被用来计算从一首歌到另一首歌的欧氏距离和余弦距离。我们将所有歌曲之间的这些关系保存在一个NoSQL数据库中,该数据库为我们的服务层跟踪1,000首与所有其他歌曲最相似的歌曲。

计算机代写|机器学习代写Machine Learning代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。
微观经济学代写
微观经济学是主流经济学的一个分支,研究个人和企业在做出有关稀缺资源分配的决策时的行为以及这些个人和企业之间的相互作用。my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在数学Mathematics作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在图论代写Graph Theory代写方面经验极为丰富,各种图论代写Graph Theory相关的作业也就用不着 说。
线性代数代写
线性代数是数学的一个分支,涉及线性方程,如:线性图,如:以及它们在向量空间和通过矩阵的表示。线性代数是几乎所有数学领域的核心。
博弈论代写
现代博弈论始于约翰-冯-诺伊曼(John von Neumann)提出的两人零和博弈中的混合策略均衡的观点及其证明。冯-诺依曼的原始证明使用了关于连续映射到紧凑凸集的布劳威尔定点定理,这成为博弈论和数学经济学的标准方法。在他的论文之后,1944年,他与奥斯卡-莫根斯特恩(Oskar Morgenstern)共同撰写了《游戏和经济行为理论》一书,该书考虑了几个参与者的合作游戏。这本书的第二版提供了预期效用的公理理论,使数理统计学家和经济学家能够处理不确定性下的决策。
微积分代写
微积分,最初被称为无穷小微积分或 “无穷小的微积分”,是对连续变化的数学研究,就像几何学是对形状的研究,而代数是对算术运算的概括研究一样。
它有两个主要分支,微分和积分;微分涉及瞬时变化率和曲线的斜率,而积分涉及数量的累积,以及曲线下或曲线之间的面积。这两个分支通过微积分的基本定理相互联系,它们利用了无限序列和无限级数收敛到一个明确定义的极限的基本概念 。
计量经济学代写
什么是计量经济学?
计量经济学是统计学和数学模型的定量应用,使用数据来发展理论或测试经济学中的现有假设,并根据历史数据预测未来趋势。它对现实世界的数据进行统计试验,然后将结果与被测试的理论进行比较和对比。
根据你是对测试现有理论感兴趣,还是对利用现有数据在这些观察的基础上提出新的假设感兴趣,计量经济学可以细分为两大类:理论和应用。那些经常从事这种实践的人通常被称为计量经济学家。
Matlab代写
MATLAB 是一种用于技术计算的高性能语言。它将计算、可视化和编程集成在一个易于使用的环境中,其中问题和解决方案以熟悉的数学符号表示。典型用途包括:数学和计算算法开发建模、仿真和原型制作数据分析、探索和可视化科学和工程图形应用程序开发,包括图形用户界面构建MATLAB 是一个交互式系统,其基本数据元素是一个不需要维度的数组。这使您可以解决许多技术计算问题,尤其是那些具有矩阵和向量公式的问题,而只需用 C 或 Fortran 等标量非交互式语言编写程序所需的时间的一小部分。MATLAB 名称代表矩阵实验室。MATLAB 最初的编写目的是提供对由 LINPACK 和 EISPACK 项目开发的矩阵软件的轻松访问,这两个项目共同代表了矩阵计算软件的最新技术。MATLAB 经过多年的发展,得到了许多用户的投入。在大学环境中,它是数学、工程和科学入门和高级课程的标准教学工具。在工业领域,MATLAB 是高效研究、开发和分析的首选工具。MATLAB 具有一系列称为工具箱的特定于应用程序的解决方案。对于大多数 MATLAB 用户来说非常重要,工具箱允许您学习和应用专业技术。工具箱是 MATLAB 函数(M 文件)的综合集合,可扩展 MATLAB 环境以解决特定类别的问题。可用工具箱的领域包括信号处理、控制系统、神经网络、模糊逻辑、小波、仿真等。