如果你也在 怎样代写运筹学Operations Research这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。假设检验Hypothesis是假设检验是统计学中的一种行为,分析者据此检验有关人口参数的假设。分析师采用的方法取决于所用数据的性质和分析的原因。假设检验是通过使用样本数据来评估假设的合理性。
运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
二战中运筹学的应用
在二战时期,作战研究被定义为 “一种科学方法,为执行部门提供有关其控制的行动的决策的量化依据”。它的其他名称包括作战分析(英国国防部从1962年开始)和定量管理。
在第二次世界大战期间,英国有近1000名男女从事作战研究。大约有200名作战研究科学家为英国军队工作。
帕特里克-布莱克特在战争期间为几个不同的组织工作。战争初期,在为皇家飞机研究所(RAE)工作时,他建立了一个被称为 “马戏团 “的团队,帮助减少了击落一架敌机所需的防空炮弹数量,从不列颠战役开始时的平均超过20,000发减少到1941年的4,000发。
my-assignmentexpert™ 运筹学Operations Research作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在运筹学Operations Research作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的假设检验Hypothesis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 商业分析 Business Analysis
- 计算机科学 Computer Science
- 数据挖掘/数据科学/大数据 Data Mining / Data Science / Big Data
- 决策分析 Decision Analytics
- 金融工程 Financial Engineering
- 数据预测 Data Forecasting
- 博弈论 Game Theory
- 地理/地理信息科学 Geography/Geographic Information Science
- 图论 Graph Theory
- 工业工程 Industrial Engineering
- 库存控制 Inventory control
- 数学建模 Mathematical Modeling
- 数学优化 Mathematical Optimization
- 概率和统计 Probability and statistics
- 排队论 Queueing theory
- 社交网络/交通预测模型 Social network/traffic prediction modeling
- 随机过程 Stochastic processes
- 供应链管理 Supply chain management
运筹学代写
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|Problem Formulation
Adidas AG is the second largest sportswear manufacturer in the world. The company is looking to open one of its retail stores in a major capital city. The retailer has shortlisted two locations: a famous shopping mall (location A) which is located at the outskirts of city and other a popular shopping plaza (location B) located at heart of city. The fixed cost of location $\mathrm{A}$ is $\$ 7,500$ and of location $\mathrm{B}$ is $\$ 7,000$ per month. Variable costs at $\mathrm{A}$ and $\mathrm{B}$ are expected to be $\$ 4$ and $\$ 3$ per unit, respectively. Total cost is a combination of fixed and variable costs. It is a function of the number of units sold. Even if no units are sold, the total cost would be equal to the fixed cost. However, with an increase in sales, total cost would increase by variable cost incurred to sell that unit as the retailer has to pay for utilities and extra labour. The quantity of units produced depends on the demand for shoes. Demand varies with the change in price of shoes. At initial price with no increase, demand was found to be 4,500 units per month at A and 5,200 at B. However, with every increase in price by one unit, the decrease in demand was estimated to be by 50 units at A and by 40 at B. Given this information, the company intends to find the price of shoe at both locations, which would yield maximum profit.
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|Model Development
The following notations are used to form a mathematical expression for given problem:
Operations Research: An Introduction
Number of units sold $=\mathrm{x}$
Price of one unit $=\mathrm{p}$
Fixed cost $=\mathrm{FC}=\$ 7,500$ for $\mathrm{A}$ and $\$ 7,000$ for $\mathrm{B}$
Variable cost $=\mathrm{VC}=\$ 4$ for $\mathrm{A}$ and $\$ 3$ for $\mathrm{B}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
&\text { Total cost }=\mathrm{TC}=\mathrm{FC}+\mathrm{VC} \
&\text { Profit }=\mathrm{P}=\text { revenue }-\mathrm{cost}
\end{aligned}
$$
$\mathrm{VC}$ is a function of the number of units sold. So for $\mathrm{A}$ it would be $4 \mathrm{x}$ and for B $3 \mathrm{x}$.
So, the cost function for location $\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{f}$ (no. of units $\mathrm{x})=7,500+4 \mathrm{x}$
Cost function for location $B=f$ (no. of units $x)=7,000+3 x$
Demand function for location $A=f($ price per unit $p)=4,500-50 p$
Demand function for location $B=f($ price per unit $p)=5,200-40 p$
The number of units sold ‘ $\mathrm{x}$ ‘ is represented by demand at a particular location.
Therefore, the cost function is converted as follows:
So, the cost function
for location $A$ : $f($ no. of units $x)=7,500+4 x$
$$
f(p)=7,500+4 *(4,500-50 p)=25,500-200 p
$$
Similarly, for B:
$$
f(p)=7,000+3 x=7,000+3 *(5,200-40 p)=22,600-120 p
$$
Revenue is a function of the price of product and demand for shoes. So, the revenue function
at location $\mathrm{A}=(4,500-50 \mathrm{p}) * \mathrm{p}=4,500 \mathrm{p}-50 \mathrm{p}^{2}$
at location $\mathrm{B}=(5,200-40 \mathrm{p}) * \mathrm{p}=5,200 \mathrm{p}-40 \mathrm{p}^{2}$
The objective function (Z) is to maximize profit, which is formulated as follows:
$$
\begin{aligned}
\operatorname{Maximize} \text { Profit }(\mathrm{A})=&\left(4,500 \mathrm{p}-50 \mathrm{p}^{2}\right)-(25,500-200 \mathrm{p}) \
=&-50 \mathrm{p}^{2}+4,300 \mathrm{p}-25,500 \
\text { MaximizeProfit }(\mathrm{B})=&\left(5,200 \mathrm{p}-40 \mathrm{p}^{2}\right)-(22,600-120 \mathrm{p}) \
=&-40 \mathrm{p}^{2}+5,320 \mathrm{p}-22,600
\end{aligned}
$$
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|Model Solution
Maximization of profit for location $A$ :
- First derivative of profit equation:
$$
f^{\prime}(p)=f^{\prime}\left(-50 p^{2}+4,300 p-25,500\right)
$$
$$
=-100 p+4,300
$$
- Solve for decision variable $\mathrm{Q}$ by putting the first derivative to zero:
$$
-100 p+4,300=0
$$
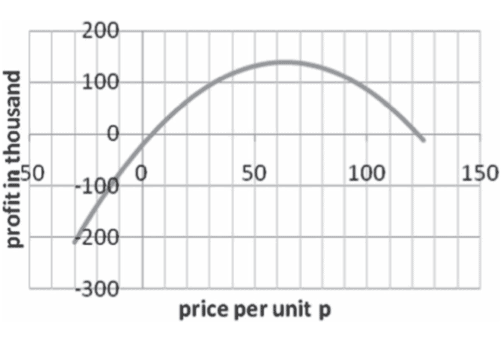
Thus, $p=\$ 43$ - Is this the highest point on curve? For that, take the second derivative:
$$
\mathrm{f}^{\prime \prime}(\mathrm{p})=-100<0 .
$$
It would always be less than zero, implying calculated $p$ would be the maximum point on the curve (Figure 1.6). It would yield maximum profit. - Find profit by putting a value of $p=\$ 43$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\operatorname{Profit}(\mathrm{A}) &=-50 \mathrm{p}^{2}+4,300 \mathrm{p}-25,500 \
&=-50 * 43 * 43+4,300 * 43-25,500 \
&=\$ 66,950
\end{aligned}
$$
运筹学代考
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|PROBLEM FORMULATION
阿迪达斯公司是世界第二大运动服装制造商。该公司正寻求在一个主要首都城市开设一家零售店。该零售商入围了两个地点:一个著名的购物中心一世○C一种吨一世○n一种位于城市郊区和其他受欢迎的购物广场一世○C一种吨一世○n乙位于市中心。位置的固定成本一种是$7,500和位置乙是$7,000每月。可变成本一种和乙预计将$4和$3每单位,分别。总成本是固定成本和可变成本的组合。它是销售单位数量的函数。即使没有单位出售,总成本也将等于固定成本。然而,随着销售额的增加,总成本将因销售该单位所产生的可变成本而增加,因为零售商必须支付公用事业和额外的劳动力。生产的单位数量取决于对鞋子的需求。需求随着鞋子价格的变化而变化。在没有上涨的初始价格下,A 的需求为每月 4,500 件,B 的需求为 5,200。然而,价格每上涨 1 个单位,估计 A 的需求减少 50 个单位,而 B 的需求减少 40 个单位。在 B。鉴于此信息,该公司打算在两个地点找到鞋子的价格,这将产生最大的利润。
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|MODEL DEVELOPMENT
以下符号用于形成给定问题的数学表达式:
运筹学:简介
售出的单位数量=X
一个单位的价格=p
固定成本=FC=$7,500为了一种和$7,000为了乙
可变成本=五C=$4为了一种和$3为了乙
总花费 =吨C=FC+五C 利润 =磷= 收入 −C○s吨
五C是销售单位数量的函数。因此对于一种这将是4X对于 B3X.
因此,位置的成本函数一种=F n○.○F你n一世吨s$X=7,500+4 \mathrm{x}C○s吨F你nC吨一世○nF○r一世○C一种吨一世○nB=f(n○.○F你n一世吨sx)=7,000+3 xD和米一种ndF你nC吨一世○nF○r一世○C一种吨一世○nA=f$pr一世C和p和r你n一世吨$p=4,500-50 pD和米一种ndF你nC吨一世○nF○r一世○C一种吨一世○nB=f$pr一世C和p和r你n一世吨$p=5,200-40 人吨H和n你米b和r○F你n一世吨ss○一世d‘\数学{x}‘一世sr和pr和s和n吨和db和d和米一种nd一种吨一种p一种r吨一世C你一世一种r一世○C一种吨一世○n.吨H和r和F○r和,吨H和C○s吨F你nC吨一世○n一世sC○nv和r吨和d一种sF○一世一世○在s:小号○,吨H和C○s吨F你nC吨一世○nF○r一世○C一种吨一世○n一种:F$n○.○F你n一世吨s$X=7,500+4 xF(p)=7,500+4∗(4,500−50p)=25,500−200p小号一世米一世一世一种r一世和,F○r乙:F(p)=7,000+3X=7,000+3∗(5,200−40p)=22,600−120pR和v和n你和一世s一种F你nC吨一世○n○F吨H和pr一世C和○Fpr○d你C吨一种ndd和米一种ndF○rsH○和s.小号○,吨H和r和v和n你和F你nC吨一世○n一种吨一世○C一种吨一世○n\mathrm{A}=4,500−50p* \mathrm{p}=4,500 \mathrm{p}-50 \mathrm{p}^{2}一种吨一世○C一种吨一世○n\mathrm{B}=5,200−40p* \mathrm{p}=5,200 \mathrm{p}-40 \mathrm{p}^{2}吨H和○bj和C吨一世v和F你nC吨一世○n(和)一世s吨○米一种X一世米一世和和pr○F一世吨,在H一世CH一世sF○r米你一世一种吨和d一种sF○一世一世○在s:最大化 利润 (一种)=(4,500p−50p2)−(25,500−200p) =−50p2+4,300p−25,500 最大化利润 (乙)=(5,200p−40p2)−(22,600−120p) =−40p2+5,320p−22,600$
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|MODEL SOLUTION
位置利润最大化一种:
- 利润方程的一阶导数:
F′(p)=F′(−50p2+4,300p−25,500)
=−100p+4,300
- 求解决策变量问通过将一阶导数归零:
−100p+4,300=0
因此,p=$43 - 这是曲线上的最高点吗?为此,取二阶导数:
F′′(p)=−100<0.
它总是小于零,意味着计算p将是曲线上的最大值F一世G你r和1.6. 它将产生最大的利润。 - 通过设置值来查找利润p=$43
利润(一种)=−50p2+4,300p−25,500 =−50∗43∗43+4,300∗43−25,500 =$66,950