如果你也在 怎样代写运筹学Operations Research这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。假设检验Hypothesis是假设检验是统计学中的一种行为,分析者据此检验有关人口参数的假设。分析师采用的方法取决于所用数据的性质和分析的原因。假设检验是通过使用样本数据来评估假设的合理性。
运筹学(Operation)是近代应用数学的一个分支。它把具体的问题进行数学抽象,然后用像是统计学、数学模型和算法等方法加以解决,以此来寻找复杂问题中的最佳或近似最佳的解答。
二战中运筹学的应用
在二战时期,作战研究被定义为 “一种科学方法,为执行部门提供有关其控制的行动的决策的量化依据”。它的其他名称包括作战分析(英国国防部从1962年开始)和定量管理。
在第二次世界大战期间,英国有近1000名男女从事作战研究。大约有200名作战研究科学家为英国军队工作。
帕特里克-布莱克特在战争期间为几个不同的组织工作。战争初期,在为皇家飞机研究所(RAE)工作时,他建立了一个被称为 “马戏团 “的团队,帮助减少了击落一架敌机所需的防空炮弹数量,从不列颠战役开始时的平均超过20,000发减少到1941年的4,000发。
my-assignmentexpert™ 运筹学Operations Research作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。my-assignmentexpert™, 最高质量的运筹学Operations Research作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此运筹学Operations Research作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
my-assignmentexpert™ 为您的留学生涯保驾护航 在运筹学Operations Research作业代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的应用数学applied math代写服务。我们的专家在运筹学Operations Research代写方面经验极为丰富,各种运筹学Operations Research相关的作业也就用不着 说。
我们提供的假设检验Hypothesis及其相关学科的代写,服务范围广, 其中包括但不限于:
- 商业分析 Business Analysis
- 计算机科学 Computer Science
- 数据挖掘/数据科学/大数据 Data Mining / Data Science / Big Data
- 决策分析 Decision Analytics
- 金融工程 Financial Engineering
- 数据预测 Data Forecasting
- 博弈论 Game Theory
- 地理/地理信息科学 Geography/Geographic Information Science
- 图论 Graph Theory
- 工业工程 Industrial Engineering
- 库存控制 Inventory control
- 数学建模 Mathematical Modeling
- 数学优化 Mathematical Optimization
- 概率和统计 Probability and statistics
- 排队论 Queueing theory
- 社交网络/交通预测模型 Social network/traffic prediction modeling
- 随机过程 Stochastic processes
- 供应链管理 Supply chain management
运筹学代写
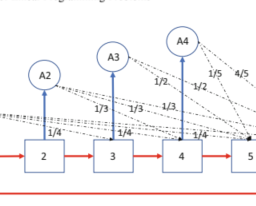
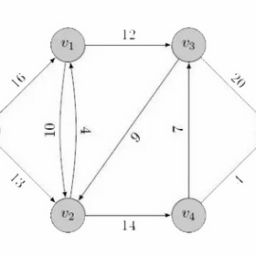
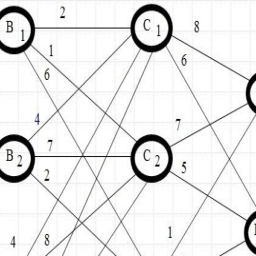
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|max-flow min-cut
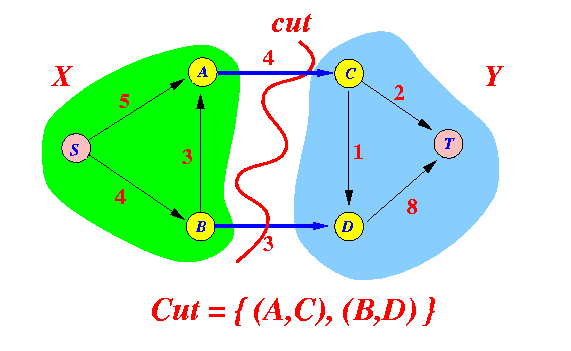
Minimum cut is an important concept in the study of the maximum flow problem. In what follows, we will generalize this definition for the time-varying network and introduce the time-varying version of the max-flow min-cut theorem.
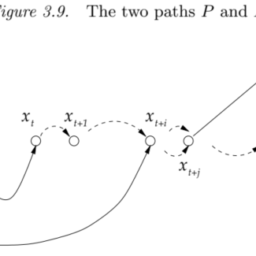
Definition 3.5 A vertex $y$ is said to be reachable from another vertex $x$, if there exists a feasible dynamic path from $x$ to $y$.
Definition 3.6 A generalized cut $K$ of $N$ separating vertex $s$ and $\rho$ is a set-valued function of time defined as
$$
K={K(t) \mid K(t) \subset V, s \in K(t), \rho \notin K(t), t=0,1, \ldots, T} .
$$
Definition 3.7 The capacity of the generalized cut $K$ is defined as
$$
\begin{gathered}
\text { CapK = } \sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in s(t), y \in \rho\left(t^{\prime}\right)} l(x, y, t) \
+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{(x, u) \in X(t)} \min {l(x, t), \ldots, l(x, t+u)}
\end{gathered}
$$
where $X(t)={(x, u) \mid x \in s(t), x \in h(t+1), \ldots, x \in h(t+u), x \in \rho(t+$ $\left.u+1), 0 \leq u<u_{x}\right}, s(t)={$ all those vertices $x$ in $K(t)$ such that $x$ is reachable from $s$ with arrival time $t$ at $x}, \rho(t)={$ all those vertices $x$ in $\bar{K}(t)=V \backslash K(t)$ such that $\rho$ is reachable from $x$ with departure time $t$ at $x}, t+b(x, y, t)=t^{\prime}, h(t)=V \backslash{s(t) \cup \rho(t)}$, and $u_{x}$ is a given nonnegative integer.
Note that we have used $u_{x}$ to denote the bound of waiting time at vertex $x$. If $u_{x}=0$, then there is no constraint on the waiting time at $x$. Specifically, when the waiting time at a vertex must be zero or can be arbitrary, Definition $3.7$ can be replaced by the following.
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|The capacity of the generalized cut
Definition 3.8 The capacity of the generalized cut can be defined as
$$
\text { CapK }=\sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in K(t), y \in \bar{K}\left(t^{\prime}\right)} l(x, y, t)
$$
if no waiting time is allowed at any vertices, or
$$
\text { CapK }=\sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in K(t), y \in \bar{K}\left(t^{\prime}\right)} l(x, y, t)+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{x \in K(t), x \in \bar{K}(t+1)} l(x, t)
$$
if waiting time is arbitrarily allowed at any vertices, where $t^{\prime}=t+$ $b(x, y, t)$.
Theorem 3.2 Let $v$ be the value of any feasible dynamic flow $f$ on $N$, and CapK be the value of any generalized cut $K$ in $N$. Then, $v \leq$ CapK.
Proof. Since any generalized cut $K$ separates $s$ and $\rho$ for any dynamic flow $f$, we have
$$
v=f^{+}(K)-f^{-}(K)
$$
where $f^{+}(K)$ and $f^{-}(K)$ are the flow values that flow out of and flow in $K$ respectively. Because $f$ is a dynamic flow on $N$, it must satisfy all capacity constraints. Therefore
$$
\begin{gathered}
0 \leq f(x, y, t) \leq l(x, y, t), \quad \forall(x, y) \in A \text { and } \forall t \
0 \leq f(x, t) \leq l(x, t), \quad \forall x \in V \text { and } \forall t
\end{gathered}
$$
Thus, we have
$$
\begin{gathered}
f^{+}(K)=\sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in K(t), y \in \bar{K}(t+b(x, y, t))} f(x, y, t)+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{x \in K(t), x \in \bar{K}(t+1))} f(x, t) \
=\sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in s(t), y \in \rho\left(t^{\prime}\right)} f(x, y, t)+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{(x, u) \in X(t)} f(x, u) \
\leq \sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in s(t), y \in \rho\left(t^{\prime}\right)} l(x, y, t)+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{(x, u) \in X(t)} \min {l(x, t), \ldots, l(x, t+u)} \
=C a p K
\end{gathered}
$$
The second equality comes from the fact that $f(x, y, t)=0$ for those vertices $x \in K(t) \backslash s(t)$, since there is no dynamic path from $s$ to $x$ at time $t$. Noting that $f^{-}(K) \geq 0$, we have
$$
v=f^{+}(K)-f^{-}(K) \leq \operatorname{CapK}
$$
This completes the proof.
运筹学代考
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|MAX-FLOW MIN-CUT
最小割是研究最大流问题的一个重要概念。在下文中,我们将把这个定义推广到时变网络,并介绍最大流最小割定理的时变版本。
定义 3.5 一个顶点是据说可以从另一个顶点到达X, 如果存在一条可行的动态路径X到是.
定义 3.6 广义割到的ñ分离顶点s和ρ是时间的集值函数,定义为
$$
K={K(t) \mid K(t) \subset V, s \in K(t), \rho \notin K(t), t=0,1, \ldots, T} .
$$
Definition 3.7 The capacity of the generalized cut $K$ is defined as
$$
\begin{gathered}
\text { CapK = } \sum_{t=0}^{T} \sum_{x \in s(t), y \in \rho\left(t^{\prime}\right)} l(x, y, t) \
+\sum_{t=0}^{T-1} \sum_{(x, u) \in X(t)} \min {l(x, t), \ldots, l(x, t+u)}
\end{gathered}
$$
where $X(t)={(x, u) \mid x \in s(t), x \in h(t+1), \ldots, x \in h(t+u), x \in \rho(t+$ $\left.u+1), 0 \leq u<u_{x}\right}, s(t)={$ all those vertices $x$ in $K(t)$ such that $x$ is reachable from $s$ with arrival time $t$ at $x}, \rho(t)={$ all those vertices $x$ in $\bar{K}(t)=V \backslash K(t)$ such that $\rho$ is reachable from $x$ with departure time $t$ at $x}, t+b(x, y, t)=t^{\prime}, h(t)=V \backslash{s(t) \cup \rho(t)}$, and $u_{x}$, 和你X是给定的非负整数。
请注意,我们使用了你X表示顶点等待时间的界限X. 如果你X=0, 那么等待时间没有限制X. 具体来说,当一个顶点的等待时间必须为零或可以是任意的时,定义3.7可以换成下面的。
数学代写|运筹学作业代写OPERATIONS RESEARCH代考|THE CAPACITY OF THE GENERALIZED CUT
定义 3.8 广义割的容量可以定义为
电容 =∑吨=0吨∑X∈到(吨),是∈到¯(吨′)一世(X,是,吨)
如果任何顶点都不允许等待时间,或者
电容 =∑吨=0吨∑X∈到(吨),是∈到¯(吨′)一世(X,是,吨)+∑吨=0吨−1∑X∈到(吨),X∈到¯(吨+1)一世(X,吨)
如果任意顶点允许等待时间,则吨′=吨+ b(X,是,吨).
定理 3.2 让v是任何可行动态流的值F在ñ, CapK 是任何广义割的值到在ñ. 然后,v≤卡普K。
证明。由于任何广义割到分开s和ρ对于任何动态流F, 我们有
v=F+(到)−F−(到)
在哪里F+(到)和F−(到)是流出和流入的流量值到分别。因为F是一个动态流ñ,它必须满足所有容量限制。所以
0≤F(X,是,吨)≤一世(X,是,吨),∀(X,是)∈一种 和 ∀吨 0≤F(X,吨)≤一世(X,吨),∀X∈五 和 ∀吨
因此,我们有
F+(到)=∑吨=0吨∑X∈到(吨),是∈到¯(吨+b(X,是,吨))F(X,是,吨)+∑吨=0吨−1∑X∈到(吨),X∈到¯(吨+1))F(X,吨) =∑吨=0吨∑X∈s(吨),是∈ρ(吨′)F(X,是,吨)+∑吨=0吨−1∑(X,你)∈X(吨)F(X,你) ≤∑吨=0吨∑X∈s(吨),是∈ρ(吨′)一世(X,是,吨)+∑吨=0吨−1∑(X,你)∈X(吨)分钟一世(X,吨),…,一世(X,吨+你) =C一种p到
第二个相等来自以下事实:F(X,是,吨)=0对于那些顶点X∈到(吨)∖s(吨),因为没有从s到X有时吨. 注意到F−(到)≥0, 我们有
v=F+(到)−F−(到)≤电容
这样就完成了证明。