如果你也在 怎样代写有限元方法finite differences method 这个学科遇到相关的难题,请随时右上角联系我们的24/7代写客服。有限元方法finite differences method在数值分析中,是一类通过用有限差分逼近导数解决微分方程的数值技术。空间域和时间间隔(如果适用)都被离散化,或被分成有限的步骤,通过解决包含有限差分和附近点的数值的代数方程来逼近这些离散点的解的数值。
有限元方法finite differences method有限差分法将可能是非线性的常微分方程(ODE)或偏微分方程(PDE)转换成可以用矩阵代数技术解决的线性方程系统。现代计算机可以有效地进行这些线性代数计算,再加上其相对容易实现,使得FDM在现代数值分析中得到了广泛的应用。今天,FDM与有限元方法一样,是数值解决PDE的最常用方法之一。
有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,免费提交作业要求, 满意后付款,成绩80\%以下全额退款,安全省心无顾虑。专业硕 博写手团队,所有订单可靠准时,保证 100% 原创。 最高质量的有限元方法finite differences method作业代写,服务覆盖北美、欧洲、澳洲等 国家。 在代写价格方面,考虑到同学们的经济条件,在保障代写质量的前提下,我们为客户提供最合理的价格。 由于统计Statistics作业种类很多,同时其中的大部分作业在字数上都没有具体要求,因此有限元方法finite differences method作业代写的价格不固定。通常在经济学专家查看完作业要求之后会给出报价。作业难度和截止日期对价格也有很大的影响。
同学们在留学期间,都对各式各样的作业考试很是头疼,如果你无从下手,不如考虑my-assignmentexpert™!
my-assignmentexpert™提供最专业的一站式服务:Essay代写,Dissertation代写,Assignment代写,Paper代写,Proposal代写,Proposal代写,Literature Review代写,Online Course,Exam代考等等。my-assignmentexpert™专注为留学生提供Essay代写服务,拥有各个专业的博硕教师团队帮您代写,免费修改及辅导,保证成果完成的效率和质量。同时有多家检测平台帐号,包括Turnitin高级账户,检测论文不会留痕,写好后检测修改,放心可靠,经得起任何考验!
想知道您作业确定的价格吗? 免费下单以相关学科的专家能了解具体的要求之后在1-3个小时就提出价格。专家的 报价比上列的价格能便宜好几倍。
我们在数学Mathematics代写方面已经树立了自己的口碑, 保证靠谱, 高质且原创的数学Mathematics代写服务。我们的专家在微积分Calculus Assignment代写方面经验极为丰富,各种微积分Calculus Assignment相关的作业也就用不着 说。
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|Numerical Simulations
While the derivation of the governing equations for most problems is not unduly difficult (in fact, for most problems they can be found in textbooks), their solution by exact methods of analysis is often difficult due to geometric and material complexities. In such cases, numerical methods of analysis provide a means of finding solutions. By a numerical simulation of a process, we mean the solution of the governing equations (or mathematical model) of the process using a numerical method and a computer. Numerical methods typically transform differential equations governing a continuum to a set of algebraic relations among the values of dependent variables of a discrete model of the continuum, and these algebraic equations are solved using computers.
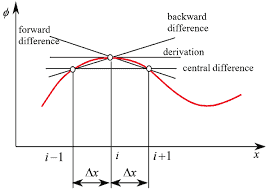
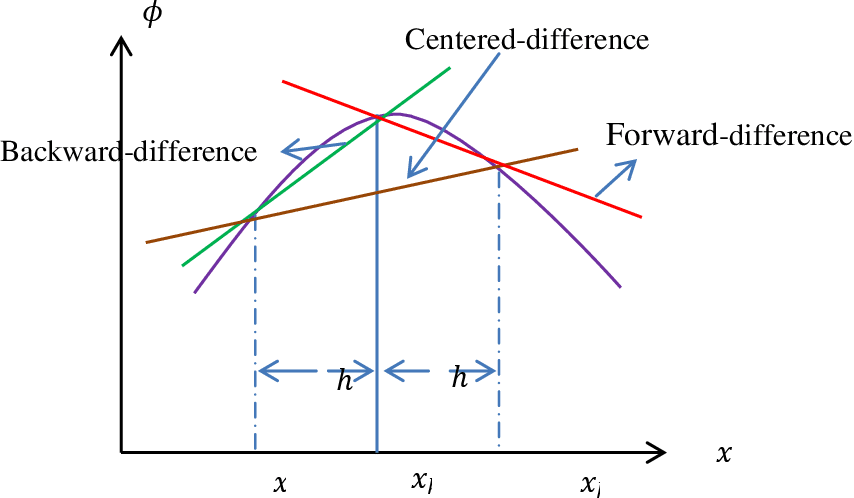
There exist a number of numerical methods, many of which are developed to solve differential equations. In the finite difference approximation of a differential equation, the derivatives in the latter are replaced by difference quotients (or the function is expanded in a Taylor series) that involve the values of the solution at discrete mesh points of the domain. The resulting algebraic equations are solved for the values of the solution at the mesh points after imposing the boundary conditions. We note that the finite difference method is not based on the concept of minimization of error introduced in the approximation of the differential equation. It simply provides a means to compute a solution.
In the solution of a differential equation by a classical variational method, the equation is expressed as an equivalent weighted-integral statement, which often means making the error in the approximation of the differential equation orthogonal to the set of weight functions. In solid mechanics, the integral statement is equivalent to an energy principle [4]. Then the approximate solution over the domain is assumed to be a linear combination $\left(\sum_j c_j \phi_j\right)$ of appropriately chosen approximation functions $\phi_j$ and coefficients $c_j$ to be determined. The coefficients $c_j$ are determined such that the integral statement is satisfied. Various variational methods, for example, the Ritz, Galerkin, collocation, and least-squares methods, differ from each other in the choice of the integral form and weight functions. A more detailed discussion of variational methods is presented in Chapter 2 (also, see [4]). The classical variational methods, which are truly meshless methods, are powerful methods that provide globally continuous solutions but suffer from the drawback that the approximation functions for problems with arbitrary domains are difficult to construct. The modern meshless methods seem to provide a way to construct approximation functions for arbitrary domains, but they also have their own disadvantages.
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|The Basic Idea
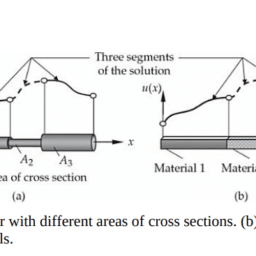
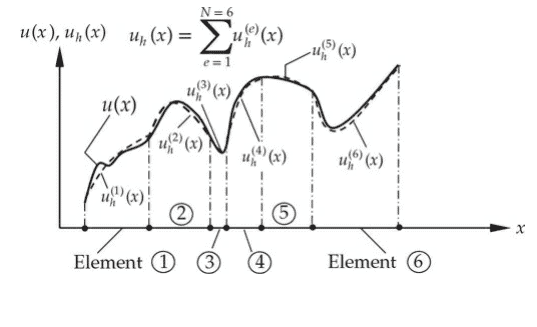
The finite element method is a numerical method like the finite difference method, but is more general and powerful in its application to real-world problems, which may involve multi-physics and complicated geometry and boundary conditions. In the finite element method, a given domain is viewed as a collection of subdomains, and over each subdomain the governing equation is approximated by any of the traditional variational methods or any method that is suitable. The main reason behind seeking approximate solutions on a collection of subdomains is the fact that it is easier to represent a complicated function as a collection of simple polynomials, as can be seen from Fig. 1.4.1. Of course, each individual segment of the solution should fit with its neighbors in the sense that the function and possibly its derivatives up to a chosen order are continuous (i.e., single-valued) at the connecting points. These ideas will be more clear in the sequel.
The finite element method is endowed with three distinct features that account for its superiority over other competing methods. These features are outlined next.
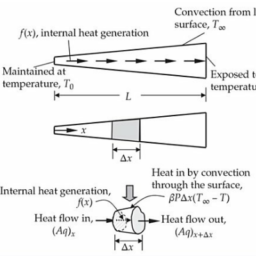
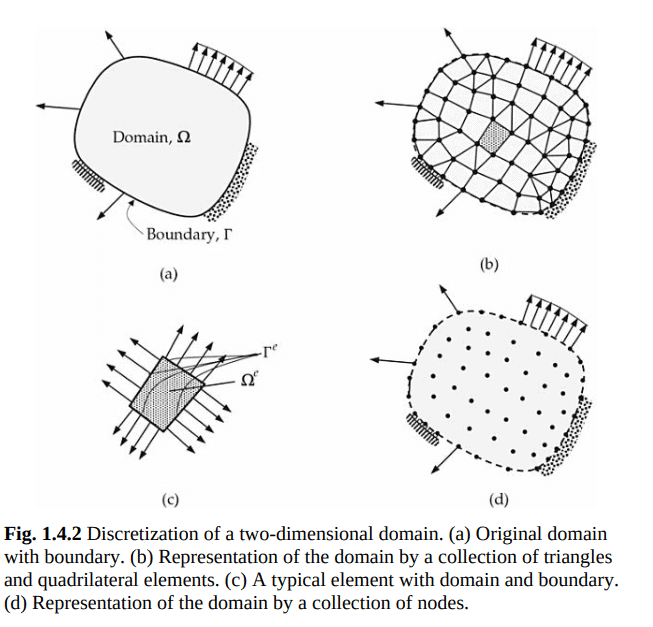
A geometrically complex domain $\Omega$ of the problem, such as the one in Fig. 1.4.2(a), is represented as a collection, called mesh, of geometrically simple subdomains as indicated in Fig. 1.4.2(b). A subdomain is called a finite element [see Fig. 1.4.2(c)]. Here the word “domain” refers to the geometric region over which the equations are solved. Note that not all geometric shapes can qualify as finite elements; only those shapes that allow the derivation of the approximation functions can qualify as finite elements. In reality, the discretized domain is a collection of points, as shown in Fig. 1.4.2(d).
Over each finite element, algebraic relations between the values of the duality pairs (i.e., cause and effect or primary and secondary degrees of freedom) of the problem at element nodes are derived using (a) statements equivalent to the governing equations of the problem and (b) a method of approximation. Alternatively, one may use physical principles directly to obtain the relationships. In principle, any suitable method of approximation can be used to derive the algebraic relations. The set of resulting algebraic equations among the nodal values of the duality pairs (e.g., displacements and forces) is termed a finite element model.
The equations from all elements, $\bar{\Omega}^e \equiv \Omega^e \cup \Gamma^e$, are assembled (i.e., elements are put back into their original positions of the mesh) using (a) continuity of the primary variables (e.g., displacements) and (b) balance of secondary variables (e.g., forces).
有限元方法代写
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|Numerical Simulations
虽然大多数问题的控制方程的推导并不太难(事实上,对于大多数问题,它们可以在教科书中找到),但由于几何和材料的复杂性,用精确的分析方法来解决它们往往是困难的。在这种情况下,数值分析方法提供了一种寻找解的方法。通过过程的数值模拟,我们指的是使用数值方法和计算机求解过程的控制方程(或数学模型)。数值方法通常将控制连续统的微分方程转换为连续统离散模型的因变量值之间的一组代数关系,并用计算机求解这些代数方程。有许多数值方法,其中许多是用来解微分方程的。在微分方程的有限差分近似中,后者的导数被差商(或函数在泰勒级数中展开)所取代,这些差商涉及到域中离散网格点的解的值。在施加边界条件后,求解得到的代数方程在网格点处的解值。我们注意到,有限差分法不是基于微分方程近似中引入的误差最小化的概念。它只是提供了一种计算解决方案的方法。
在用经典变分方法求解微分方程时,方程被表示为等效加权积分语句,这通常意味着微分方程的近似误差与权函数集正交。在固体力学中,积分表述等价于能量原理[4]。然后假定域上的近似解为适当选择的近似函数$\phi_j$和待确定的系数$c_j$的线性组合$\left(\sum_j c_j \phi_j\right)$。系数$c_j$的确定使得积分语句得到满足。各种变分方法,如里兹法、伽辽金法、搭配法、最小二乘法等,在积分形式和权函数的选择上各不相同。关于变分方法的更详细的讨论在第2章(也见[4])中提出。经典的变分方法是一种真正的无网格方法,是一种提供全局连续解的强大方法,但其缺点是难以构造任意域问题的近似函数。现代无网格方法似乎提供了一种构建任意域近似函数的方法,但它们也有自己的缺点。
数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考|The Basic Idea
有限元法与有限差分法一样是一种数值方法,但在涉及多物理场和复杂几何和边界条件的实际问题中应用更为普遍和强大。在有限元法中,一个给定的域被看作是一个子域的集合,在每个子域上,控制方程可以用任何传统的变分方法或任何合适的方法来逼近。在子域集合上寻求近似解的主要原因是,将复杂函数表示为简单多项式集合更容易,如图1.4.1所示。当然,解的每个单独的部分应该与它的邻居相匹配,因为函数及其可能的导数在一个选定的阶数下在连接点上是连续的(即单值)。这些想法将在续集中更加清晰。
有限元法具有三个明显的特点,这些特点使它优于其他竞争方法。下面将概述这些特性。
问题的几何复杂域$\Omega$,如图1.4.2(A)所示,表示为几何简单子域的集合,称为mesh,如图1.4.2(b)所示。子域称为有限元[见图1.4.2(c)]。这里的“域”一词指的是方程被解的几何区域。请注意,并非所有几何形状都可以作为有限元素;只有那些允许推导近似函数的形状才有资格作为有限单元。实际上,离散域是点的集合,如图1.4.2(d)所示。
在每个有限元上,对偶对的值之间的代数关系(即因果关系或初等关系)

数学代写|有限元方法作业代写finite differences method代考 请认准UprivateTA™. UprivateTA™为您的留学生涯保驾护航。